|
Hadza People
The Hadza, or Hadzabe (''Wahadzabe'' in Swahili), are a Tanzanian indigenous ethnic group mostly based in southwest Karatu District of Arusha Region. They live around Lake Eyasi in the central Rift Valley and in the neighboring Serengeti Plateau. There are, as of 2015, between 1,200 and 1,300 Hadza people living in Tanzania, however only around 400 Hadza still survive exclusively based on the traditional means of foraging. Additionally, the increasing impact of tourism and encroaching pastoralists pose serious threats to the continuation of their traditional way of life. Genetically, the Hadza are not closely related to any other people. Once classified among the Khoisan languages, primarily because it has clicks, the Hadza language (Hadzane) is actually thought to be an isolate, unrelated to any other. Hadzane is an entirely oral language, but it is not predicted to be in danger of extinction. UNESCO states that the language is not endangered but vulnerable because most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Persistence Hunting
Persistence hunting is pursuit until the prey can no longer flee and succumbs to exhaustion or heat stroke. History and definition Some researchers have insisted that the point of persistence hunting is not to induce exhaustion but specifically to induce heat stroke. However, a decade later, they understood persistence hunting to include pursuit until injury or heat stroke or exhaustion; and driving prey to ambushes, natural traps like cliffs and rivers and ravines, or man-made ditches and stakes. There do not seem to be descriptions which take account of ''heat dissipation theory''. Hunters Startled animals respond in characteristic ways that may be effective against animal predators. People learn how prey respond and plan (and prepare themselves) to overcome that response. They learn how to monitor their own condition and stay within their limits, while pushing the prey animal beyond its physiological limits. Research and discussion about persistence hunting has often ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hadza Montage
Hadza may refer to: *Hadza people, or ''Hadzabe'', a hunter-gatherer people of Tanzania *Hadza language Hadza is a language isolate spoken along the shores of Lake Eyasi in Tanzania by around 1,000 Hadza people, who include in their number the last full-time hunter-gatherers in Africa. It is one of only three languages in East Africa with click con ..., the isolate language spoken by the Hadza people {{Disambiguation Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pastoralism
Pastoralism is a form of animal husbandry where domesticated animals (known as " livestock") are released onto large vegetated outdoor lands ( pastures) for grazing, historically by nomadic people who moved around with their herds. The animal species involved include cattle, camels, goats, yaks, llamas, reindeer, horses and sheep. Pastoralism occurs in many variations throughout the world, generally where environmental characteristics such as aridity, poor soils, cold or hot temperatures, and lack of water make crop-growing difficult or impossible. Operating in more extreme environments with more marginal lands means that pastoral communities are very vulnerable to the effects of global warming. Pastoralism remains a way of life in many geographic areas, including Africa, the Tibetan plateau, the Eurasian steppes, the Andes, Patagonia, the Pampas, Australia and many other places. , between 200 million and 500 million people globally practised pastora ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nilotic Peoples
The Nilotic peoples are people indigenous to the Nile Valley who speak Nilotic languages. They inhabit South Sudan, Sudan, Ethiopia, Uganda, Kenya, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Rwanda, Burundi and Tanzania. Among these are the Burun-speaking peoples, Karo peoples, Luo peoples, Ateker peoples, Kalenjin peoples, Datooga, Dinka, Nuer, Atwot, Lotuko, and the Maa-speaking peoples. The Nilotes constitute the majority of the population in South Sudan, an area that is believed to be their original point of dispersal. After the Bantu peoples, they constitute the second-most numerous group of peoples inhabiting the African Great Lakes region around the East African Rift. They make up a notable part of the population of southwestern Ethiopia as well. The Nilotic peoples primarily adhere to Christianity and traditional faiths, including the Dinka religion. Some Nilotic peoples also adhere to Islam. Name The terms "Nilotic" and "Nilote"' were previously used as racial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bantu Peoples
The Bantu peoples, or Bantu, are an ethnolinguistic grouping of approximately 400 distinct ethnic groups who speak Bantu languages. They are native to 24 countries spread over a vast area from Central Africa to Southeast Africa and into Southern Africa. There are several hundred Bantu languages. Depending on the definition of "language" or "dialect", it is estimated that there are between 440 and 680 distinct languages. The total number of speakers is in the hundreds of millions, ranging at roughly 350 million in the mid-2010s (roughly 30% of the population of Africa, or roughly 5% of the total world population). About 60 million speakers (2015), divided into some 200 ethnic or tribal groups, are found in the Democratic Republic of the Congo alone. The larger of the individual Bantu groups have populations of several million, e.g. the people of Rwanda and Burundi (25 million), the Baganda people of Uganda (10 million as of 2019), the Shona of Zimbabwe (15 million ), the Z ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Admixture
Genetic admixture occurs when previously diverged or isolated genetic lineages mix.⅝ Admixture results in the introduction of new genetic lineages into a population. Examples Climatic cycles facilitate genetic admixture in cold periods and genetic diversification in warm periods. Natural flooding can cause genetic admixture within populations of migrating fish species. Genetic admixture may have an important role for the success of populations that colonise a new area and interbreed with individuals of native populations. Mapping Admixture mapping is a method of gene mapping that uses a population of mixed ancestry (an admixed population) to find the genetic loci that contribute to differences in diseases or other phenotypes found between the different ancestral populations. The method is best applied to populations with recent admixture from two populations that were previously genetically isolated. The method attempts to correlate the degree of ancestry near a genetic locus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sandawe People
The Sandawe are an indigenous ethnic group of Southeast Africa, based in the Chemba District of Dodoma Region in central Tanzania. In 2000, the Sandawe population was estimated to be 40,000. The Sandawe language is a tonal language that uses click consonants, as do the Khoe languages of southern Africa. There is no other proven connection between the two. History Origins Although the Khoisan were originally thought to possess the oldest human DNA lineages, those of the Sandawe are older. This suggests southern Khoisan originated in East Africa. The Sandawe today are considered descendants of an original Bushmen-like people, unlike their modern neighbours, the Gogo. They live in the geographic centre of old German East Africa, the 'Street of Caravans' crossing their southern edge. The Sandawe language may share a common ancestor with the Khoe languages of southern Africa. It has clicks and the surrounding Bantu peoples find it difficult to learn. It is unrelated to the nei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Click Consonant
Click consonants, or clicks, are speech sounds that occur as consonants in many languages of Southern Africa and in three languages of East Africa. Examples familiar to English-speakers are the ''tut-tut'' (British spelling) or '' tsk! tsk!'' (American spelling) used to express disapproval or pity, the '' tchick!'' used to spur on a horse, and the '' clip-clop!'' sound children make with their tongue to imitate a horse trotting. Anatomically, clicks are obstruents articulated with two closures (points of contact) in the mouth, one forward and one at the back. The enclosed pocket of air is rarefied by a sucking action of the tongue (in technical terminology, clicks have a lingual ingressive airstream mechanism). The forward closure is then released,This is the case for all clicks used as consonants in words. Paralinguistically, however, there are other methods of making clicks: ''under'' the tongue or as above but by releasing the rear occlusion first. See #Places of articul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oral History
Oral history is the collection and study of historical information about individuals, families, important events, or everyday life using audiotapes, videotapes, or transcriptions of planned interviews. These interviews are conducted with people who participated in or observed past events and whose memories and perceptions of these are to be preserved as an aural record for future generations. Oral history strives to obtain information from different perspectives and most of these cannot be found in written sources. ''Oral history'' also refers to information gathered in this manner and to a written work (published or unpublished) based on such data, often preserved in archives and large libraries.oral history. (n.d.) The Columbia Electronic Encyclopedia®. (2013). Retrieved March 12, 2018 from https://encyclopedia2.thefreedictionary.com/oral+history Knowledge presented by Oral History (OH) is unique in that it shares the tacit perspective, thoughts, opinions and understanding of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Safari
A safari (; ) is an overland journey to observe wild animals, especially in eastern or southern Africa. The so-called "Big Five" game animals of Africa – lion, leopard, rhinoceros, elephant, and Cape buffalo – particularly form an important part of the safari market, both for wildlife viewing and big-game hunting. Etymology The Swahili word means "journey", originally from the Arabic noun ar, سفر, safar, label=none, meaning "journey", "travel", "trip", or "tour"; the verb for "to travel" in Swahili is . These words are used for any type of journey, e.g. by bus from Nairobi to Mombasa or by ferry from Dar es Salaam to Unguja. ''Safari'' entered the English language at the end of the 1850s thanks to explorer Richard Francis Burton. The Regimental March of the King's African Rifles was "Funga Safari", literally 'set out on a journey', or, in other words, pack up equipment ready for travel. Which is, in English: On Kenya's independence from the United Kingdom, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
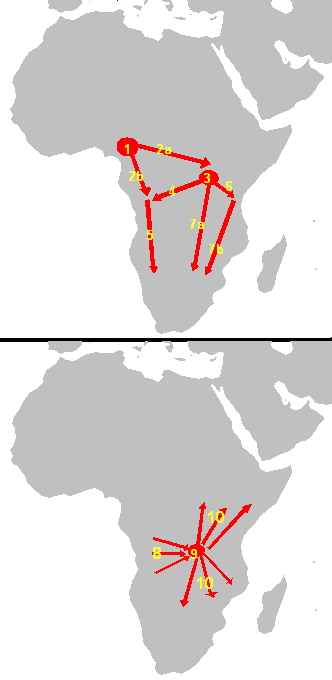
Bantu Expansion
The Bantu expansion is a hypothesis about the history of the major series of migrations of the original Proto-Bantu-speaking group, which spread from an original nucleus around Central Africa across much of sub-Saharan Africa. In the process, the Proto-Bantu-speaking settlers displaced or absorbed pre-existing hunter-gatherer and pastoralist groups that they encountered. The primary evidence for this expansion is linguistic – a great many of the languages which are spoken across Sub-Equatorial Africa are remarkably similar to each other, suggesting the common cultural origin of their original speakers. The linguistic core of the Bantu languages, which comprise a branch of the Atlantic-Congo language family, was located in the southern regions of Cameroon. However, attempts to trace the exact route of the expansion, to correlate it with archaeological evidence and genetic evidence, have not been conclusive; thus although the expansion is widely accepted as having taken pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It has 193 member states and 12 associate members, as well as partners in the non-governmental, intergovernmental and private sector. Headquartered at the World Heritage Centre in Paris, France, UNESCO has 53 regional field offices and 199 national commissions that facilitate its global mandate. UNESCO was founded in 1945 as the successor to the League of Nations's International Committee on Intellectual Cooperation.English summary). Its constitution establishes the agency's goals, governing structure, and operating framework. UNESCO's founding mission, which was shaped by the Second World War, is to advance peace, sustainable development and human rights by facilitating collaboration and dialogue among nations. It pursues this objec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)