|
HTV-3
Kounotori 3 ( ja, こうのとり3号機; English: "white stork" ), also known as HTV-3, was the third flight of the Japanese H-II Transfer Vehicle. It was launched on 21 July 2012 to resupply the International Space Station (ISS) aboard the H-IIB Launch Vehicle No. 3 (H-IIB F3) manufactured by Mitsubishi Heavy Industries (MHI) and JAXA. Kounotori 3 arrived at the ISS on 27 July 2012, and Expedition 32 Flight Engineer and JAXA astronaut Akihiko Hoshide used the International Space Station's Canadarm2 robotic arm to install Kounotori 3, to its docking port on the Earth-facing side (nadir) of the Harmony module at 14:34 UTC. After the supplies are unloaded, Kounotori 3 was loaded with waste material from ISS, including used experiment equipment and used clothes. Then Kounotori 3 was unberthed from the ISS on 11 September 2012 and burned up upon reentering in the atmosphere of Earth on 14 September 2012. Specifications Major changes of Kounotori 3 from previous Kounotori are: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raiko
RAIKO ( ja, 雷鼓, literally ''thunder drum'') is a Japanese satellite which was built and operated by Tohoku University, Tohoku and Wakayama University, Wakayama Universities. A two-unit CubeSat, RAIKO was deployed from the International Space Station (ISS) on 4 October 2012, having been launched on 21 July 2012. RAIKO was launched aboard the Kounotori 3 (HTV-3) spacecraft, atop an H-IIB launch vehicle flying from pad LC-Y2 of the Yoshinobu Launch Complex at the Tanegashima Space Center. The launch occurred at 02:06:18 Coordinated Universal Time, UTC on 21 July 2012. Four other CubeSats were launched with RAIKO; WE WISH, Niwaka, FITSAT-1, TechEdSat, TechEdSat-1 and F-1 (satellite), F-1. The five CubeSats was delivered to the International Space Station for deployment. CubeSats were deployed from Japanese Experiment Module (JEM) ''Kibō (ISS module), Kibō'' via the J-SSOD system on 4 October 2012. Named after a Japanese god of thunder, RAIKO is a spacecraft, which was used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
F-1 (satellite)
F-1 is a CubeSat built by FSpace laboratory at FPT University, in Hanoi, Vietnam, in partnership with Angstrom Space Technology Center (ASTC), Uppsala University, Sweden and Nanoracks LLC, United States. Its mission is to train young engineers and students about aerospace engineering and evaluate an advanced three-axis magnetometer, Spin-Dependent Tunneling Magnetometer (SDTM) designed in Sweden by ASTC. F-1 was launched on 21 July 2012 and delivered to the International Space Station (ISS) aboard Kounotori 3 (HTV-3) along with the RAIKO, WE WISH, Niwaka and TechEdSat-1 cubesats. Then, on 4 October 2012, it was deployed into orbit from the ISS using the JEM-Small Satellite Orbital Deployer (J-SSOD) which was attached to the Kibō module's robotic arm. As of 2 November 2012, F-1 failed to confirm communication after the orbital deployment. Hardware * Structure: aluminium alloy T-6061 * Power supply: body-mounted solar cells, rechargeable Li-Polymer battery * PIC16 an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harmony Module
''Harmony'', also known as ''Node 2'', is the "utility hub" of the International Space Station. It connects the laboratory modules of the United States, Europe and Japan, as well as providing electrical power and electronic data. Sleeping cabins for four of the crew are housed here. ''Harmony'' was successfully launched into space aboard Space Shuttle flight STS-120 on 23 October 2007. After temporarily being attached to the port side of the ''Unity'' module, it was moved to its permanent location on the forward end of the ''Destiny'' module on 14 November 2007. ''Harmony'' added to the station's living volume, an increase of almost 20%, from to . Its successful installation meant that from NASA's perspective, the station was considered to be "U.S. Core Complete". Origin of name The unit formerly known as ''Node 2'' was renamed ''Harmony'' in March 2004. The name was chosen in a competition where more than 2,200 students from 32 states participated. The ''Node 2 Ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harmony (ISS Module)
''Harmony'', also known as ''Node 2'', is the "utility hub" of the International Space Station. It connects the laboratory modules of the United States, Europe and Japan, as well as providing electrical power and electronic data. Sleeping cabins for four of the crew are housed here. ''Harmony'' was successfully launched into space aboard Space Shuttle The Space Shuttle is a retired, partially reusable low Earth orbital spacecraft system operated from 1981 to 2011 by the U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) as part of the Space Shuttle program. Its official program na ... flight STS-120 on 23 October 2007. After temporarily being attached to the port side of the Unity (ISS module), ''Unity'' module, it was moved to its permanent location on the forward end of the Destiny (ISS module), ''Destiny'' module on 14 November 2007. ''Harmony'' added to the station's living volume, an increase of almost 20%, from to . Its successful installation meant th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Akihiko Hoshide
is a Japanese engineer, JAXA astronaut, and former Commander of the International Space Station. On August 30, 2012, Hoshide became the third Japanese astronaut to walk in space. Early life and education He was born in 1968 in Tokyo, Japan. He received an International Baccalaureate Diploma from the United World College of South East Asia, Singapore in 1987, a bachelor's degree in mechanical engineering from Keio University in 1992, and a Master of Science degree in aerospace engineering from the University of Houston Cullen College of Engineering in 1997. Experience Hoshide joined the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA) in 1992 and worked in the development of the H-II launch vehicle for two years. From 1994 to 1999, he was as an astronaut support engineer for the NASDA Astronaut Office, supporting the development of the astronaut training program, and he supported astronaut Koichi Wakata during Wakata's training and mission on STS-72. Astronaut career In Feb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Niwaka
Niwaka or FITSAT-1 is a 1U CubeSat satellite deployed from the International Space Station (ISS) on 4 October 2012. The Niwaka satellite includes high power LEDs which are driven by 200 watts pulses, allowing Morse code style communication from the sky to the ground. FITSAT-1 (Niwaka) communicates with ground by means of 5.8 GHz high-speed (115200 bit/s) transmitter. It also has a 437 MHz (amateur band) beacon and transmitter with data rate 1200 bit/s for telemetry downlink. The name Niwaka derives from "Hakata Niwaka", which is traditional impromptu comical talking with masks. It is also the old name of the city Fukuoka, site of the Fukuoka Institute of Technology in Japan which created the satellite. WE WISH, RAIKO, FITSAT-1, F-1, and TechEdSat-1 travelled to orbit aboard Kounotori 3 (HTV-3). It reentered in the atmosphere of Earth on 4 July 2013. Launch See also * 2012 in spaceflight * Ginrei Ginrei or ShindaiSat was a 400x400x450mm cube-like microsatellite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
We-Wish
WE WISH (World Environmental Watching and Investigation from Space Height) was a small commercial CubeSat which was deployed from the International Space Station (ISS) in October 2012 and which deorbited in March 2013. It was built by the Japanese technology company Meisei Electric"WE WISH" Space.skyrocket.de Retrieved 12 January 2021 and the Meisei Amateur Radio Club, and could transmit pictures taken by a small via radio at 437.515 ."Tag Archives: W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TechEdSat
Technology Education Satellite (TechEdSat) is a successful nano-sat flight series conducted from the NASA Ames Research Center in collaboration with numerous universities (San Jose State University, University of Idaho, University of California, University of Minnesota, Smith College). While one of the principal aims has been to introduce young professionals and university students to the practical realm of developing space flight hardware, considerable innovations have been introduced. In addition, this evolving flight platform has tested concepts for Low Earth Orbit (LEO) sample return, as well as planetary nano-sat class mission concepts. TechEdSat-1 The first TechEdSat (later renamed "TechEdSat-1" or "TES-1") was a 1U-Cubesat designed to evaluate Space Plug-and-play Avionics (SPA) designed in Sweden by ÅAC Microtec. It was also originally intended to perform a communications experiment utilizing the Iridium and Orbcomm satellite phone network, although this functi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
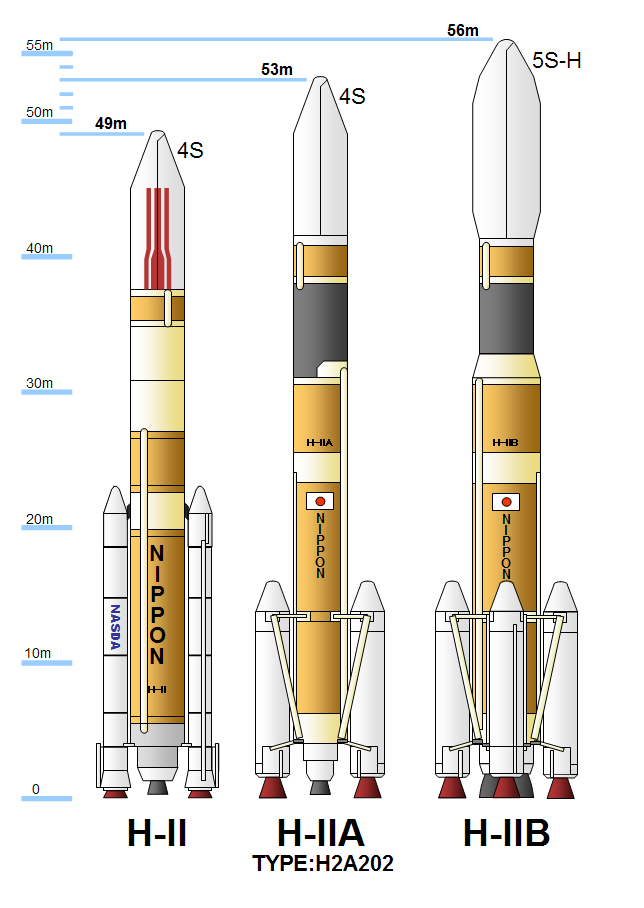
H-IIB
H-IIB (H2B) was an expendable space launch system jointly developed by the Japanese government's space agency JAXA and Mitsubishi Heavy Industries. It was used to launch the H-II Transfer Vehicle (HTV, or ''Kōnotori'') cargo spacecraft for the International Space Station. The H-IIB was a liquid-fueled rocket, with solid-fuel strap-on boosters and was launched from the Tanegashima Space Center in southern Japan. H-IIB made its first flight in 2009, and had made a total of nine flights through 2020 with no failures. H-IIB was able to carry a payload of up to to Geostationary transfer orbit (GTO), compared with the payload of 4000-6000 kg for the H-IIA, a predecessor design. Its performance to low Earth orbit (LEO) was sufficient for the H-II Transfer Vehicle (HTV). The first H-IIB was launched in September 2009 and the last H-IIB was launched in May 2020. Development The H-IIB was a space launch vehicle jointly designed, manufactured and operated by JAXA and Mitsub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IHI Corporation
, formerly known as , is a Japanese engineering corporation headquartered in Tokyo, Japan that produces and offers ships, space launch vehicles, aircraft engines, marine diesel engines, gas turbines, gas engines, railway systems, turbochargers for automobiles, plant engineering, industrial machinery, power station boilers and other facilities, suspension bridges and other structures. IHI is listed on the Tokyo Stock Exchange Section 1. History * 1853 – establishment of Ishikawajima Shipyard in the Chuo district of Tokyo. * 1854 - 1856: construction of the Japanese warship Asahi Maru at Ishikawajima shipyard. * 1889 – incorporation of Ishikawajima Shipyard as Ishikawajima Shipbuilding & Engineering Co., Ltd. * 1907 – establishment of Harima Dock Co., Ltd. * 1929 – spinoff of Harima's automobile section as Ishikawajima Automotive Works (later Isuzu through a series of mergers) * 1960 – establishment of Ishikawajima-Harima Heavy Industries Co., Ltd. through a merger o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reentry Breakup Recorder
A Reentry Breakup Recorder (REBR) is a device that is designed to be placed aboard a spacecraft to record pertinent data when the spacecraft (intentionally) breaks up as it re-enters Earth's atmosphere. The device records data regarding the thermal, acceleration, rotational and other stresses the vehicle is subject to. In the final stages it transmits the data back to a laboratory before it is destroyed when it hits the surface. History Two REBRs were launched in January 2011 on the Japanese Kounotori 2 transfer vehicle. One recorded the subsequent re-entry of that vehicle, and the other was placed aboard the Johannes Kepler ATV, which reentered Earth's atmosphere on 21 June 2011. The Kounotori 2 vehicle re-entered on 30 March 2011. Its REBR successfully collected and returned its data; it survived the impact with the ocean and while floating continued to transmit. It took between 6 and 8 weeks to analyze the data. The second unit was intended to collect data during the reentr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kibō (ISS Module)
The Japanese Experiment Module (JEM), nicknamed , is a Japanese science module for the International Space Station (ISS) developed by JAXA. It is the largest single ISS module, and is attached to the ''Harmony'' module. The first two pieces of the module were launched on Space Shuttle missions STS-123 and STS-124. The third and final components were launched on STS-127. Components In initial configuration, ''Kibō'' consisted of six major elements: * Pressurized Module (PM) * Exposed Facility (EF) * Experiment Logistics Module (ELM) Pressurized Section (ELM-PS) * Experiment Logistics Module (ELM) Exposed Section (ELM-ES) * Japanese Experiment Module remote manipulator system (JEMRMS) * Inter-orbit communication system (ICS) Pressurized Module The Pressurized Module (PM) is the core component connected to the port hatch of ''Harmony''. It is cylindrical in shape and contains twenty-three International Standard Payload Racks (ISPRs), ten of which are dedicated to sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |