|
HSPG2
Perlecan (PLC) also known as basement membrane-specific heparan sulfate proteoglycan core protein (HSPG) or heparan sulfate proteoglycan 2 (HSPG2), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''HSPG2'' gene. The HSPG2 gene codes for a 4,391 amino acid protein with a molecular weight of 468,829. It is one of the largest known proteins. Perlecan was originally isolated from a tumor cell line and shown to be present in all native basement membranes. Perlecan is a large multidomain (five domains, labeled I-V) proteoglycan that binds to and cross-links many extracellular matrix (ECM) components and cell-surface molecules. Perlecan is synthesized by both vascular endothelial and smooth muscle cells and deposited in the extracellular matrix of parahoxozoans. Perlecan is highly conserved across species and the available data indicate that it has evolved from ancient ancestors by gene duplication and exon shuffling. Structure Perlecan consists of a core protein of molecular weight 4 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
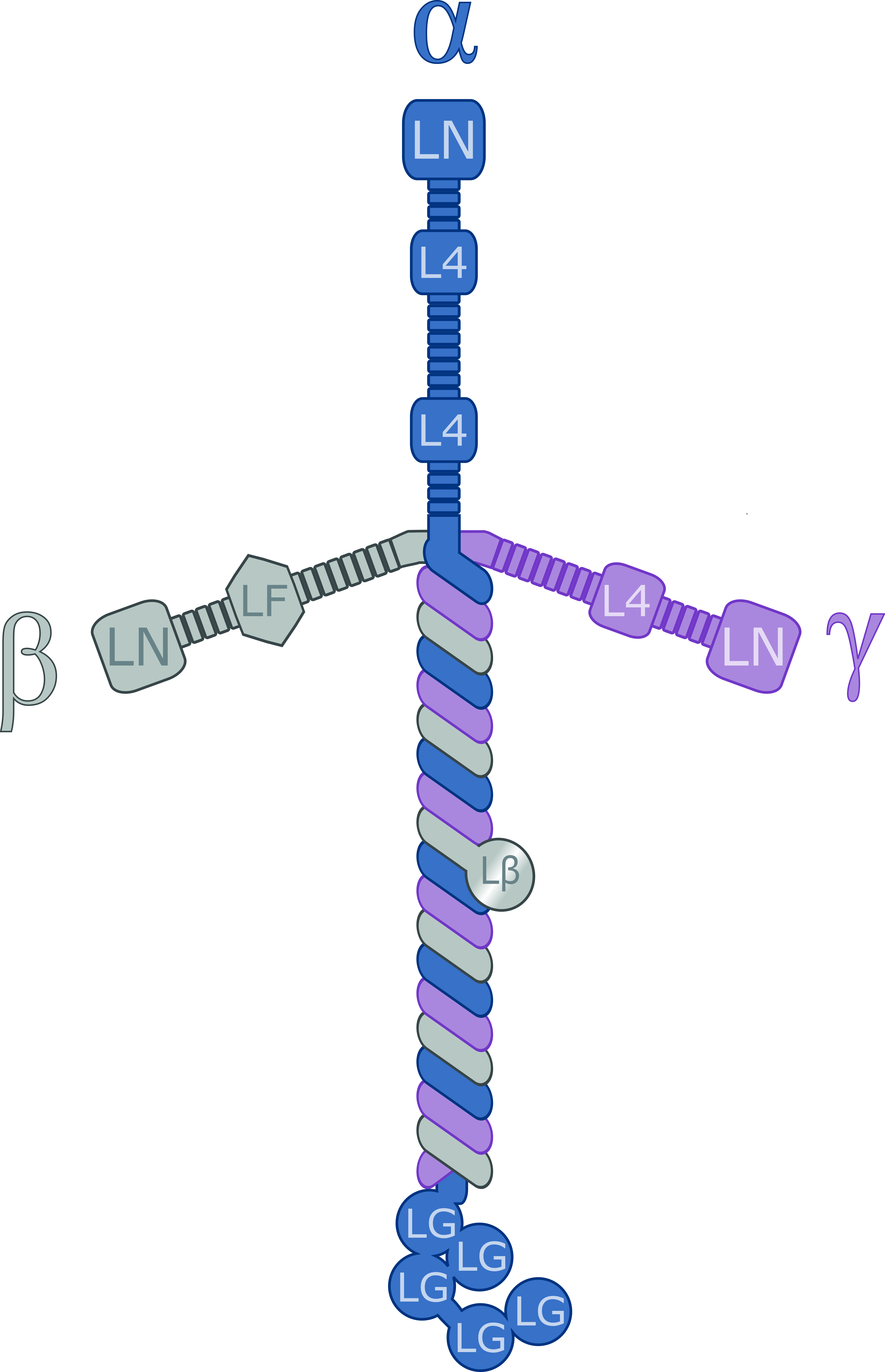
Laminin
Laminins are a family of glycoproteins of the extracellular matrix of all animals. They are major components of the basal lamina (one of the layers of the basement membrane), the protein network foundation for most cells and organs. The laminins are an important and biologically active part of the basal lamina, influencing cell differentiation, migration, and adhesion. Laminins are heterotrimeric proteins with a high molecular mass (~400 to ~900 kDa). They contain three different chains (α, β and γ) encoded by five, four, and three paralogous genes in humans, respectively. The laminin molecules are named according to their chain composition. Thus, laminin-511 contains α5, β1, and γ1 chains. Fourteen other chain combinations have been identified ''in vivo''. The trimeric proteins intersect to form a cross-like structure that can bind to other cell membrane and extracellular matrix molecules. The three shorter arms are particularly good at binding to other laminin molecules, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immunoglobulin Superfamily
The immunoglobulin superfamily (IgSF) is a large protein superfamily of cell surface and soluble proteins that are involved in the recognition, binding, or adhesion processes of cells. Molecules are categorized as members of this superfamily based on shared structural features with immunoglobulins (also known as antibodies); they all possess a domain known as an immunoglobulin domain or fold. Members of the IgSF include cell surface antigen receptors, co-receptors and co-stimulatory molecules of the immune system, molecules involved in antigen presentation to lymphocytes, cell adhesion molecules, certain cytokine receptors and intracellular muscle proteins. They are commonly associated with roles in the immune system. Otherwise, the sperm-specific protein IZUMO1, a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily, has also been identified as the only sperm membrane protein essential for sperm-egg fusion. Immunoglobulin domains Proteins of the IgSF possess a structural domain known as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morpholino
A Morpholino, also known as a Morpholino oligomer and as a phosphorodiamidate Morpholino oligomer (PMO), is a type of oligomer molecule (colloquially, an oligo) used in molecular biology to modify gene expression. Its molecular structure contains DNA bases attached to a backbone of methylenemorpholine rings linked through phosphorodiamidate groups. Morpholinos block access of other molecules to small (~25 base) specific sequences of the base-pairing surfaces of ribonucleic acid (RNA). Morpholinos are used as research tools for reverse genetics by knocking down gene function. This article discusses only the Morpholino antisense oligomers, which are nucleic acid analogs. The word "Morpholino" can occur in other chemical names, referring to chemicals containing a six-membered morpholine ring. To help avoid confusion with other morpholine-containing molecules, when describing oligos "Morpholino" is often capitalized as a trade name, but this usage is not consistent across scienti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfotransferase
Sulfotransferases (SULTs) are transferase enzymes that catalyze the transfer of a sulfo group from a donor molecule to an acceptor alcohol or amine. The most common sulfo group donor is 3'-phosphoadenosine-5'-phosphosulfate (PAPS). In the case of alcohol as acceptor, the product is a sulfate (R-OSO3−), whereas an amine leads to a sulfamate (R-NH-SO3−). Both reactive groups for a sulfonation via sulfotransferases may be part of a protein, lipid, carbohydrate or steroid. Examples The following are examples of sulfotransferases: * carbohydrate sulfotransferase: CHST1, CHST2, CHST3, CHST4, CHST5, CHST6, CHST7, CHST8, CHST9, CHST10, CHST11, CHST12, CHST13, CHST14 * galactose-3-O-sulfotransferase: GAL3ST1, GAL3ST2, GAL3ST3, GAL3ST4 * heparan sulfate 2-O-sulfotransferase: HS2ST1 * heparan sulfate 3-O-sulfotransferase: HS3ST1, HS3ST2, HS3ST3A1, HS3ST3B1, HS3ST4, HS3ST5, HS3ST6 * heparan sulfate 6-O-sulfotransferase: HS6ST1, HS6ST2, HS6ST3 * N-deacetylase ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glomerulus
''Glomerulus'' () is a common term used in anatomy to describe globular structures of entwined vessels, fibers, or neurons. ''Glomerulus'' is the diminutive of the Latin ''glomus'', meaning "ball of yarn". ''Glomerulus'' may refer to: * the filtering unit of the kidney; see Glomerulus (kidney). * a structure in the olfactory bulb; see Glomerulus (olfaction). * the contact between specific cells in the cerebellum; see Glomerulus (cerebellum) The cerebellar glomerulus is a small, intertwined mass of nerve fiber terminals in the granular layer of the cerebellar cortex. It consists of post-synaptic granule cell dendrites and pre-synaptic Golgi cell axon terminals surrounding the pre- .... See also * Glomerulation, a hemorrhage of the bladder {{SIA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Puromycin
Puromycin is an antibiotic protein synthesis inhibitor which causes premature chain termination during translation. Inhibition of translation Puromycin is an aminonucleoside antibiotic, derived from the '' Streptomyces alboniger'' bacterium, that causes premature chain termination during translation taking place in the ribosome. Part of the molecule resembles the 3' end of the aminoacylated tRNA. It enters the A site and transfers to the growing chain, causing the formation of a puromycylated nascent chain and premature chain release. The exact mechanism of action is unknown at this time but the 3' position contains an amide linkage instead of the normal ester linkage of tRNA. That makes the molecule much more resistant to hydrolysis and stops the ribosome. Puromycin is selective for either prokaryotes or eukaryotes. Also of note, puromycin is critical in mRNA display. In this reaction, a puromycin molecule is chemically attached to the end of an mRNA template, which is then ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nephron
The nephron is the minute or microscopic structural and functional unit of the kidney. It is composed of a renal corpuscle and a renal tubule. The renal corpuscle consists of a tuft of capillaries called a glomerulus and a cup-shaped structure called Bowman's capsule. The renal tubule extends from the capsule. The capsule and tubule are connected and are composed of epithelial cells with a lumen. A healthy adult has 1 to 1.5 million nephrons in each kidney. Blood is filtered as it passes through three layers: the endothelial cells of the capillary wall, its basement membrane, and between the foot processes of the podocytes of the lining of the capsule. The tubule has adjacent peritubular capillaries that run between the descending and ascending portions of the tubule. As the fluid from the capsule flows down into the tubule, it is processed by the epithelial cells lining the tubule: water is reabsorbed and substances are exchanged (some are added, others are removed); first with t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesenchyme
Mesenchyme () is a type of loosely organized animal embryonic connective tissue of undifferentiated cells that give rise to most tissues, such as skin, blood or bone. The interactions between mesenchyme and epithelium help to form nearly every organ in the developing embryo. Vertebrates Structure Mesenchyme is characterized morphologically by a prominent ground substance matrix containing a loose aggregate of reticular fibers and unspecialized mesenchymal stem cells. Mesenchymal cells can migrate easily (in contrast to epithelial cells, which lack mobility), are organized into closely adherent sheets, and are polarized in an apical-basal orientation. Development The mesenchyme originates from the mesoderm. From the mesoderm, the mesenchyme appears as an embryologically primitive "soup". This "soup" exists as a combination of the mesenchymal cells plus serous fluid plus the many different tissue proteins. Serous fluid is typically stocked with the many serous elements, such a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycosylation
Glycosylation is the reaction in which a carbohydrate (or ' glycan'), i.e. a glycosyl donor, is attached to a hydroxyl or other functional group of another molecule (a glycosyl acceptor) in order to form a glycoconjugate. In biology (but not always in chemistry), glycosylation usually refers to an enzyme-catalysed reaction, whereas glycation (also 'non-enzymatic glycation' and 'non-enzymatic glycosylation') may refer to a non-enzymatic reaction (though in practice, 'glycation' often refers more specifically to Maillard-type reactions). Glycosylation is a form of co-translational and post-translational modification. Glycans serve a variety of structural and functional roles in membrane and secreted proteins. The majority of proteins synthesized in the rough endoplasmic reticulum undergo glycosylation. Glycosylation is also present in the cytoplasm and nucleus as the ''O''-GlcNAc modification. Aglycosylation is a feature of engineered antibodies to bypass glycosylation. Five clas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chondroitin Sulfate
Chondroitin sulfate is a sulfated glycosaminoglycan (GAG) composed of a chain of alternating sugars ( N-acetylgalactosamine and glucuronic acid). It is usually found attached to proteins as part of a proteoglycan. A chondroitin chain can have over 100 individual sugars, each of which can be sulfated in variable positions and quantities. Chondroitin sulfate is an important structural component of cartilage, and provides much of its resistance to compression. Along with glucosamine, chondroitin sulfate has become a widely used dietary supplement for treatment of osteoarthritis, although large clinical trials failed to demonstrate any symptomatic benefit of chondroitin. Medical use Chondroitin is used in dietary supplements as an alternative medicine to treat osteoarthritis. It is also approved and regulated as a symptomatic slow-acting drug for this disease (SYSADOA) in Europe and some other countries. It is commonly sold together with glucosamine. A 2015 Cochrane review of clini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basic Fibroblast Growth Factor
Fibroblast growth factor 2, also known as basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) and FGF-β, is a growth factor and signaling protein encoded by the ''FGF2'' gene. It binds to and exerts effects via specific fibroblast growth factor receptor ''(FGFR) proteins'', themselves a family of closely related molecules. Fibroblast growth factor protein was first purified in 1975; soon thereafter three variants were isolated: 'basic FGF' (FGF2); Heparin-binding growth factor-2; and Endothelial cell growth factor-2. Gene sequencing revealed that this group is the same FGF2 protein and is a member of a family of FGF proteins. Function Like other FGF family members, basic fibroblast growth factor possess broad mitogenic and cell survival activities, and is involved in a variety of biological processes, including embryonic development, cell growth, morphogenesis, tissue repair, tumor growth and invasion. In normal tissue, bFGF is present in basement membranes and in the subendothelial ext ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
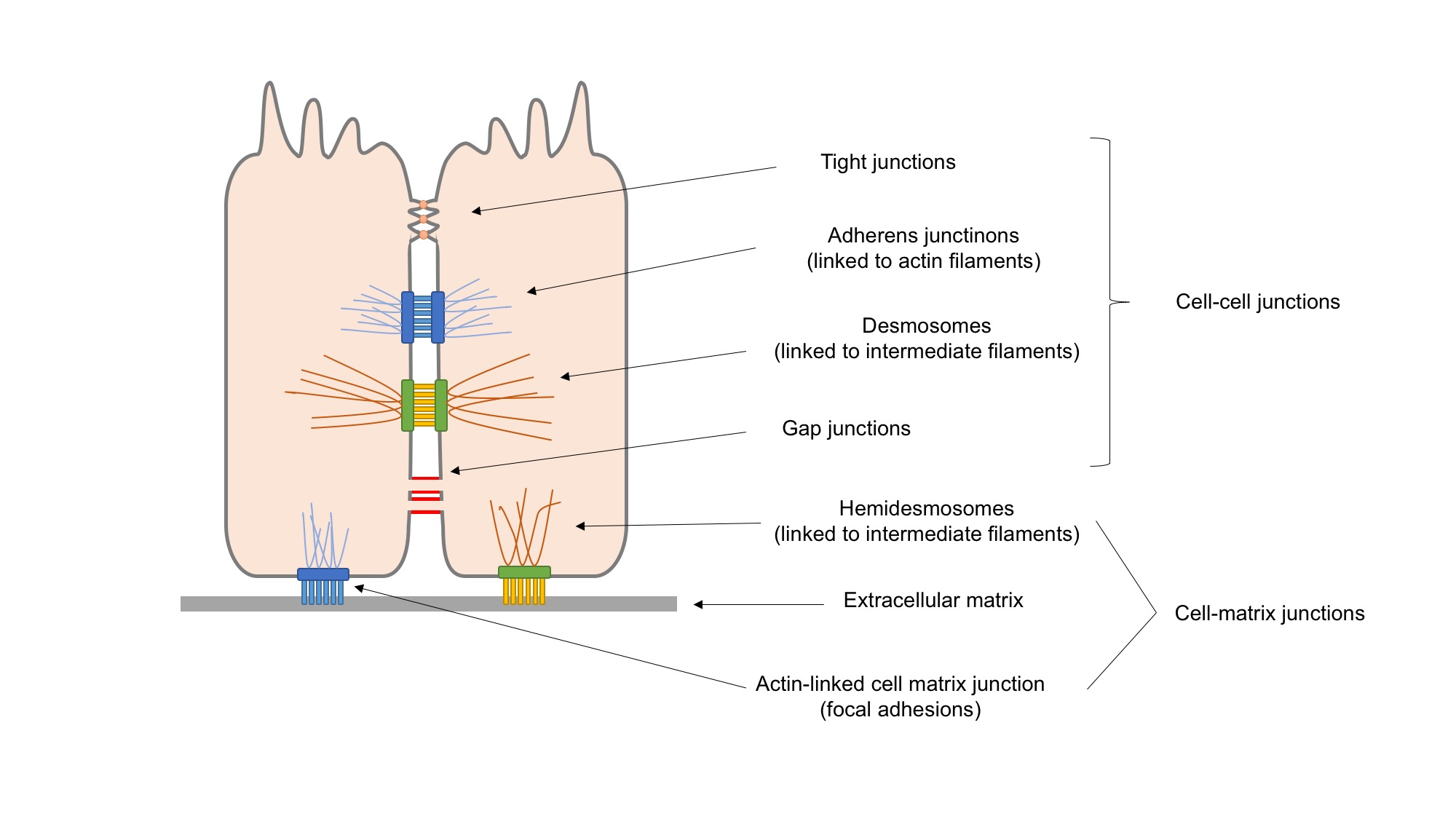
Cell Adhesion
Cell adhesion is the process by which cells interact and attach to neighbouring cells through specialised molecules of the cell surface. This process can occur either through direct contact between cell surfaces such as cell junctions or indirect interaction, where cells attach to surrounding extracellular matrix, a gel-like structure containing molecules released by cells into spaces between them. Cells adhesion occurs from the interactions between cell-adhesion molecules (CAMs), transmembrane proteins located on the cell surface. Cell adhesion links cells in different ways and can be involved in signal transduction for cells to detect and respond to changes in the surroundings. Other cellular processes regulated by cell adhesion include cell migration and tissue development in multicellular organisms. Alterations in cell adhesion can disrupt important cellular processes and lead to a variety of diseases, including cancer and arthritis. Cell adhesion is also essential for in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |