|
HSP90AB1
Heat shock protein HSP 90-beta also called HSP90beta is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''HSP90AB1'' gene. Function HSP90AB1 is a molecular chaperone. Chaperones are proteins that bind to other proteins, thereby stabilizing them in an ATP-dependent manner. Chaperones stabilize new proteins during translation, mature proteins which are partially unstable but also proteins that have become partially denatured due to various kinds of cellular stress. In case proper folding or refolding is impossible, HSPs mediate protein degradation. They also have specialized functions, such as intracellular transport into organelles. Classification Human HSPs are classified into 5 major groups according to the HGNC: * HSP70 * DnaJ (HSP40) * HSPB (small heat shock proteins) * HSPC (HSP90) * chaperonins Chaperonins are characterized by their barrel-shaped structure with binding sites for client proteins inside the barrels. The human HSP90 group consists of 5 members according to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HSP90AA1
Heat shock protein HSP 90-alpha is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''HSP90AA1'' gene. Function The gene, HSP90AA1, encodes the human stress-inducible 90-kDa heat shock protein alpha (Hsp90A). Complemented by the constitutively expressed paralog Hsp90B which shares over 85% amino acid sequence identity, Hsp90A expression is initiated when a cell experiences proteotoxic stress. Once expressed Hsp90A dimers operate as molecular chaperones that bind and fold other proteins into their functional 3-dimensional structures. This molecular chaperoning ability of Hsp90A is driven by a cycle of structural rearrangements fueled by ATP hydrolysis. Current research on Hsp90A focuses in its role as a drug target due to its interaction with a large number of tumor promoting proteins and its role in cellular stress adaptation. Gene structure Human HSP90AA1 is encoded on the complement strand of Chromosome 14q32.33 and spans over 59 kbp. Several pseudogenes of HSP90AA1 exist th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HSP90
Hsp90 (heat shock protein 90) is a chaperone protein that assists other proteins to fold properly, stabilizes proteins against heat stress, and aids in protein degradation. It also stabilizes a number of proteins required for tumor growth, which is why Hsp90 inhibitors are investigated as anti-cancer drugs. Heat shock proteins, as a class, are among the most highly expressed cellular proteins across all species. As their name implies, heat shock proteins protect cells when stressed by elevated temperatures. They account for 1–2% of total protein in unstressed cells. However, when cells are heated, the fraction of heat shock proteins increases to 4–6% of cellular proteins. Heat shock protein 90 (Hsp90) is one of the most common of the heat-related proteins. The "90" comes from the fact that it has a mass of roughly 90 kilodaltons. A 90 kDa protein is considered fairly large for a non-fibrous protein. Hsp90 is found in bacteria and all branches of eukarya ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MAPK14
Mitogen-activated protein kinase 14, also called p38-α, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''MAPK14'' gene. MAPK14 encodes p38α mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) which is the prototypic member of the p38 MAPK family. p38 MAPKs are also known as stress-activated serine/threonine-specific kinases (SAPKs). In addition to MAPK14 for p38α MAPK, the p38 MAPK family has three additional members, including MAPK11, MAPK12 and MAPK13 which encodes p38β MAPK, p38γ MAPK and p38δ MAPK isoforms, respectively. p38α MAPK was originally identified as a tyrosine phosphorylated protein detected in activated immune cell macrophages with an essential role in inflammatory cytokine induction, such as Tumor Necrotic Factor α (TNFα). However, p38α MAPK mediated kinase activity has been implicated in many tissues beyond immune systems. p38α MAPK is mainly activated through MAPK kinase kinase cascades and exerts its biological function via downstream substrate phosphorylati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transcription Factor
In molecular biology, a transcription factor (TF) (or sequence-specific DNA-binding factor) is a protein that controls the rate of transcription of genetic information from DNA to messenger RNA, by binding to a specific DNA sequence. The function of TFs is to regulate—turn on and off—genes in order to make sure that they are expressed in the desired cells at the right time and in the right amount throughout the life of the cell and the organism. Groups of TFs function in a coordinated fashion to direct cell division, cell growth, and cell death throughout life; cell migration and organization (body plan) during embryonic development; and intermittently in response to signals from outside the cell, such as a hormone. There are up to 1600 TFs in the human genome. Transcription factors are members of the proteome as well as regulome. TFs work alone or with other proteins in a complex, by promoting (as an activator), or blocking (as a repressor) the recruitment of RNA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
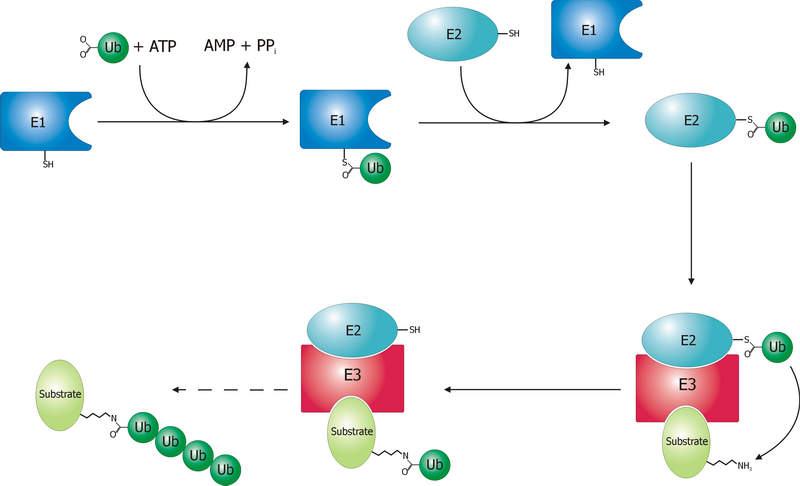
Ubiquitin Ligase
A ubiquitin ligase (also called an E3 ubiquitin ligase) is a protein that recruits an E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme that has been loaded with ubiquitin, recognizes a protein substrate, and assists or directly catalyzes the transfer of ubiquitin from the E2 to the protein substrate. In simple and more general terms, the ligase enables movement of ubiquitin from a ubiquitin carrier to another thing (the substrate) by some mechanism. The ubiquitin, once it reaches its destination, ends up being attached by an isopeptide bond to a lysine residue, which is part of the target protein. E3 ligases interact with both the target protein and the E2 enzyme, and so impart substrate specificity to the E2. Commonly, E3s polyubiquitinate their substrate with Lys48-linked chains of ubiquitin, targeting the substrate for destruction by the proteasome. However, many other types of linkages are possible and alter a protein's activity, interactions, or localization. Ubiquitination by E3 ligases reg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kinase
In biochemistry, a kinase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of phosphate groups from high-energy, phosphate-donating molecules to specific substrates. This process is known as phosphorylation, where the high-energy ATP molecule donates a phosphate group to the substrate molecule. This transesterification produces a phosphorylated substrate and ADP. Conversely, it is referred to as dephosphorylation when the phosphorylated substrate donates a phosphate group and ADP gains a phosphate group (producing a dephosphorylated substrate and the high energy molecule of ATP). These two processes, phosphorylation and dephosphorylation, occur four times during glycolysis. Kinases are part of the larger family of phosphotransferases. Kinases should not be confused with phosphorylases, which catalyze the addition of inorganic phosphate groups to an acceptor, nor with phosphatases, which remove phosphate groups (dephosphorylation). The phosphorylation state of a molecule, whet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steroid Hormone Receptor
Steroid hormone receptors are found in the nucleus, cytosol, and also on the plasma membrane of target cells. They are generally intracellular receptors (typically cytoplasmic or nuclear) and initiate signal transduction for steroid hormones which lead to changes in gene expression over a time period of hours to days. The best studied steroid hormone receptors are members of the nuclear receptor subfamily 3 (NR3) that include receptors for estrogen (group NR3A) and 3-ketosteroids (group NR3C). In addition to nuclear receptors, several G protein-coupled receptors and ion channels act as cell surface receptors for certain steroid hormones. Types Nuclear receptors Steroid receptors of the nuclear receptor family are all transcription factors. Depending upon the type of receptor, they are either located in the cytosol and move to the cell nucleus upon activation, or remain in the nucleus waiting for the steroid hormone to enter and activate them. This uptake into the nucleus is fac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geldanamycin
Geldanamycin is a 1,4-benzoquinone ansamycin antitumor antibiotic that inhibits the function of Hsp90 (Heat Shock Protein 90) by binding to the unusual ADP/ATP-binding pocket of the protein. HSP90 client proteins play important roles in the regulation of the cell cycle, cell growth, cell survival, apoptosis, angiogenesis and oncogenesis. Geldanamycin induces the degradation of proteins that are mutated or overexpressed in tumor cells such as v-Src, Bcr-Abl, p53, and ERBB2. This effect is mediated via HSP90. Despite its potent antitumor potential, geldanamycin presents several major drawbacks as a drug candidate such as hepatotoxicity, further, Jilani ''et al.''. reported that geldanamycin induces the apoptosis of erythrocytes under physiological concentrations. These side effects have led to the development of geldanamycin analogues, in particular analogues containing a derivatisation at the 17 position: * 17-AAG * 17-DMAG Biosynthesis Geldanamycin was originally discovered i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetratricopeptide
The tetratricopeptide repeat (TPR) is a structural motif. It consists of a Degeneracy (biology), degenerate 34 amino acid protein tandem repeats, tandem repeat identified in a wide variety of proteins. It is found in tandem arrays of 3–16 motifs, which form scaffolds to mediate protein–protein interactions and often the assembly of multiprotein complexes. These alpha-helix pair repeats usually protein folding, fold together to produce a single, linear solenoid protein domain, solenoid domain called a TPR domain. Proteins with such domains include the anaphase-promoting complex (APC) subunits CDC16, cdc16, CDC23, cdc23 and CDC27, cdc27, the NADPH oxidase subunit neutrophil cytosolic factor 2, p67-phox, hsp90-binding immunophilins, transcription factors, the protein kinase R (PKR), the major receptor for peroxisomal matrix protein import PEX5, protein arginine methyltransferase 9 (PRMT9), and mitochondrial import proteins. Structure The structure of the PPP5C, PP5 protein w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C-terminal
The C-terminus (also known as the carboxyl-terminus, carboxy-terminus, C-terminal tail, C-terminal end, or COOH-terminus) is the end of an amino acid chain (protein or polypeptide), terminated by a free carboxyl group (-COOH). When the protein is translated from messenger RNA, it is created from N-terminus to C-terminus. The convention for writing peptide sequences is to put the C-terminal end on the right and write the sequence from N- to C-terminus. Chemistry Each amino acid has a carboxyl group and an amine group. Amino acids link to one another to form a chain by a dehydration reaction which joins the amine group of one amino acid to the carboxyl group of the next. Thus polypeptide chains have an end with an unbound carboxyl group, the C-terminus, and an end with an unbound amine group, the N-terminus. Proteins are naturally synthesized starting from the N-terminus and ending at the C-terminus. Function C-terminal retention signals While the N-terminus of a protein often cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
N-terminal
The N-terminus (also known as the amino-terminus, NH2-terminus, N-terminal end or amine-terminus) is the start of a protein or polypeptide, referring to the free amine group (-NH2) located at the end of a polypeptide. Within a peptide, the amine group is bonded to the carboxylic group of another amino acid, making it a chain. That leaves a free carboxylic group at one end of the peptide, called the C-terminus, and a free amine group on the other end called the N-terminus. By convention, peptide sequences are written N-terminus to C-terminus, left to right (in LTR writing systems). This correlates the translation direction to the text direction, because when a protein is translated from messenger RNA, it is created from the N-terminus to the C-terminus, as amino acids are added to the carboxyl end of the protein. Chemistry Each amino acid has an amine group and a carboxylic group. Amino acids link to one another by peptide bonds which form through a dehydration reaction that j ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |