|
HP Superdome
The HP Superdome is a high-end server computer designed and manufactured by Hewlett Packard Enterprise (formerly Hewlett-Packard). The product's most recent version, "Superdome 2," was released in 2010. Superdome 2 supports 2 to 32 sockets (up to 128 cores) and 4 TB of memory. The Superdome used PA-RISC processors when it debuted in 2000. Since 2002, there has been a second version of the machine based on Itanium 2 processors, marketed as the HP Integrity Superdome. The classic PA-RISC Superdome was later renamed HP 9000 Superdome. The HP V-Class was the Superdome's predecessor (which was based on a design acquired from Convex). The HP Integrity Superdome 2 utilizes the Intel Itanium 93xx-series microprocessor, otherwise known as " Tukwila" and is totally redesigned with parts from the HP BladeSystem C7000 enclosure. Since 2012 Intel Itanium 95xx microprocessor Poulson are available too. In 2017, Intel announced that their most recent Itanium chip (code-named Kittson) would be t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HP Superdome Itanium
HP may refer to: Businesses and organisations * HP Inc., an American technology company ** Hewlett-Packard, the predecessor to HP Inc. * HP Foods ** HP Sauce, formerly made by HP Foods * Handley Page, an aircraft company * Hindustan Petroleum * America West Airlines (1981-2006), an American airline (IATA code HP) * Amapola Flyg (2004-present), a Swedish airline (IATA code HP) * HP Books, an imprint of the Penguin Group Media, music, and entertainment * ''Harry Potter'', a novel series by J.K. Rowling * Hello Project, a J-pop idol brand under Japanese music company Up-Front Group * '' Horse-Power: Ballet Symphony'', a 1932 ballet composed by Carlos Chávez * Hot Package, a TV show created by Adult Swim Places * Harrison Plaza, a shopping mall in the Philippines that closed down in 2019 * Heart Peaks, a volcano in Canada * Himachal Pradesh, a state in India * HP postcode area, UK Science and technology * Haptoglobin, a protein * Hypersensitivity pneumonitis, a respiratory in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Backplane
A backplane (or "backplane system") is a group of electrical connectors in parallel with each other, so that each pin of each connector is linked to the same relative pin of all the other connectors, forming a computer bus. It is used as a backbone to connect several printed circuit boards together to make up a complete computer system. Backplanes commonly use a printed circuit board, but wire-wrapped backplanes have also been used in minicomputers and high-reliability applications. A backplane is generally differentiated from a motherboard by the lack of on-board processing and storage elements. A backplane uses plug-in cards for storage and processing. Usage Early microcomputer systems like the Altair 8800 used a backplane for the processor and expansion cards. Backplanes are normally used in preference to cables because of their greater reliability. In a cabled system, the cables need to be flexed every time that a card is added or removed from the system; this flexing eve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
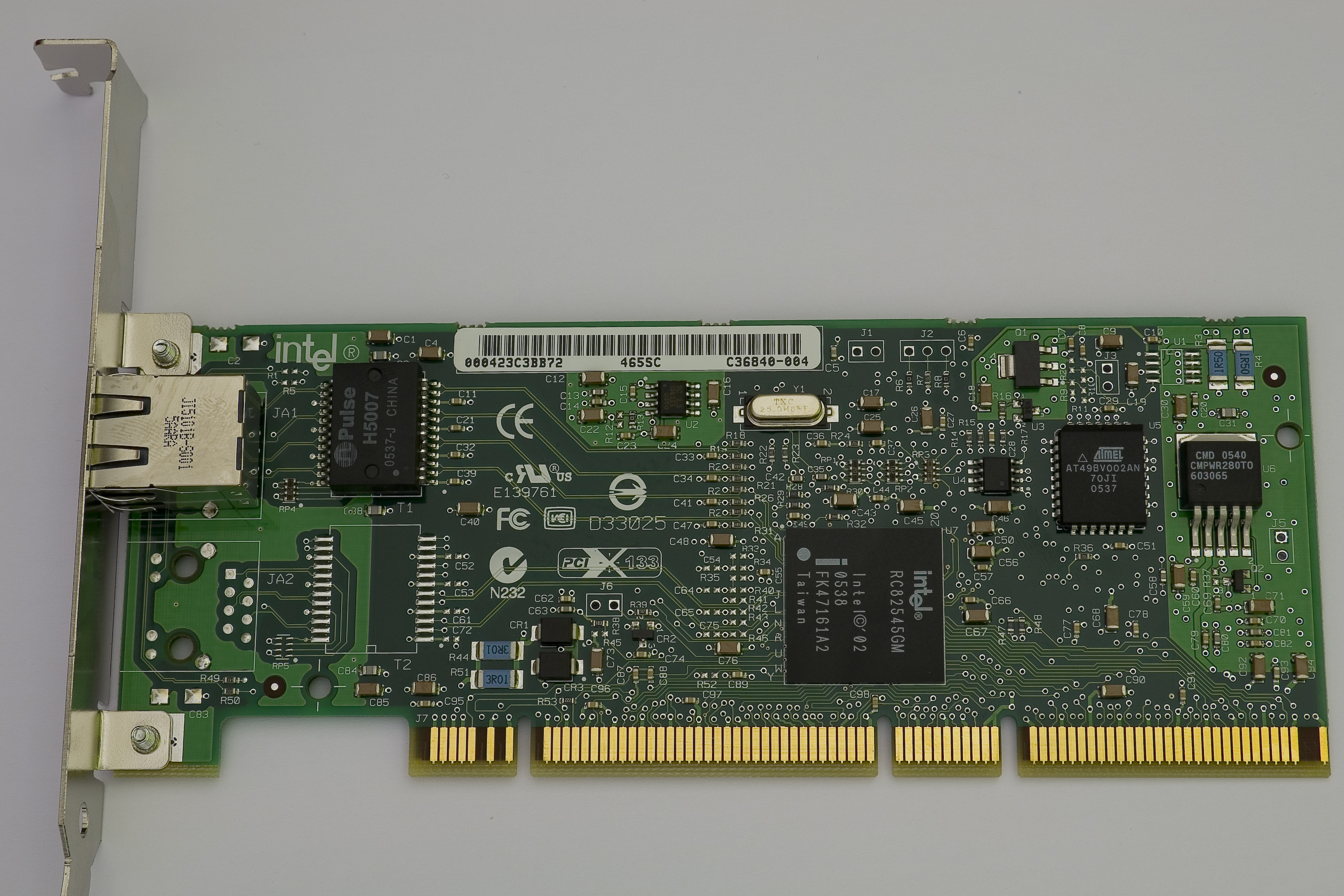
Mezzanine Card
In computing, an expansion card (also called an expansion board, adapter card, peripheral card or accessory card) is a printed circuit board that can be inserted into an electrical connector, or expansion slot (also referred to as a bus slot) on a computer's motherboard (see also backplane) to add functionality to a computer system. Sometimes the design of the computer's case and motherboard involves placing most (or all) of these slots onto a separate, removable card. Typically such cards are referred to as a riser card in part because they project upward from the board and allow expansion cards to be placed above and parallel to the motherboard. Expansion cards allow the capabilities and interfaces of a computer system to be extended or supplemented in a way appropriate to the tasks it will perform. For example, a high-speed multi-channel data acquisition system would be of no use in a personal computer used for bookkeeping, but might be a key part of a system used for in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
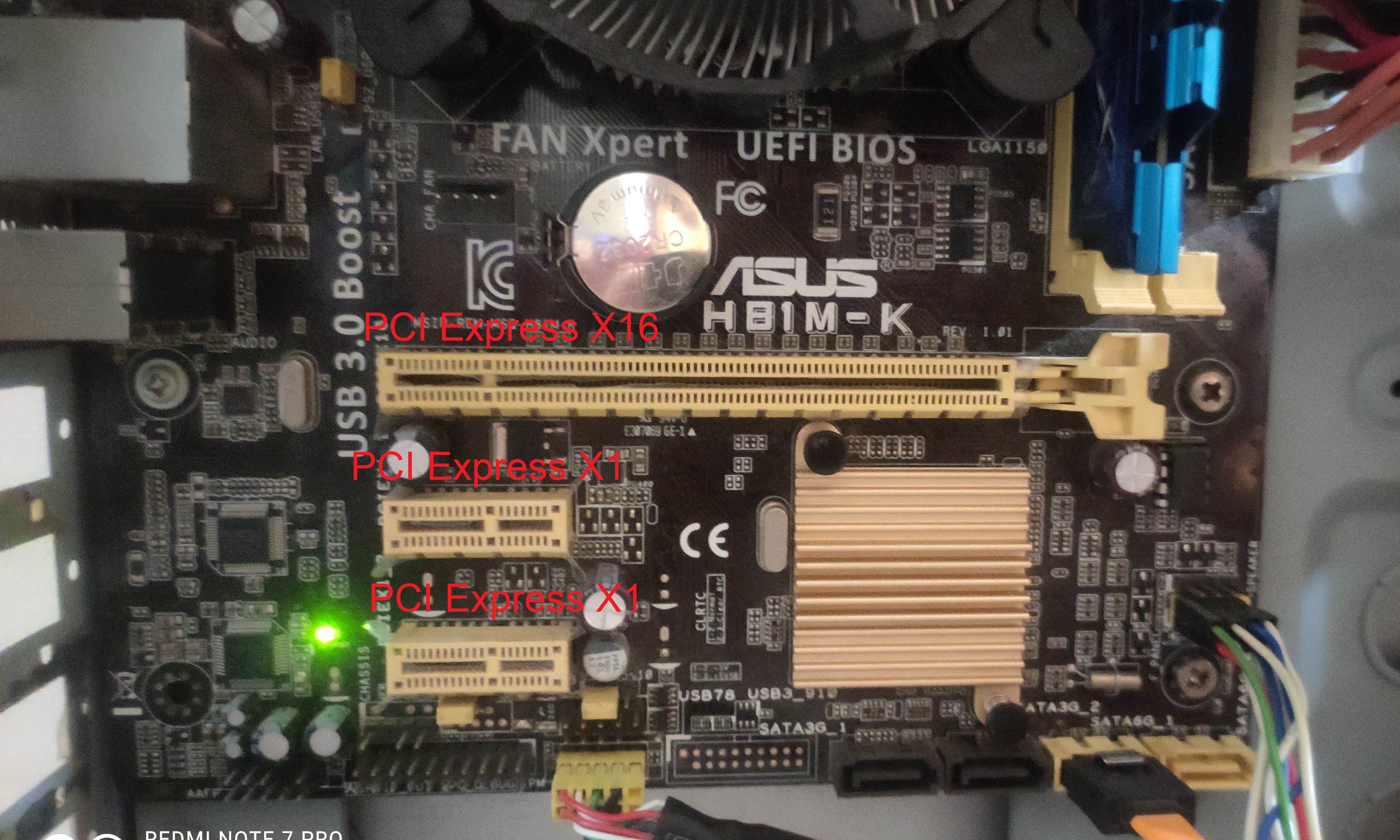
PCI-Express
PCI Express (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express), officially abbreviated as PCIe or PCI-e, is a high-speed serial computer expansion bus standard, designed to replace the older PCI, PCI-X and AGP bus standards. It is the common motherboard interface for personal computers' graphics cards, hard disk drive host adapters, SSDs, Wi-Fi and Ethernet hardware connections. PCIe has numerous improvements over the older standards, including higher maximum system bus throughput, lower I/O pin count and smaller physical footprint, better performance scaling for bus devices, a more detailed error detection and reporting mechanism (Advanced Error Reporting, AER), and native hot-swap functionality. More recent revisions of the PCIe standard provide hardware support for I/O virtualization. The PCI Express electrical interface is measured by the number of simultaneous lanes. (A lane is a single send/receive line of data. The analogy is a highway with traffic in both directions.) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HP NPar (Hard Partitioning)
nPar partitions are electrically isolated from other nPar partitions within the same chassis. Cells (a unit of processors/IO/memory) make up nPar partitions. Being electrically isolated means that if a nPar partition were to fail due to hardware failure, then the other nPar partitions would continue to work. This is contrasted with vPar partitions which exist within nPar partitions in which a failure at the hardware level for a nPar would affect all vPars within that nPar. The principle of nPartitioning in HP Cell based systems is to combine several cells to increase the computing power of a system by adding more memory/processors/IO. This in contrast to vPartitioning where you slice bigger hardware (nPars) into smaller systems to which you dedicate hardware. This is valid for all mid-range (rp74/rx7600, rp84/rx8600) and all Superdome servers. Advantages When buying a mid-range server from HP with only one cell, the customer might realize over time that his database system requi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disk Enclosure
A disk enclosure is a specialized casing designed to hold and power disk drives while providing a mechanism to allow them to communicate to one or more separate computers. Drive enclosures provide power to the drives therein and convert the data sent across their native data bus into a format usable by an external connection on the computer to which it is connected. In some cases, the conversion is as trivial as carrying a signal between different connector types. In others, it is complicated enough to require a separate embedded system to retransmit data over connector and signal of a different standard. Factory-assembled external hard disk drives, external DVD-ROM drives, and others consist of a storage device in a disk enclosure. Benefits Key benefits to using external disk enclosures include: *Adding additional storage space and media types to small form factor and laptop computers, as well as sealed embedded systems such as digital video recorders and video game con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hard Disk
A hard disk drive (HDD), hard disk, hard drive, or fixed disk is an electro-mechanical data storage device that stores and retrieves digital data using magnetic storage with one or more rigid rapidly rotating platters coated with magnetic material. The platters are paired with magnetic heads, usually arranged on a moving actuator arm, which read and write data to the platter surfaces. Data is accessed in a random-access manner, meaning that individual blocks of data can be stored and retrieved in any order. HDDs are a type of non-volatile storage, retaining stored data when powered off. Modern HDDs are typically in the form of a small rectangular box. Introduced by IBM in 1956, HDDs were the dominant secondary storage device for general-purpose computers beginning in the early 1960s. HDDs maintained this position into the modern era of servers and personal computers, though personal computing devices produced in large volume, like cell phones and tablets, re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NPar
nPar partitions are electrically isolated from other nPar partitions within the same chassis. Cells (a unit of processors/IO/memory) make up nPar partitions. Being electrically isolated means that if a nPar partition were to fail due to hardware failure, then the other nPar partitions would continue to work. This is contrasted with vPar partitions which exist within nPar partitions in which a failure at the hardware level for a nPar would affect all vPars within that nPar. The principle of nPartitioning in HP Cell based systems is to combine several cells to increase the computing power of a system by adding more memory/processors/IO. This in contrast to vPartitioning where you slice bigger hardware (nPars) into smaller systems to which you dedicate hardware. This is valid for all mid-range (rp74/rx7600, rp84/rx8600) and all Superdome servers. Advantages When buying a mid-range server from HP with only one cell, the customer might realize over time that his database system requi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PCI-X
PCI-X, short for Peripheral Component Interconnect eXtended, is a computer bus and expansion card standard that enhances the 32-bit PCI local bus for higher bandwidth demanded mostly by servers and workstations. It uses a modified protocol to support higher clock speeds (up to 133 MHz), but is otherwise similar in electrical implementation. PCI-X 2.0 added speeds up to 533 MHz, with a reduction in electrical signal levels. The slot is physically a 3.3 V PCI slot, with exactly the same size, location and pin assignments. The electrical specifications are compatible, but stricter. However, while most conventional PCI slots are the 85 mm long 32-bit version, most PCI-X devices use the 130 mm long 64-bit slot, to the point that 64-bit PCI connectors and PCI-X support are seen as synonymous. PCI-X is in fact fully specified for both 32- and 64-bit PCI connectors, and PCI-X 2.0 added a 16-bit variant for embedded applications. It has been replace ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PA-8900
The PA-8000 (PCX-U), code-named ''Onyx'', is a microprocessor developed and fabricated by Hewlett-Packard (HP) that implemented the PA-RISC 2.0 instruction set architecture (ISA). Hunt 1995 It was a completely new design with no circuitry derived from previous PA-RISC microprocessors. The PA-8000 was introduced on 2 November 1995 when shipments began to members of the Precision RISC Organization (PRO). It was used exclusively by PRO members and was not sold on the merchant market. All follow-on PA-8x00 processors (PA-8200 to PA-8900, described further below) are based on the basic PA-8000 processor core. The PA-8000 was used by: * HP in its HP 9000 workstations and servers * NEC in its TX7/P590 server * Stratus Technologies in its Continuum fault-tolerant servers Description The PA-8000 is a four-way superscalar microprocessor that executes instructions out-of-order and speculatively. These features were not found in previous PA-RISC implementations, making the PA-8000 the f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.jpg)