|
HPTE
HPTE, also known as hydroxychlor, ''p,p'''-hydroxy-DDT, or 2,2-bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)-1,1,1-trichloroethane, is a metabolite of methoxychlor, a synthetic compound, synthetic insecticide related to DDT. Like bisphenol A with similar chemical structure, HPTE is an endocrine disruptor which has estrogen (medication), estrogenic activity, and also inhibits Cholesterol side-chain cleavage enzyme (P450scc, CYP11A1) and 3α-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (3α-HSD). References 3α-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase inhibitors Cholesterol side-chain cleavage enzyme inhibitors Endocrine disruptors Bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)methanes Trichloromethyl compounds Xenoestrogens {{drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methoxychlor
Methoxychlor is a synthetic organochloride insecticide, now obsolete. Usage Methoxychlor was used to protect crops, ornamentals, livestock, and pets against fleas, mosquitoes, cockroaches, and other insects. It was intended to be a replacement for DDT, but has since been banned for use as a pesticide based on its acute toxicity, bioaccumulation, and endocrine disruption activity. The amount of methoxychlor in the natural environment, environment changes seasonally due to its use in farming and foresting. It does not dissolve readily in water, so it is mixed with a petroleum-based fluid and sprayed, or used as a dust. Sprayed methoxychlor settles on the ground or in aquatic ecosystems, where it can be detected in sediments. Its degradation may take many months. Methoxychlor is ingested and absorbed by living organisms, and it accumulates in the food chain. Some metabolites may have unwanted side effects. Banned The use of methoxychlor as a pesticide was banned in the United State ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bisphenol A
Bisphenol A (BPA) is a chemical compound primarily used in the manufacturing of various plastics. It is a colourless solid which is soluble in most common organic solvents, but has very poor solubility in water. BPA is produced on an industrial scale by the condensation of phenol and acetone, and has a global production scale which is expected to reach 10 million tonnes in 2022. BPA's largest single application is as a co-monomer in the production of polycarbonates, which accounts for 65–70% of all BPA production. The manufacturing of epoxy resins and vinyl ester resins account for 25–30% of BPA use. The remaining 5% is used as a major component of several high-performance plastics, and as a minor additive in PVC, polyurethane, thermal paper, and several other materials. It is not a plasticizer, although it is often wrongly labelled as such. The health effects of BPA have been the subject of prolonged public and scientific debate. BPA is a xenoestrogen, exhibiting hormone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metabolite
In biochemistry, a metabolite is an intermediate or end product of metabolism. The term is usually used for small molecules. Metabolites have various functions, including fuel, structure, signaling, stimulatory and inhibitory effects on enzymes, catalytic activity of their own (usually as a cofactor to an enzyme), defense, and interactions with other organisms (e.g. pigments, odorants, and pheromones). A primary metabolite is directly involved in normal "growth", development, and reproduction. Ethylene exemplifies a primary metabolite produced large-scale by industrial microbiology. A secondary metabolite is not directly involved in those processes, but usually has an important ecological function. Examples include antibiotics and pigments such as resins and terpenes etc. Some antibiotics use primary metabolites as precursors, such as actinomycin, which is created from the primary metabolite tryptophan. Some sugars are metabolites, such as fructose or glucose, which are both p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synthetic Compound
In chemistry, organic compounds are generally any chemical compounds that contain carbon-hydrogen or carbon-carbon bonds. Due to carbon's ability to catenate (form chains with other carbon atoms), millions of organic compounds are known. The study of the properties, reactions, and syntheses of organic compounds comprise the discipline known as organic chemistry. For historical reasons, a few classes of carbon-containing compounds (e.g., carbonate salts and cyanide salts), along with a few other exceptions (e.g., carbon dioxide, hydrogen cyanide), are not classified as organic compounds and are considered inorganic. Other than those just named, little consensus exists among chemists on precisely which carbon-containing compounds are excluded, making any rigorous definition of an organic compound elusive. Although organic compounds make up only a small percentage of Earth's crust, they are of central importance because all known life is based on organic compounds. Living t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insecticide
Insecticides are substances used to kill insects. They include ovicides and larvicides used against insect eggs and larvae, respectively. Insecticides are used in agriculture, medicine, industry and by consumers. Insecticides are claimed to be a major factor behind the increase in the 20th-century's agricultural productivity. Nearly all insecticides have the potential to significantly alter ecosystems; many are toxic to humans and/or animals; some become concentrated as they spread along the food chain. Insecticides can be classified into two major groups: systemic insecticides, which have residual or long term activity; and contact insecticides, which have no residual activity. The mode of action describes how the pesticide kills or inactivates a pest. It provides another way of classifying insecticides. Mode of action can be important in understanding whether an insecticide will be toxic to unrelated species, such as fish, birds and mammals. Insecticides may be repellent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Structure
A chemical structure determination includes a chemist's specifying the molecular geometry and, when feasible and necessary, the electronic structure of the target molecule or other solid. Molecular geometry refers to the spatial arrangement of atoms in a molecule and the chemical bonds that hold the atoms together, and can be represented using structural formulae and by molecular models; complete electronic structure descriptions include specifying the occupation of a molecule's molecular orbitals. Structure determination can be applied to a range of targets from very simple molecules (e.g., diatomic oxygen or nitrogen), to very complex ones (e.g., such as protein or DNA). Background Theories of chemical structure were first developed by August Kekulé, Archibald Scott Couper, and Aleksandr Butlerov, among others, from about 1858. These theories were first to state that chemical compounds are not a random cluster of atoms and functional groups, but rather had a definite order ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endocrine Disruptor
Endocrine disruptors, sometimes also referred to as hormonally active agents, endocrine disrupting chemicals, or endocrine disrupting compounds are chemicals that can interfere with endocrine (or hormonal) systems. These disruptions can cause cancerous tumors, birth defects, and other developmental disorders. Found in many household and industrial products, endocrine disruptors "interfere with the synthesis, secretion, transport, binding, action, or elimination of natural hormones in the body that are responsible for development, behavior, fertility, and maintenance of homeostasis (normal cell metabolism)." Any system in the body controlled by hormones can be derailed by hormone disruptors. Specifically, endocrine disruptors may be associated with the development of learning disabilities, severe attention deficit disorder, cognitive and brain development problems. There has been controversy over endocrine disruptors, with some groups calling for swift action by regulators to re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Estrogen (medication)
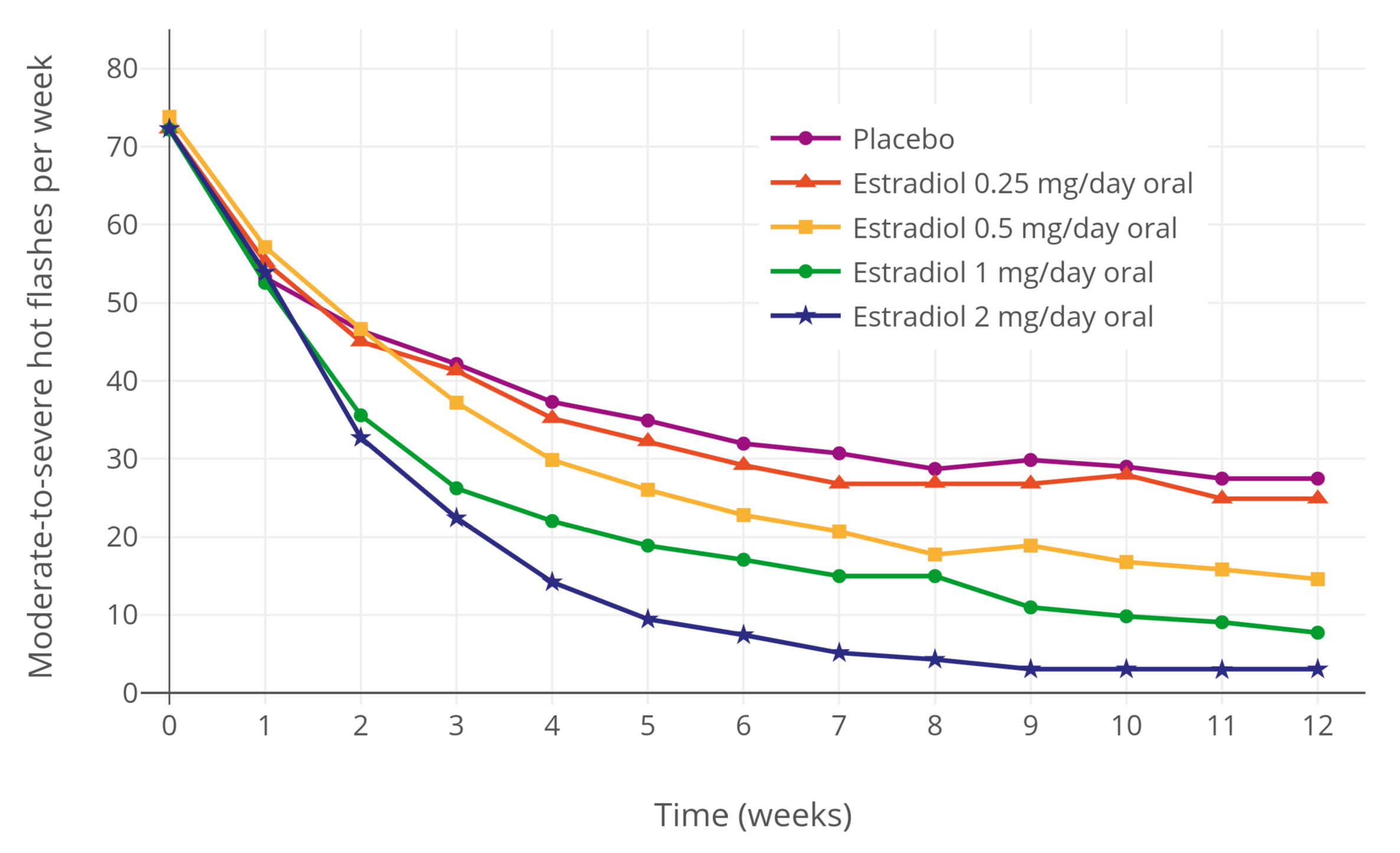
An estrogen (E) is a type of medication which is used most commonly in hormonal birth control and menopausal hormone therapy, and as part of feminizing hormone therapy for transgender women. They can also be used in the treatment of hormone-sensitive cancers like breast cancer and prostate cancer and for various other indications. Estrogens are used alone or in combination with progestogens. They are available in a wide variety of formulations and for use by many different routes of administration. Examples of estrogens include bioidentical estradiol, natural conjugated estrogens, synthetic steroidal estrogens like ethinylestradiol, and synthetic nonsteroidal estrogens like diethylstilbestrol. Estrogens are one of three types of sex hormone agonists, the others being androgens/anabolic steroids like testosterone and progestogens like progesterone. Side effects of estrogens include breast tenderness, breast enlargement, headache, nausea, fluid retention, and edema among other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cholesterol Side-chain Cleavage Enzyme
Cholesterol side-chain cleavage enzyme is commonly referred to as P450scc, where "scc" is an acronym for side-chain cleavage. P450scc is a mitochondrial enzyme that catalyzes conversion of cholesterol to pregnenolone. This is the first reaction in the process of steroidogenesis in all mammalian tissues that specialize in the production of various steroid hormones. P450scc is a member of the cytochrome P450 superfamily of enzymes (family 11, subfamily A, polypeptide 1) and is encoded by the gene. Nomenclature The systematic name of this enzyme class is cholesterol, reduced-adrenal-ferredoxin:oxygen oxidoreductase (side-chain-cleaving). Other names include: * C27-side-chain cleavage enzyme * cholesterol 20-22-desmolase * cholesterol C20-22 desmolase * cholesterol desmolase * cholesterol side-chain cleavage enzyme * cholesterol side-chain-cleaving enzyme * cytochrome P-450scc * desmolase, steroid 20-22 * enzymes, cholesterol side-chain-cleaving * steroid 20-22 desmola ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cholesterol Side-chain Cleavage Enzyme Inhibitors
Cholesterol side-chain cleavage enzyme is commonly referred to as P450scc, where "scc" is an acronym for side-chain cleavage. P450scc is a mitochondrial enzyme that catalyzes conversion of cholesterol to pregnenolone. This is the first reaction in the process of steroidogenesis in all mammalian tissues that specialize in the production of various steroid hormones. P450scc is a member of the cytochrome P450 superfamily of enzymes (family 11, subfamily A, polypeptide 1) and is encoded by the gene. Nomenclature The systematic name of this enzyme class is cholesterol, reduced-adrenal-ferredoxin:oxygen oxidoreductase (side-chain-cleaving). Other names include: * C27-side-chain cleavage enzyme * cholesterol 20-22-desmolase * cholesterol C20-22 desmolase * cholesterol desmolase * cholesterol side-chain cleavage enzyme * cholesterol side-chain-cleaving enzyme * cytochrome P-450scc * desmolase, steroid 20-22 * enzymes, cholesterol side-chain-cleaving * steroid 20-22 desmolas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |