|
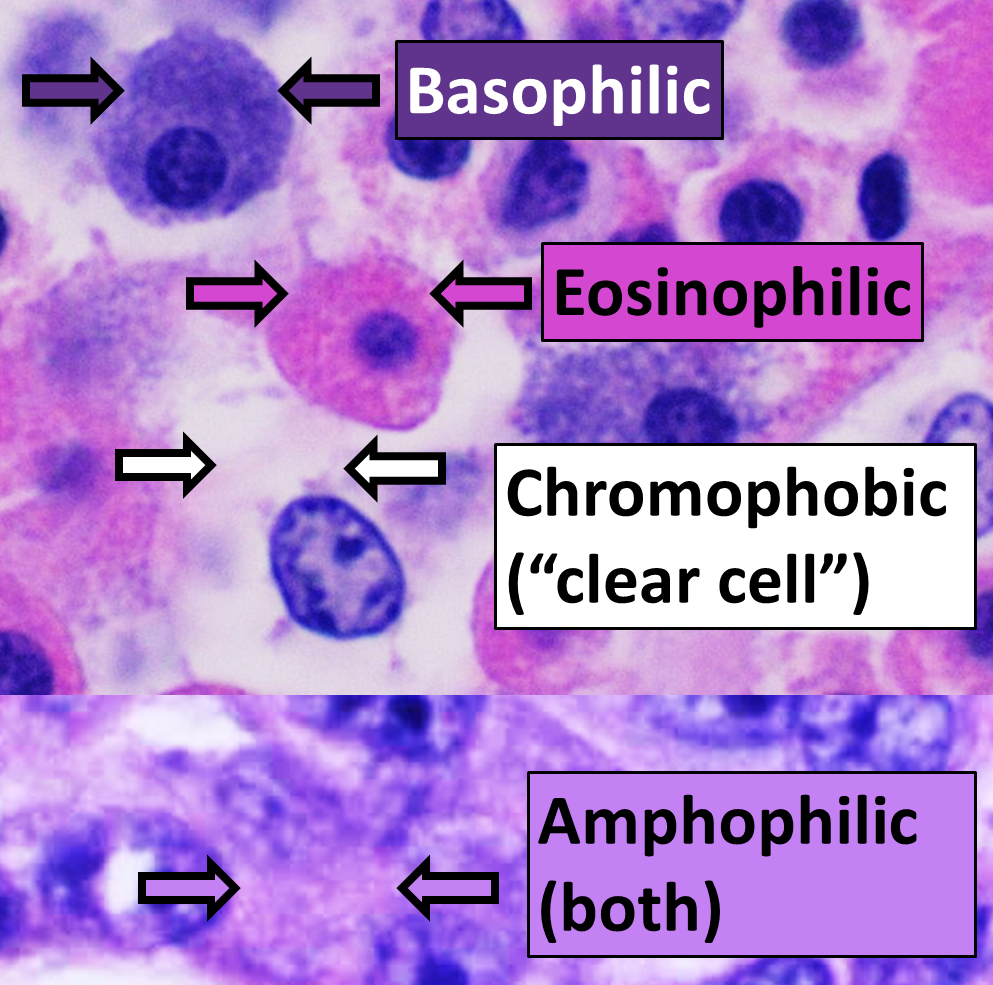
HPS Stain
In histology, the HPS stain, or hematoxylin phloxine saffron stain, is a way of marking tissues. HPS is similar to H&E, the standard bearer in histology. However, it differentiates between the most common connective tissue (collagen) and muscle and cytoplasm by staining the former yellow and the latter two pink, . polysciences.com. Accessed 6 December 2009. unlike an H&E stain, which stains all three pink. HPS stained sections are more expensive than H&E stained sections, primarily due to the cost of saffron. See also *Histopathology
Histopathology (compound of three Greek words: ''histos'' "tissue", πάθος ''pathos'' "suffering ...
[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Histology
Histology, also known as microscopic anatomy or microanatomy, is the branch of biology which studies the microscopic anatomy of biological tissues. Histology is the microscopic counterpart to gross anatomy, which looks at larger structures visible without a microscope. Although one may divide microscopic anatomy into ''organology'', the study of organs, ''histology'', the study of tissues, and ''cytology'', the study of cells, modern usage places all of these topics under the field of histology. In medicine, histopathology is the branch of histology that includes the microscopic identification and study of diseased tissue. In the field of paleontology, the term paleohistology refers to the histology of fossil organisms. Biological tissues Animal tissue classification There are four basic types of animal tissues: muscle tissue, nervous tissue, connective tissue, and epithelial tissue. All animal tissues are considered to be subtypes of these four principal tissue types ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hematoxylin
Haematoxylin or hematoxylin (), also called natural black 1 or C.I. 75290, is a compound extracted from heartwood of the logwood tree (''Haematoxylum campechianum'') with a chemical formula of . This naturally derived dye has been used as a histologic stain, ink and as a dye in the textile and leather industry. As a dye, haematoxylin has been called Palo de Campeche, logwood extract, bluewood and blackwood. In histology, haematoxylin staining is commonly followed (counterstained), with eosin, when paired, this staining procedure is known as H&E staining, and is one of the most commonly used combinations in histology. In addition to its use in the H&E stain, haematoxylin is also a component of the Papanicolaou stain (or PAP stain) which is widely used in the study of cytology specimens. Although the stain is commonly called ''haematoxylin'', the active colourant is the oxidized form haematein, which forms strongly coloured complexes with certain metal ions (commonly Fe(III) and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phloxine
Phloxine B (commonly known simply as phloxine) is a water-soluble red dye used for coloring drugs and cosmetics in the United States and coloring food in Japan. It is derived from fluorescein, but differs by the presence of four bromine atoms at positions 2, 4, 5 and 7 of the xanthene ring and four chlorine atoms in the carboxyphenyl ring. It has an absorption maximum around 540 nm and an emission maximum around 564 nm. Apart from industrial use, phloxine B has functions as an antimicrobial substance, viability dye and biological stain. For example, it is used in hematoxylin-phloxine-saffron ( HPS) staining to color the cytoplasm and connective tissue in shades of red. Antimicrobial properties Lethal dosage levels In the presence of light, phloxine B has a bactericidal effect on gram-positive strains, such as ''Bacillus subtilis'', ''Bacillus cereus'', and several methicillin-resistant '' Staphylococcus aureus'' (MRSA) strains. At a minimum inhibitory concen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saffron
Saffron () is a spice derived from the flower of ''Crocus sativus'', commonly known as the "saffron crocus". The vivid crimson stigma and styles, called threads, are collected and dried for use mainly as a seasoning and colouring agent in food. Although some doubts remain on its origin, it is believed that saffron originated in Iran. However, Greece and Mesopotamia have also been suggested as the possible region of origin of this plant. Saffron crocus slowly propagated throughout much of Eurasia and was later brought to parts of North Africa, North America, and Oceania. Saffron's taste and iodoform-like or hay-like fragrance result from the phytochemicals picrocrocin and safranal. It also contains a carotenoid pigment, crocin, which imparts a rich golden-yellow hue to dishes and textiles. Its recorded history is attested in a 7th-century BC Assyrian botanical treatise, and has been traded and used for thousands of years. In the 21st century, Iran produces some 90% of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Staining
Staining is a technique used to enhance contrast in samples, generally at the microscopic level. Stains and dyes are frequently used in histology (microscopic study of biological tissues), in cytology (microscopic study of cells), and in the medical fields of histopathology, hematology, and cytopathology that focus on the study and diagnoses of diseases at the microscopic level. Stains may be used to define biological tissues (highlighting, for example, muscle fibers or connective tissue), cell populations (classifying different blood cells), or organelles within individual cells. In biochemistry, it involves adding a class-specific ( DNA, proteins, lipids, carbohydrates) dye to a substrate to qualify or quantify the presence of a specific compound. Staining and fluorescent tagging can serve similar purposes. Biological staining is also used to mark cells in flow cytometry, and to flag proteins or nucleic acids in gel electrophoresis. Light microscopes are used for viewin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tissue (biology)
In biology, tissue is a biological organizational level between cells and a complete organ. A tissue is an ensemble of similar cells and their extracellular matrix from the same origin that together carry out a specific function. Organs are then formed by the functional grouping together of multiple tissues. The English word "tissue" derives from the French word "tissu", the past participle of the verb tisser, "to weave". The study of tissues is known as histology or, in connection with disease, as histopathology. Xavier Bichat is considered as the "Father of Histology". Plant histology is studied in both plant anatomy and physiology. The classical tools for studying tissues are the paraffin block in which tissue is embedded and then sectioned, the histological stain, and the optical microscope. Developments in electron microscopy, immunofluorescence, and the use of frozen tissue-sections have enhanced the detail that can be observed in tissues. With these tools, the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
H&E Stain
Hematoxylin and eosin stain ( or haematoxylin and eosin stain or hematoxylin-eosin stain; often abbreviated as H&E stain or HE stain) is one of the principal tissue stains used in histology. It is the most widely used stain in medical diagnosis and is often the gold standard. For example, when a pathologist looks at a biopsy of a suspected cancer, the histological section is likely to be stained with H&E. H&E is the combination of two histological stains: hematoxylin and eosin. The hematoxylin stains cell nuclei a purplish blue, and eosin stains the extracellular matrix and cytoplasm pink, with other structures taking on different shades, hues, and combinations of these colors. Hence a pathologist can easily differentiate between the nuclear and cytoplasmic parts of a cell, and additionally, the overall patterns of coloration from the stain show the general layout and distribution of cells and provides a general overview of a tissue sample's structure. Thus, pattern recogniti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standard Bearer
A standard-bearer, also known as a flag-bearer is a person (soldier or civilian) who bears an emblem known as a standard or military colours, i.e. either a type of flag or an inflexible but mobile image, which is used (and often honoured) as a formal, visual symbol of a state, prince, military unit, etc. This can either be an occasional duty, often seen as an honour (especially on parade), or a permanent charge (also on the battlefield); the second type has even led in certain cases to this task being reflected in official rank titles such as Ensign, Cornet and Fähnrich. Role of the standard-bearer In the context of the Olympic Games, a flagbearer is the athlete who carries the flag of their country during the opening and closing ceremonies. While at present a purely ceremonial function, as far back as Roman warfare and medieval warfare the standard-bearer had an important role on the battlefield. The standard-bearer acted as an indicator of where the position of a military ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Connective Tissue
Connective tissue is one of the four primary types of animal tissue, along with epithelial tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. It develops from the mesenchyme derived from the mesoderm the middle embryonic germ layer. Connective tissue is found in between other tissues everywhere in the body, including the nervous system. The three meninges, membranes that envelop the brain and spinal cord are composed of connective tissue. Most types of connective tissue consists of three main components: elastic and collagen fibers, ground substance, and cells. Blood, and lymph are classed as specialized fluid connective tissues that do not contain fiber. All are immersed in the body water. The cells of connective tissue include fibroblasts, adipocytes, macrophages, mast cells and leucocytes. The term "connective tissue" (in German, ''Bindegewebe'') was introduced in 1830 by Johannes Peter Müller. The tissue was already recognized as a distinct class in the 18th century. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Collagen
Collagen () is the main structural protein in the extracellular matrix found in the body's various connective tissues. As the main component of connective tissue, it is the most abundant protein in mammals, making up from 25% to 35% of the whole-body protein content. Collagen consists of amino acids bound together to form a triple helix of elongated fibril known as a collagen helix. It is mostly found in connective tissue such as cartilage, bones, tendons, ligaments, and skin. Depending upon the degree of mineralization, collagen tissues may be rigid (bone) or compliant (tendon) or have a gradient from rigid to compliant (cartilage). Collagen is also abundant in corneas, blood vessels, the gut, intervertebral discs, and the dentin in teeth. In muscle tissue, it serves as a major component of the endomysium. Collagen constitutes one to two percent of muscle tissue and accounts for 6% of the weight of the skeletal muscle tissue. The fibroblast is the most common cell that crea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muscle
Skeletal muscles (commonly referred to as muscles) are organs of the vertebrate muscular system and typically are attached by tendons to bones of a skeleton. The muscle cells of skeletal muscles are much longer than in the other types of muscle tissue, and are often known as muscle fibers. The muscle tissue of a skeletal muscle is striated – having a striped appearance due to the arrangement of the sarcomeres. Skeletal muscles are voluntary muscles under the control of the somatic nervous system. The other types of muscle are cardiac muscle which is also striated and smooth muscle which is non-striated; both of these types of muscle tissue are classified as involuntary, or, under the control of the autonomic nervous system. A skeletal muscle contains multiple fascicles – bundles of muscle fibers. Each individual fiber, and each muscle is surrounded by a type of connective tissue layer of fascia. Muscle fibers are formed from the fusion of developmental myoblasts in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |