|
HP-IL
The HP-IL (''Hewlett-Packard Interface Loop''), was a short-range interconnection bus or network introduced by Hewlett-Packard in the early 1980s. It enabled many devices such as printers, plotters, displays, storage devices (floppy disk drives and tape drives), test equipment, etc. to be connected to programmable calculators such as the HP-41C, HP-71B and HP-75C/D, the 80-series and HP-110 computers, as well as generic ISA bus based PCs. Principles As its name implies, an HP-IL network formed a loop (i.e. it was a Ring network): each device in the loop had a pair of two-wire connections, one designated ''in'', which received messages from the previous device in the loop; and one designated ''out'', which delivered messages to the next device in the loop. One device on the loop is designated the ''controller'', and manages all other devices on the loop. HP-IL cables utilize a unique two-pin connector design with polarizing "D"-shaped shells, and can be connected together ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HP-IL Connectors
The HP-IL (''Hewlett-Packard Interface Loop''), was a short-range interconnection bus or network introduced by Hewlett-Packard in the early 1980s. It enabled many devices such as printers, plotters, displays, storage devices (floppy disk drives and tape drives), test equipment, etc. to be connected to programmable calculators such as the HP-41C, HP-71B and HP-75C/D, the 80-series and HP-110 computers, as well as generic ISA bus based PCs. Principles As its name implies, an HP-IL network formed a loop (i.e. it was a Ring network): each device in the loop had a pair of two-wire connections, one designated ''in'', which received messages from the previous device in the loop; and one designated ''out'', which delivered messages to the next device in the loop. One device on the loop is designated the ''controller'', and manages all other devices on the loop. HP-IL cables utilize a unique two-pin connector design with polarizing "D"-shaped shells, and can be connected together wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HP-41 Extension Module
The HP-41C series are programmable, expandable, continuous memory handheld RPN calculators made by Hewlett-Packard from 1979 to 1990. The original model, HP-41C, was the first of its kind to offer alphanumeric display capabilities. Later came the HP-41CV and HP-41CX, offering more memory and functionality. The alphanumeric "revolution" The alphanumeric LCD screen of the HP-41C revolutionized the way a pocket calculator could be used, providing user friendliness (for its time) and expandability (keyboard-unassigned functions could be spelled out alphabetically). By using an alphanumeric display, the calculator could tell the user what was going on: it could display error messages, such as showing ("DATA ERROR") upon attempting to divide by zero instead of simply displaying a blinking zero; it could also specifically prompt the user for arguments ("ENTER RADIUS") instead of just displaying a question mark. Earlier calculators needed a key, or key combination, for every avai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HP-41C
The HP-41C series are programmable, expandable, continuous memory handheld RPN calculators made by Hewlett-Packard from 1979 to 1990. The original model, HP-41C, was the first of its kind to offer alphanumeric display capabilities. Later came the HP-41CV and HP-41CX, offering more memory and functionality. The alphanumeric "revolution" The alphanumeric LCD screen of the HP-41C revolutionized the way a pocket calculator could be used, providing user friendliness (for its time) and expandability (keyboard-unassigned functions could be spelled out alphabetically). By using an alphanumeric display, the calculator could tell the user what was going on: it could display error messages, such as showing ("DATA ERROR") upon attempting to divide by zero instead of simply displaying a blinking zero; it could also specifically prompt the user for arguments ("ENTER RADIUS") instead of just displaying a question mark. Earlier calculators needed a key, or key combination, for every a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HP-71B
The HP-71B was a hand-held computer or calculator programmable in BASIC, made by Hewlett-Packard from 1984 to 1989. Description Smaller and less expensive (US$595 $525 in 1984 ≈ $990 in 2005 (seInflation Conversion Factors for Dollars) MSRP) than the preceding model HP-75, the 71B had a single-line 22-character liquid crystal display, 64K system ROM and 17.5K user memory. It operated on four AAA batteries. Four plug-in ports permitted ROM-based programs or additional user memory to be added. Separate compartments could accommodate an optional magnetic card reader and an optional HP-IL interface (HP 82401A) that could be used to connect printers, storage and electronic test equipment. The 71B was the first handheld to implement the IEEE 854-1987 radix-independent floating-point standard. Programming features included a real-time clock, programmable timers and subroutine calls with parameter passing and recursion. It was also HP's first calculator based on the ''Saturn'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HP-75
The HP-75C and HP-75D were hand-held computers programmable in BASIC, made by Hewlett-Packard from 1982 to 1986. The HP-75 had a single-line liquid crystal display, 48 KiB system ROM and 16 KiB RAM, a comparatively large keyboard (albeit without a separate numeric pad), a manually operated magnetic card reader (2×650 bytes per card), 4 ports for memory expansion (1 for RAM and 3 for ROM modules), and an HP-IL interface that could be used to connect printers, storage and electronic test equipment. The BASIC interpreter also acted as a primitive operating system, providing file handling capabilities for program storage using RAM, cards, or cassettes/diskettes (via HP-IL). Other features included a text editor as well as an appointment reminder with alarms, similar to functions of modern PDAs. The HP-75D (1984–1986) added a port for a bar code wand, often used for inventory control tasks. The HP-75 was comparatively expensive with an MSRP of $995 ($2,014 in 2005) for the 75C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Token Passing
On a local area network, token passing is a channel access method where a packet called a ''token'' is passed between nodes to authorize that node to communicate. In contrast to polling access methods, there is no pre-defined "master" node. The most well-known examples are IBM Token Ring and ARCNET, but there were a range of others, including FDDI (Fiber Distributed Data Interface), which was popular in the early to mid 1990s. Token passing schemes degrade deterministically under load, which is a key reason why they were popular for industrial control LANs such as MAP, (Manufacturing Automation Protocol). The advantage over contention based channel access (such as the CSMA/CD of early Ethernet), is that collisions are eliminated, and that the channel bandwidth can be fully utilized without idle time when demand is heavy. The disadvantage is that even when demand is light, a station wishing to transmit must wait for the token, increasing latency. Some types of token passing schemes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apple Desktop Bus
Apple Desktop Bus (ADB) is a proprietary bit-serial peripheral bus connecting low-speed devices to computers. It was introduced on the Apple IIGS in 1986 as a way to support low-cost devices like keyboards and mice, allowing them to be connected together in a daisy chain without the need for hubs or other devices. Apple Device Bus was quickly introduced on later Macintosh models, on later models of NeXT computers, and saw some other third-party use as well. Like the similar PS/2 connector used in many PC-compatibles at the time, Apple Desktop Bus was rapidly replaced by USB as that system became popular in the late 1990s; the last external Apple Desktop Bus port on an Apple product was in 1999, though it remained as an internal-only bus on some Mac models into the 2000s. History AppleBus Early during the creation of the Macintosh computer, the engineering team had selected the fairly sophisticated Zilog 8530 to supply serial communications. This was initially done to allow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HP Series 80
The Hewlett-Packard series 80 of small scientific desktop computers was introduced in 1980, beginning with the popular HP-85 targeted at engineering and control applications. They provided the capability of the HP 9800 series desktop computers with an integrated monitor in a smaller package including storage and printer, at half the price. Features The first model of the Series 80 was the HP-85, introduced in January 1980. ''BYTE'' wrote "we were impressed with the performance ... the graphics alone make this an attractive, albeit not inexpensive, alternate to existing small systems on the market ... it is our guess that many personal computer experimenters and hackers will want this machine." In a typewriter-style desktop case, the HP-85 contains the CPU and keyboard, with a ROM-based operating system (like the 9800 series), 16 KB dynamic RAM, a 5-inch CRT screen (16 lines of 32 characters, or 256×192 pixels), a tape drive for DC-100 cartridges ( capacity, transfer), and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IEEE-488
IEEE 488 is a short-range digital communications 8-bit parallel multi-master interface bus specification developed by Hewlett-Packard as HP-IB (Hewlett-Packard Interface Bus). It subsequently became the subject of several standards, and is generically known as GPIB (General Purpose Interface Bus). Although the bus was created in the late 1960s to connect together automated test equipment, it also had some success during the 1970s and 1980s as a peripheral bus for early microcomputers, notably the Commodore PET. Newer standards have largely replaced IEEE 488 for computer use, but it is still used by some test equipment. Origins In the late 1960s, Hewlett-Packard (HP) manufactured various automated test and measurement instruments, such as digital multimeters and logic analyzers. They developed the ''HP Interface Bus (HP-IB)'' to enable easier interconnection between instruments and controllers (computers and other instruments). The bus was relatively easy to implemen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HP-IB
IEEE 488 is a short-range digital communications 8-bit parallel multi-master interface bus specification developed by Hewlett-Packard as HP-IB (Hewlett-Packard Interface Bus). It subsequently became the subject of several standards, and is generically known as GPIB (General Purpose Interface Bus). Although the bus was created in the late 1960s to connect together automated test equipment, it also had some success during the 1970s and 1980s as a peripheral bus for early microcomputers, notably the Commodore PET. Newer standards have largely replaced IEEE 488 for computer use, but it is still used by some test equipment. Origins In the late 1960s, Hewlett-Packard (HP) manufactured various automated test and measurement instruments, such as digital multimeters and logic analyzers. They developed the ''HP Interface Bus (HP-IB)'' to enable easier interconnection between instruments and controllers (computers and other instruments). The bus was relatively easy to imp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
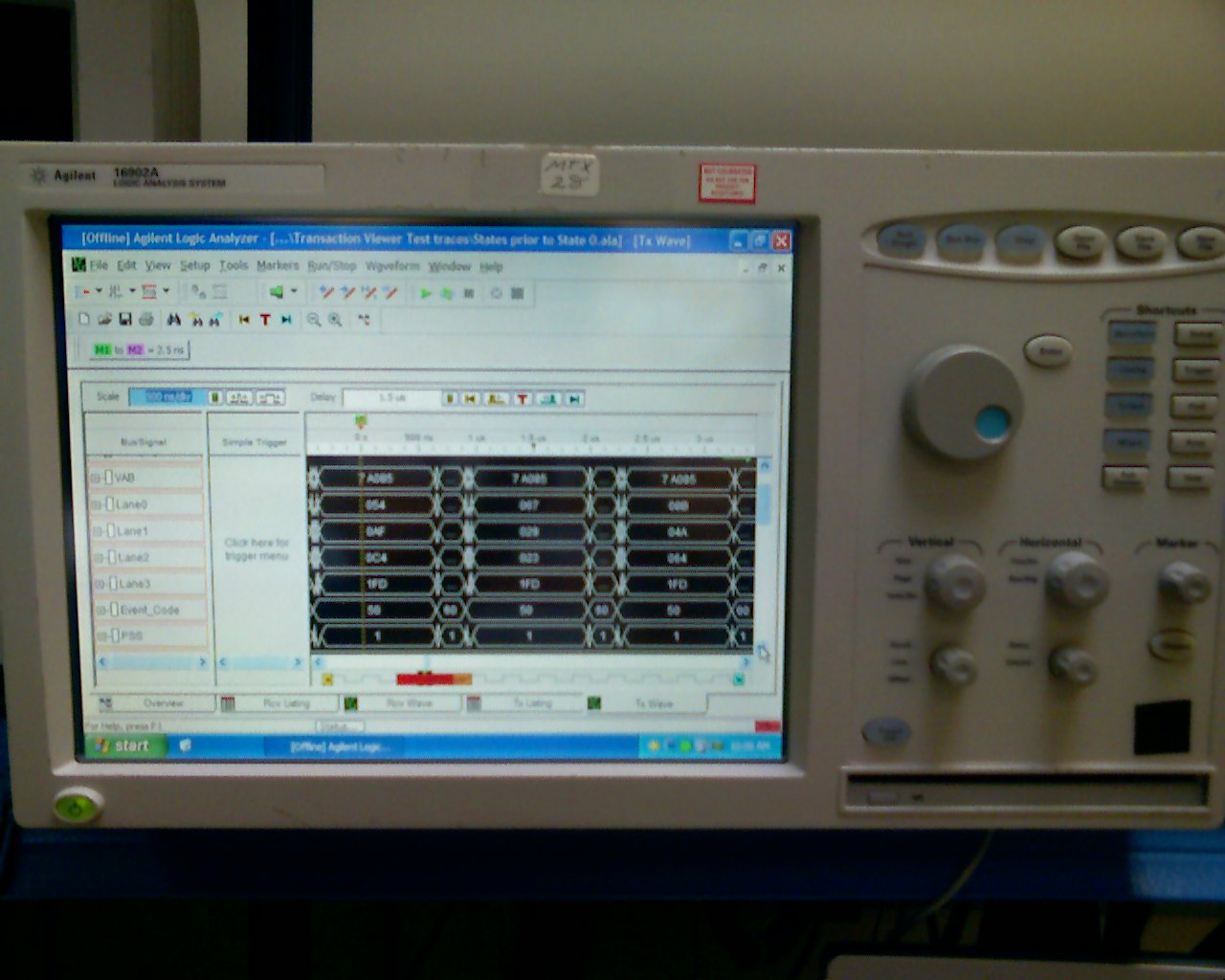
Logic Analyzer
A logic analyzer is an electronic instrument that captures and displays multiple signals from a digital system or digital circuit. A logic analyzer may convert the captured data into timing diagrams, protocol decodes, state machine traces, assembly language, or may correlate assembly with source-level software. Logic analyzers have advanced triggering capabilities, and are useful when a user needs to see the timing relationships between many signals in a digital system. Overview Presently, there are three distinct categories of logic analyzers available on the market: * Modular LAs, which consist of both a chassis or mainframe and logic analyzer modules. The mainframe/chassis contains the display, controls, control computer, and multiple slots into which the actual data-capturing hardware is installed. The modules each have a specific number of channels, and multiple modules may be combined to obtain a very high channel count. While modular logic analyzers are typically mor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multimeter
A multimeter is a measuring instrument that can measure multiple electrical properties. A typical multimeter can measure voltage, resistance, and current, in which case it is also known as a volt-ohm-milliammeter (VOM), as the unit is equipped with voltmeter, ammeter, and ohmmeter functionality, or volt-ohmmeter for short. Some feature the measurement of additional properties such as temperature and capacitance. Analog multimeters use a microammeter with a moving pointer to display readings. Digital multimeters (DMM, DVOM) have numeric displays and have made analog multimeters virtually obsolete as they are cheaper, more precise, and more physically robust than analog multimeters. Multimeters vary in size, features, and price. They can be portable handheld devices or highly-precise bench instruments. Cheap multimeters can cost under , while laboratory-grade models with certified calibration can cost over . History The first moving-pointer current-detecting device was the g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)