|
HMS Scythian (P237)
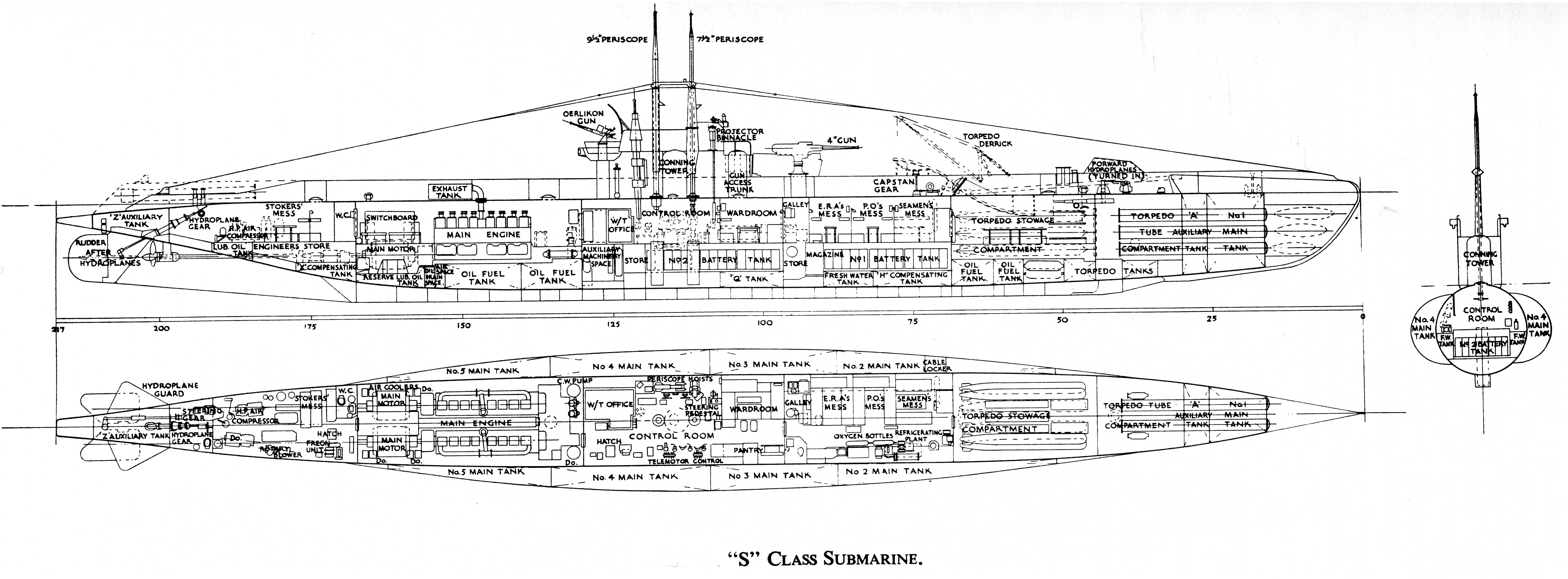
HMS ''Scythian'' was a S-class submarine of the third batch built for the Royal Navy during World War II. She survived the war and was sold for scrap in 1960. Design and description The third batch was slightly enlarged and improved over the preceding second batch of the S-class. The submarines had a length of overall, a beam of and a draft of . They displaced on the surface and submerged. The S-class submarines had a crew of 48 officers and ratings. They had a diving depth of .McCartney, p. 7 For surface running, the boats were powered by two diesel engines, each driving one propeller shaft. When submerged each propeller was driven by a electric motor. They could reach on the surface and underwater. On the surface, the third-batch boats had a range of at and at submerged. ''Scythian'' was armed with six 21 inch (533 mm) torpedo tubes in the bow. She carried six reload torpedoes for a total of a dozen torpedoes. Twelve mines could be carried in lieu of the to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British S-class Submarine (1931)
The S-class submarines of the Royal Navy were originally designed and built during the modernisation of the submarine force in the early 1930s to meet the need for smaller boats to patrol the restricted waters of the North Sea and the Mediterranean Sea, replacing the British H-class submarines. As part of the major naval construction for the Royal Navy during the Second World War, the S class became the single largest group of submarines ever built for the Royal Navy. A total of 62 were constructed over a period of 15 years, with fifty of the "improved" S class being launched between 1940 and 1945. Service The submarines operated in the waters around the United Kingdom and in the Mediterranean, and later in the Far East after being fitted with extra tankage. After the war S-class boats continued to serve in the Royal Navy until the 1960s. The last operational boat in the Royal Navy was , launched in 1945 and scrapped in February 1966. was in Israeli service as INS ''Tanin'' a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Draft (ship)
The draft or draught of a ship's hull is the vertical distance between the waterline and the bottom of the hull (keel). The draught of the vessel is the maximum depth of any part of the vessel, including appendages such as rudders, propellers and drop keels if deployed. Draft determines the minimum depth of water a ship or boat can safely navigate. The related term air draft is the maximum height of any part of the vessel above the water. The more heavily a vessel is loaded, the deeper it sinks into the water, and the greater its draft. After construction, the shipyard creates a table showing how much water the vessel displaces based on its draft and the density of the water (salt or fresh). The draft can also be used to determine the weight of cargo on board by calculating the total displacement of water, accounting for the content of the ship's bunkers, and using Archimedes' principle. The closely related term "trim" is defined as the difference between the forward and aft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1944 Ships
Events Below, the events of World War II have the "WWII" prefix. January * January 2 – WWII: ** Free France, Free French General Jean de Lattre de Tassigny is appointed to command First Army (France), French Army B, part of the Sixth United States Army Group in North Africa. ** Landing at Saidor: 13,000 US and Australian troops land on Papua New Guinea, in an attempt to cut off a Japanese retreat. * January 8 – WWII: Philippine Commonwealth troops enter the province of Ilocos Sur in northern Luzon and attack Japanese forces. * January 11 ** President of the United States Franklin D. Roosevelt proposes a Second Bill of Rights for social and economic security, in his State of the Union address. ** The Nazi German administration expands Kraków-Płaszów concentration camp into the larger standalone ''Konzentrationslager Plaszow bei Krakau'' in occupied Poland. * January 12 – WWII: Winston Churchill and Charles de Gaulle begin a 2-day conference in Marrakech ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British S-class Submarines (1931)
British may refer to: Peoples, culture, and language * British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies. ** Britishness, the British identity and common culture * British English, the English language as spoken and written in the United Kingdom or, more broadly, throughout the British Isles * Celtic Britons, an ancient ethno-linguistic group * Brittonic languages, a branch of the Insular Celtic language family (formerly called British) ** Common Brittonic, an ancient language Other uses *''Brit(ish)'', a 2018 memoir by Afua Hirsch *People or things associated with: ** Great Britain, an island ** United Kingdom, a sovereign state ** Kingdom of Great Britain (1707–1800) ** United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland (1801–1922) See also * Terminology of the British Isles * Alternative names for the British * English (other) * Britannic (other) * British Isles * Brit (other) * B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Affray (P421)
HMS ''Affray'' was a British ''Amphion''-class submarine. It was the last Royal Navy submarine to be lost at sea, on 16 April 1951, with the loss of 75 lives. ''Affray'' was built in the closing stages of the Second World War. She was one of 16 submarines of her class which were originally designed for use in the Pacific Ocean against Japan. History Early history She was laid down at the Cammell Laird yard in Birkenhead on 16 January 1944, launched on 12 April and commissioned on 25 November 1945. ''Affray'' and her sisters were state-of-the-art submarines at the time of their launching. They were the culmination of a rapid submarine development driven by the Second World War. Some elements of her design were taken from captured Nazi German U-boats. Her modular style of manufacture and all-welded hull were unique at the time. For work in the Far East she was equipped with refrigeration and two huge air conditioners, and all her accommodation was placed as far away from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Sirdar (P226)
HMS ''Sirdar'' was an S-class submarine built for the Royal Navy during the Second World War, and part of the Third Group built of that class. She was built by Scotts, of Greenock and launched on 26 March 1943. Design and description The S-class submarines were designed to patrol the restricted waters of the North Sea and the Mediterranean Sea. The third batch was slightly enlarged and improved over the preceding second batch of the S-class. The submarines had a length of overall, a beam of and a draught of . They displaced on the surface and submerged. The S-class submarines had a crew of 48 officers and ratings. They had a diving depth of .McCartney, p. 7 For surface running, the boats were powered by two diesel engines, each driving one propeller shaft. When submerged each propeller was driven by a electric motor. They could reach on the surface and underwater. On the surface, the third-batch boats had a range of at and at submerged. The boats were armed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Scorcher (P258)
HMS ''Scorcher'' was an S-class submarine of the Royal Navy, and part of the third group built of that class. She was built by Cammell Laird and launched on 18 December 1944. So far she has been the only ship of the Royal Navy to bear the name ''Scorcher''. She was launched by Thomas Beacham, a Foreman Driller employed by Cammell Laird. Built as the Second World War was drawing to a close, she did not see much action. Along with her sisters, HMS ''Sirdar'' and ''Scythian'', ''Scorcher'' took part in the search for the missing HMS ''Affray'' in 1951. ''Scorcher'' too had her fair share of accidents. She was damaged in a collision on 4 February 1956, and suffered a fire during exercises on 22 November 1956. In 1953 she took part in the Fleet Review to celebrate the Coronation of Queen Elizabeth II.Souvenir Programme, ''Coronation Review of the Fleet, Spithead, 15th June 1953'', HMSO, Gale and Polden ''Scorcher'' was eventually paid off Ship commissioning is the act or ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis powers. World War II was a total war that directly involved more than 100 million personnel from more than 30 countries. The major participants in the war threw their entire economic, industrial, and scientific capabilities behind the war effort, blurring the distinction between civilian and military resources. Aircraft played a major role in the conflict, enabling the strategic bombing of population centres and deploying the only two nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II was by far the deadliest conflict in human history; it resulted in 70 to 85 million fatalities, mostly among civilians. Tens of millions died due to genocides (including the Holocaust), starvation, ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naval Mine
A naval mine is a self-contained explosive device placed in water to damage or destroy surface ships or submarines. Unlike depth charges, mines are deposited and left to wait until they are triggered by the approach of, or contact with, any vessel or a particular vessel type, akin to anti-infantry vs. anti-vehicle mines. Naval mines can be used offensively, to hamper enemy shipping movements or lock vessels into a harbour; or defensively, to protect friendly vessels and create "safe" zones. Mines allow the minelaying force commander to concentrate warships or defensive assets in mine-free areas giving the adversary three choices: undertake an expensive and time-consuming minesweeping effort, accept the casualties of challenging the minefield, or use the unmined waters where the greatest concentration of enemy firepower will be encountered. Although international law requires signatory nations to declare mined areas, precise locations remain secret; and non-complying individ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British 21 Inch Torpedo
There have been several British 21-inch (533 mm) torpedoes used by the Royal Navy since their first development just before the First World War. Torpedoes of 21 inch calibre were the largest torpedoes in common use in the RN. They were used by surface ships and submarines rather than aircraft, which used smaller 18-inch torpedoes. Mark I The first British 21-inch torpedo came in two lengths, "Short" at , and "Long" at . The explosive charge was of gun cotton increased later to . Mark II The Mark II, chiefly used by destroyers, entered service in 1914. Apart from some older British ships, it was used with the old US (destroyers-for-bases deal) Town-class destroyers provided to the UK during the early part of the Second World War. The running speed was reduced from (over 3,000 yards) for better reliability. The Mark II*, an improved Mark II, was used by battleships and battlecruisers. A wet heater design, it could run for at . Mark IV From 1912, used by destro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Propeller Shaft
A drive shaft, driveshaft, driving shaft, tailshaft (Australian English), propeller shaft (prop shaft), or Cardan shaft (after Girolamo Cardano) is a component for transmitting mechanical power and torque and rotation, usually used to connect other components of a drivetrain that cannot be connected directly because of distance or the need to allow for relative movement between them. As torque carriers, drive shafts are subject to torsion and shear stress, equivalent to the difference between the input torque and the load. They must therefore be strong enough to bear the stress, while avoiding too much additional weight as that would in turn increase their inertia. To allow for variations in the alignment and distance between the driving and driven components, drive shafts frequently incorporate one or more universal joints, jaw couplings, or rag joints, and sometimes a splined joint or prismatic joint. History The term ''driveshaft'' first appeared during the mid-19th centu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |