|
HMS Sandwich (1679)
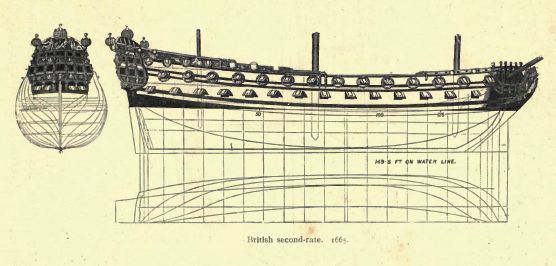
HMS ''Sandwich'' was a 90-gun second rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, launched in May 1679 at Harwich. At the battle of Barfleur, she failed to anchor during the flood tide at evening and as a result was swept through the French fleet taking several raking shots with the captain Antony Hastings being killed. She underwent a rebuild at Chatham Dockyard, from where she was relaunched on 21 April 1712 as a 90-gun second rate built to the 1706 Establishment The 1706 Establishment was the first formal set of dimensions for ships of the Royal Navy. Two previous sets of dimensions had existed before, though these were only for specific shipbuilding programs running for only a given amount of time. In .... ''Sandwich'' was broken up in 1770. From March 1720 - November 1721, William Smellie, who became a man-midwife and the 'master of British midwifery', 'it seems certain' was naval surgeon on HMS ''Sandwich''.Oxford Dictionary of National Biography Notes Referen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Great Britain
The Kingdom of Great Britain (officially Great Britain) was a Sovereign state, sovereign country in Western Europe from 1 May 1707 to the end of 31 December 1800. The state was created by the 1706 Treaty of Union and ratified by the Acts of Union 1707, which united the kingdoms of Kingdom of England, England (which included Wales) and Kingdom of Scotland, Scotland to form a single kingdom encompassing the whole island of Great Britain and its outlying islands, with the exception of the Isle of Man and the Channel Islands. The unitary state was governed by a single Parliament of Great Britain, parliament at the Palace of Westminster, but distinct legal systems – English law and Scots law – remained in use. The formerly separate kingdoms had been in personal union since the 1603 "Union of the Crowns" when James VI of Scotland became King of England and King of Ireland. Since James's reign, who had been the first to refer to himself as "king of Great Britain", a political un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naval Ensign Of Great Britain (1707-1800)
A navy, naval force, or maritime force is the branch of a nation's armed forces principally designated for naval warfare, naval and amphibious warfare; namely, lake-borne, riverine, littoral zone, littoral, or ocean-borne combat operations and related functions. It includes anything conducted by surface Naval ship, ships, amphibious warfare, amphibious ships, submarines, and seaborne naval aviation, aviation, as well as ancillary support, communications, training, and other fields. The strategic offensive role of a navy is Power projection, projection of force into areas beyond a country's shores (for example, to protect Sea lane, sea-lanes, deter or confront piracy, ferry troops, or attack other navies, ports, or shore installations). The strategic defensive purpose of a navy is to frustrate seaborne projection-of-force by enemies. The strategic task of the navy also may incorporate nuclear deterrence by use of submarine-launched ballistic missiles. Naval operations can be broa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Rate
In the rating system of the Royal Navy used to categorise sailing warships, a second-rate was a ship of the line which by the start of the 18th century mounted 90 to 98 guns on three gun decks; earlier 17th-century second rates had fewer guns and were originally two-deckers or had only partially armed third gun decks. A "second rate" was the second largest class of warships in a hierarchical system of six "ratings" based on size and firepower. They were essentially smaller and hence cheaper versions of the three-decker first rates. Like the first rates, they fought in the line of battle, but unlike the first rates, which were considered too valuable to risk in distant stations, the second rates often served also in major overseas stations as flagships. They had a reputation for poor handling and slow sailing. They were popular as flagships of admirals commanding the Windward and/or Leeward Islands station, which was usually a Rear-admiral of the red. Rating Typically measuri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ship Of The Line
A ship of the line was a type of naval warship constructed during the Age of Sail from the 17th century to the mid-19th century. The ship of the line was designed for the naval tactic known as the line of battle, which depended on the two columns of opposing warships maneuvering to volley fire with the cannons along their broadsides. In conflicts where opposing ships were both able to fire from their broadsides, the opponent with more cannons firingand therefore more firepowertypically had an advantage. Since these engagements were almost invariably won by the heaviest ships carrying more of the most powerful guns, the natural progression was to build sailing vessels that were the largest and most powerful of their time. From the end of the 1840s, the introduction of steam power brought less dependence on the wind in battle and led to the construction of screw-driven wooden-hulled ships of the line; a number of purely sail-powered ships were converted to this propulsion mech ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Full-rigged Ship
A full-rigged ship or fully rigged ship is a sailing vessel's sail plan with three or more masts, all of them square-rigged. A full-rigged ship is said to have a ship rig or be ship-rigged. Such vessels also have each mast stepped in three segments: lower mast, top mast, and topgallant mast. Other large, multi-masted sailing vessels may be regarded as ships while lacking one of the elements of a full-rigged ship, e.g. having one or more masts support only a fore-and-aft sail or having a mast that only has two segments. Masts The masts of a full-rigged ship, from bow to stern, are: * Foremast, which is the second tallest mast * Mainmast, the tallest * Mizzenmast, the third tallest * Jiggermast, which may not be present but will be fourth tallest if so If the masts are of wood, each mast is in three or more pieces. They are (in order, from bottom up): * The lowest piece is called the ''mast'' or the ''lower''. * Topmast * Topgallant mast * Royal mast, if fitted On steel-m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1706 Establishment
The 1706 Establishment was the first formal set of dimensions for ships of the Royal Navy. Two previous sets of dimensions had existed before, though these were only for specific shipbuilding programs running for only a given amount of time. In contrast, the 1706 Establishment was intended to be permanent. Origins Dimensions for ships had been established for the "Thirty Ships" building program of 1677, and while these dimensions saw use until 1695, this was merely because of the success of the 1677 ships and the lack of perceived need to change them. Dimensions were then laid down for the 1691 "Twenty-seven Ships" program to build seventeen eighty-gun and ten sixty-gun double-decked ships of the line, though the dimensions were abandoned before the program was complete, with the final four eighty-gun ships being constructed with three gun-decks. The origins of the formalized 1706 Establishment can be traced to February 1705, when Prince George of Denmark Prince George of De ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against France. The modern Royal Navy traces its origins to the early 16th century; the oldest of the UK's armed services, it is consequently known as the Senior Service. From the middle decades of the 17th century, and through the 18th century, the Royal Navy vied with the Dutch Navy and later with the French Navy for maritime supremacy. From the mid 18th century, it was the world's most powerful navy until the Second World War. The Royal Navy played a key part in establishing and defending the British Empire, and four Imperial fortress colonies and a string of imperial bases and coaling stations secured the Royal Navy's ability to assert naval superiority globally. Owing to this historical prominence, it is common, even among non-Britons, to ref ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harwich
Harwich is a town in Essex, England, and one of the Haven ports on the North Sea coast. It is in the Tendring district. Nearby places include Felixstowe to the north-east, Ipswich to the north-west, Colchester to the south-west and Clacton-on-Sea to the south. It is the northernmost coastal town in Essex. Its position on the estuaries of the Stour and Orwell rivers, with its usefulness to mariners as the only safe anchorage between the Thames and the Humber, led to a long period of civil and military maritime significance. The town became a naval base in 1657 and was heavily fortified, with Harwich Redoubt, Beacon Hill Battery, and Bath Side Battery. Harwich is the likely launch point of the ''Mayflower'', which carried English Puritans to North America, and is the presumed birthplace of ''Mayflower'' captain Christopher Jones. Harwich today is contiguous with Dovercourt and the two, along with Parkeston, are often referred to collectively as ''Harwich''. History The tow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chatham Dockyard
Chatham Dockyard was a Royal Navy Dockyard located on the River Medway in Kent. Established in Chatham in the mid-16th century, the dockyard subsequently expanded into neighbouring Gillingham (at its most extensive, in the early 20th century, two-thirds of the dockyard lay in Gillingham, one-third in Chatham). It came into existence at the time when, following the Reformation, relations with the Catholic countries of Europe had worsened, leading to a requirement for additional defences. Over 414 years Chatham Royal Dockyard provided more than 500 ships for the Royal Navy, and was at the forefront of shipbuilding, industrial and architectural technology. At its height, it employed over 10,000 skilled artisans and covered . Chatham dockyard closed in 1984, and of the Georgian dockyard is now managed as the Chatham Historic Dockyard visitor attraction by the Chatham Historic Dockyard Trust. Overview Joseph Farington (1747-1821) was commissioned by the Navy Board to paint a pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Smellie (obstetrician)
William Smellie (5 February 1697 – 5 March 1763) was a Scottish obstetrician and medical instructor who practiced and taught primarily in London. One of the first prominent male midwives in Britain, he designed an improved version of the obstetrical forceps, established safer delivery practices, and through his teaching and writing helped make obstetrics more scientifically based. He is often called the "father of British midwifery". Early life and education Smellie was born on 5 February 1697 in the town of Lesmahagow, Scotland. He was the only child of Sara Kennedy (1657–1727) and Archibald Smellie (1663/4–1735), a merchant and burgess of the town. Smellie practiced medicine before getting a license, opening an apothecary in 1720 in Lanark. It was not a particularly lucrative venture, as he also sold cloth as a side business to supplement his income, but he began reading medical books and teaching himself obstetrics at this time. By 1728, he was married to Eupham Borlan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ship's Doctor
A naval surgeon, or less commonly ship's doctor, is the person responsible for the health of the ship's company aboard a warship. The term appears often in reference to Royal Navy's medical personnel during the Age of Sail. Ancient uses Specialised crew members capable of providing medical care have been a feature of military vessels for at least two thousand years. The second-century Roman Navy under Emperor Hadrian included a surgeon aboard each of its triremes, with the position earning twice a regular officer's pay. Royal Navy During the Age of Sail, the Royal Navy carried trained medical officers aboard its warships, who usually learned their trade before coming on board ship. They were generally called surgeons. The Navy Board qualified surgeons through an examination at the Barber-Surgeons' Company and they were responsible to the Sick and Wounded Board under the Navy Board. Surgeons were required to keep two logbooks detailing treatments and procedures carried out under ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ships Of The Line Of The Royal Navy
A ship is a large watercraft that travels the world's oceans and other sufficiently deep waterways, carrying cargo or passengers, or in support of specialized missions, such as defense, research, and fishing. Ships are generally distinguished from boats, based on size, shape, load capacity, and purpose. Ships have supported exploration, trade, warfare, migration, colonization, and science. After the 15th century, new crops that had come from and to the Americas via the European seafarers significantly contributed to world population growth. Ship transport is responsible for the largest portion of world commerce. The word ''ship'' has meant, depending on the era and the context, either just a large vessel or specifically a ship-rigged sailing ship with three or more masts, each of which is square-rigged. As of 2016, there were more than 49,000 merchant ships, totaling almost 1.8 billion dead weight tons. Of these 28% were oil tankers, 43% were bulk carriers, and 13% were con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |