|
HMS Royal Oak (1809)
HMS ''Royal Oak'' was a 74-gun third rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, launched on 4 March 1809 at Dudman's yard at Deptford Wharf. Her first commanding officer was Captain Pulteney Malcolm. Napoleonic Wars In 1812 ''Royal Oak'' was under the command of Captain Thomas George Shortland, who was superseded by Captain Edward Dix in 1813. During this time she was the flagship of Rear-Admiral Lord Amelius Beauclerk, of the Texel. War of 1812 ''Royal Oak'' shared with other vessels in the proceeds of the capture on 17 December 1813 of the American vessel ''Maria Antoinette''. On 1 June 1814 Rear-Admiral Pulteney Malcolm, who had hoisted his flag aboard ''Royal Oak'', proceeded with troops under Brigadier-General Robert Ross to North America. Malcolm accompanied Sir Alexander Cochrane on the expedition up the Chesapeake and regulated the debarkation and embarkation of the troops employed against Washington and Baltimore. Ross was killed on 12 September 1814 in Baltimor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fame (1805)
Fame is the quality of being well-known and in the public eye. Celebrities are famous by definition. Fame may also refer to: Books * '' Fame: an art project'', a 2013 book and series of paintings by Robert Priseman * ''Fame'' (novel) (German ''Ruhm''), a 2009 novel by Daniel Kehlmann * ''Fame'', a 2005 novel by Karen Kingsbury * ''Fame'', a 2008 novel by Mark Rowlands * ''Fame'', a 2011 novel by Tilly Bagshawe Film, television and stage * ''Fame'' (1980 film), a musical film ** ''Fame'' (1982 TV series), a 1982–1987 television adaptation of the film ** ''Fame'' (2009 film), a remake of the musical film ** ''Fame'' (musical), a stage adaptation of the film that premiered in 1988 ** ''Fame'' (2003 TV series), a talent competition *** ''Fame: The Musical'' (Irish TV series), an Irish version of the NBC talent show * ''Fame'' (2007 film), a stand-up tour and DVD by Ricky Gervais * "Fame" (''Law & Order''), a 2006 episode of ''Law & Order'' * "Fame", a 2010 episode of '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flagship
A flagship is a vessel used by the commanding officer of a group of naval ships, characteristically a flag officer entitled by custom to fly a distinguishing flag. Used more loosely, it is the lead ship in a fleet of vessels, typically the first, largest, fastest, most heavily armed, or best known. Over the years, the term "flagship" has become a metaphor used in industries such as broadcasting, automobiles, education, technology, airlines, and retail to refer to their highest profile or most expensive products and locations. Naval use In common naval use, the term ''flagship'' is fundamentally a temporary designation; the flagship is wherever the admiral's flag is being flown. However, admirals have always needed additional facilities, including a meeting room large enough to hold all the captains of the fleet and a place for the admiral's staff to make plans and draw up orders. Historically, only larger ships could accommodate such requirements. The term was also used by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Starr (1805)
HMS ''Starr'' was a 16-gun ''Merlin''-class ship sloop of the Royal Navy. She was built by Tanner, of Dartmouth, to plans by Sir William Rule, and launched in July 1805. As a sloop she served on convoy duty, though she also participated in the invasion of Martinique in early 1809. She was rebuilt as a bomb vessel in May 1812 and renamed ''Meteor''. As ''Meteor'' she served in the Baltic and then off the United States, participating in attacks on up the Potomac and on Baltimore and New Orleans. She was sold in October 1816. Napoleonic Wars She was commissioned in October 1805 under Commander John Simpson. On 3 January 1806 she recaptured the ships ''Argo'' and ''Adventure'', and shared in the recapture of the ''Good Intent''. ''Starr'' was off Villa de Conde, Portugal, when she intercepted the vessels, which had been taken from a convoy that had been escorting from Newfoundland to Portugal, and both of which had been carrying cargoes of fish. ''Starr'' sighted ''Good Inten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Third-rate
In the rating system of the Royal Navy, a third rate was a ship of the line which from the 1720s mounted between 64 and 80 guns, typically built with two gun decks (thus the related term two-decker). Years of experience proved that the third rate ships embodied the best compromise between sailing ability (speed, handling), firepower, and cost. So, while first-rates and second-rates were both larger and more powerful, third-rate ships were the optimal configuration. Rating When the rating system was first established in the 1620s, the third rate was defined as those ships having at least 200 but not more than 300 men; previous to this, the type had been classified as "middling ships". By the 1660s, the means of classification had shifted from the number of men to the number of carriage-mounted guns, and third rates at that time mounted between 48 and 60 guns. By the turn of the century, the criterion boundaries had increased and third rate carried more than 60 guns, with seco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
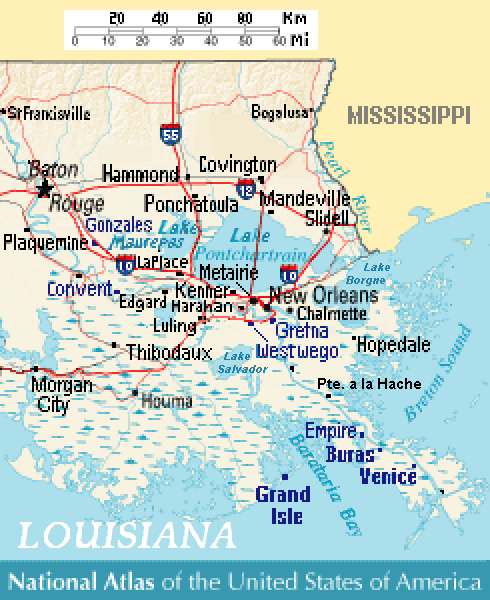
Lake Borgne
Lake Borgne (french: Lac Borgne, es, Lago Borgne) is a lagoon of the Gulf of Mexico in southeastern Louisiana. Although early maps show it as a lake surrounded by land, coastal erosion has made it an arm of the Gulf of Mexico. Its name comes from the French language, French word ''borgne'', which means "one-eyed." Geography In southern Louisiana, three large lakes—Lake Maurepas, Maurepas, Lake Pontchartrain, Pontchartrain, and Borgne—cover 55% of the Pontchartrain Drainage basin, Basin. A brackish marsh land bridge and Lake St. Catherine (Louisiana), Lake St. Catherine separate Lake Pontchartrain from Lake Borgne. Rigolets, The Rigolets and Chef Menteur Pass are the two open water connections between Pontchartrain and Borgne. Coastal erosion has transformed Borgne into a lagoon connecting to the Gulf of Mexico. Early 18th-century maps show Borgne as a true lake, largely separated from the gulf by a considerable extent of wetlands that have since disappeared. In a 1902 case ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sixth-rate
In the rating system of the Royal Navy used to categorise sailing warships, a sixth-rate was the designation for small warships mounting between 20 and 28 carriage-mounted guns on a single deck, sometimes with smaller guns on the upper works and sometimes without. It thus encompassed ships with up to 30 guns in all. In the first half of the 18th century the main battery guns were 6-pounders, but by mid-century these were supplanted by 9-pounders. 28-gun sixth rates were classed as frigates, those smaller as 'post ships', indicating that they were still commanded by a full ('post') captain, as opposed to sloops of 18 guns and less under commanders. Rating Sixth-rate ships typically had a crew of about 150–240 men, and measured between 450 and 550 tons. A 28-gun ship would have about 19 officers; commissioned officers would include the captain, and two lieutenants; warrant officers would include the master, ship's surgeon, and purser. The other quarterdeck officers were the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Lake Borgne
The Battle of Lake Borgne was a coastal engagement between the Royal Navy and the U.S. Navy in the American South theatre of the War of 1812. It occurred on December 14, 1814 on Lake Borgne. The British victory allowed them to disembark their troops unhindered nine days later and to launch an offensive upon New Orleans on land. Background In August 1814, Vice Admiral Cochrane had convinced the Admiralty that a campaign against New Orleans would weaken American resolve against Canada, and hasten a successful end to the war. In the winter of 1814, the British had the objective of gaining control of the entrance of the Mississippi, and to challenge the legality of the Louisiana Purchase. To this end, an expeditionary force of about 8,000 troops under General Edward Pakenham had arrived in the Gulf Coast, to attack New Orleans. An anonymous letter sent from Pensacola, dated December 5 and addressed to Commodore Daniel Patterson warned him of this imminent threat, and was received on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
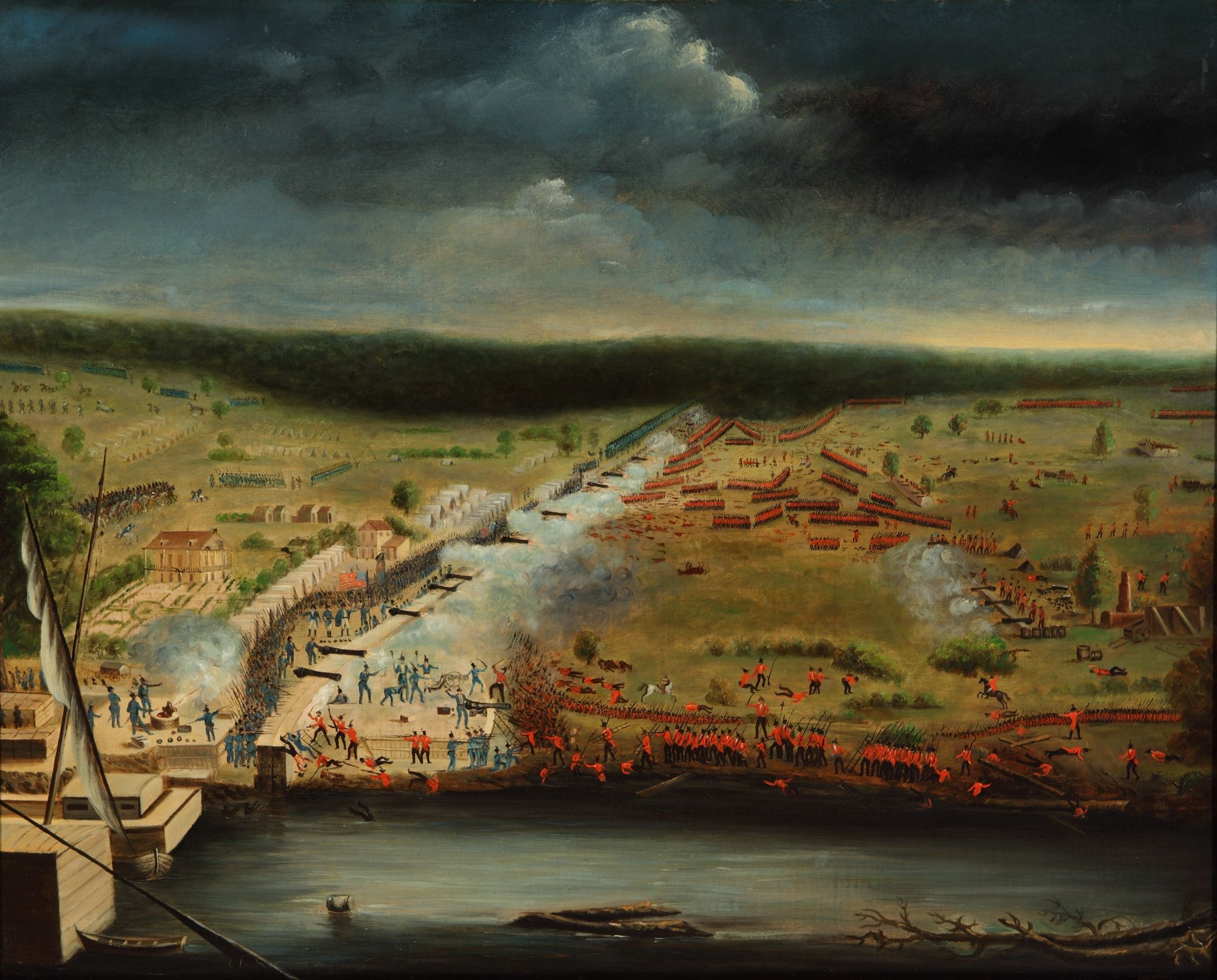
Battle Of New Orleans
The Battle of New Orleans was fought on January 8, 1815 between the British Army under Major General Sir Edward Pakenham and the United States Army under Brevet Major General Andrew Jackson, roughly 5 miles (8 km) southeast of the French Quarter of New Orleans, in the current suburb of Chalmette, Louisiana. The battle was the climax of the five-month Gulf Campaign (September 1814 to February 1815) by Britain to try to take New Orleans, West Florida, and possibly Louisiana Territory which began at the First Battle of Fort Bowyer. Britain started the New Orleans campaign on December 14, 1814, at the Battle of Lake Borgne and numerous skirmishes and artillery duels happened in the weeks leading up to the final battle. The battle took place 15 days after the signing of the Treaty of Ghent, which formally ended the War of 1812, on December 24, 1814, though it would not be ratified by the United States (and therefore did not take effect) until February 16, 1815, as news of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Cochrane
Admiral of the Blue Sir Alexander Inglis Cochrane (born Alexander Forrester Cochrane; 23 April 1758 – 26 January 1832) was a senior Royal Navy commander during the Napoleonic Wars and achieved the rank of admiral. He had previously captained HMS ''Ajax'' in Alexandria, Egypt during the Egyptian operation of 1801. Cochrane was knighted into the Order of the Bath for his services in 1806. In 1814 he became vice admiral and commander-in-chief of the North American Station, led the naval forces during the attacks on Washington and New Orleans, and was promoted to admiral in 1819 and became commander-in-chief of the Plymouth naval base. Naval career Alexander Inglis Cochrane was a younger son of the Scottish peer Thomas Cochrane, the eighth Earl of Dundonald, and his second wife, Jane Stuart. He joined the Royal Navy as a boy and served with British naval forces in North America. He served during the American War of Independence. Cochrane also participated in the Egyptian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Ross (British Army Officer)
Major-General Robert Ross (176612 September 1814) was an Irish officer in the British Army who served in the Napoleonic Wars and its theatre in North America in the War of 1812. Ross joined the British Army in 1789. He served as an officer in several battles during the Napoleonic Wars, including the Battles of Maida and Corunna, gaining promotion to Colonel. In 1809, he was sent to serve in the Peninsular War, including the Battles of Vittoria, Roncesvalles, Sorauren, and Orthez. He was wounded in the neck at the Battle of Orthez in France on 27 February 1814. Upon returning to duty later that year, Ross was made a major general and sent to North America, as commander of "all British forces on the East Coast". In August 1814, he reached Benedict, Maryland and continued on, leading the professional soldiers who quickly defeated a poorly organized American militia at the Battle of Bladensburg on 24 August; that evening, he led his troops into Washington D.C. During his command o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pence
A penny is a coin ( pennies) or a unit of currency (pl. pence) in various countries. Borrowed from the Carolingian denarius (hence its former abbreviation d.), it is usually the smallest denomination within a currency system. Presently, it is the formal name of the British penny ( p) and the ''de facto'' name of the American one-cent coin (abbr. ¢) as well as the informal Irish designation of the 1 cent euro coin (abbr. c). It is the informal name of the cent unit of account in Canada, although one-cent coins are no longer minted there. The name is used in reference to various historical currencies, also derived from the Carolingian system, such as the French denier and the German pfennig. It may also be informally used to refer to any similar smallest-denomination coin, such as the euro cent or Chinese fen. The Carolingian penny was originally a 0.940-fine silver coin, weighing pound. It was adopted by Offa of Mercia and other English kings and remained ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shilling
The shilling is a historical coin, and the name of a unit of modern currencies formerly used in the United Kingdom, Australia, New Zealand, other British Commonwealth countries and Ireland, where they were generally equivalent to 12 pence or one-twentieth of a pound before being phased out during the 20th century. Currently the shilling is used as a currency in five east African countries: Kenya, Tanzania, Uganda, Somalia, as well as the ''de facto'' country of Somaliland. The East African Community additionally plans to introduce an East African shilling. History The word ''shilling'' comes from Old English "Scilling", a monetary term meaning twentieth of a pound, from the Proto-Germanic root skiljaną meaning 'to separate, split, divide', from (s)kelH- meaning 'to cut, split.' The word "Scilling" is mentioned in the earliest recorded Germanic law codes, those of Æthelberht of Kent. There is evidence that it may alternatively be an early borrowing of Phoenician ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)





.jpg)

.jpg)
