|
HMS Resolute (1850)
HMS ''Resolute'' was a mid-19th-century barque-rigged ship of the British Royal Navy, specially outfitted for Arctic exploration. ''Resolute'' became trapped in the ice and was abandoned in 1854. Recovered by an American whaler, she was returned to Queen Victoria in 1856. Timbers from the ship were later used to construct the ''Resolute'' desk which was presented to the President of the United States and is currently located in the White House Oval Office. History In the face of rising concerns regarding the fate of the Arctic expedition of Sir John Franklin, having left Britain in 1845 in search of the North West Passage, the British Government, in 1848, sent expeditions in search of the expedition. With few existing warships deemed suitable, six merchant ships were purchased between 1848 and 1850 and soon converted to exploration ships: two steamships, HMS ''Pioneer'' and HMS ''Intrepid'', the other four (''Resolute'', , and ) seagoing sailing ships. The first ship to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blackwall Yard
Blackwall Yard is a small body of water that used to be a shipyard on the River Thames in Blackwall, engaged in ship building and later ship repairs for over 350 years. The yard closed in 1987. History East India Company Blackwall was a shipbuilding area since the Middle Ages. In 1607, the Honorable East India Company (HEIC) decided to build its own ships and leased a yard in Deptford. Initially, this change of policy proved profitable as the first ships cost the Company about £10 per ton instead of the £45 per ton that it had been paying to have ships built for it. However, the situation changed as the Deptford yard came to be expensive to run. In 1614 the East India Company outgrew Deptford and ordered William Burrell to begin work on a new yard for repair, construction and loading of out-going ships. The site Burrell selected was at Blackwall, which was further down river and had deeper water, allowing laden ships to moor closer to the dock. The new yard was fully ope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
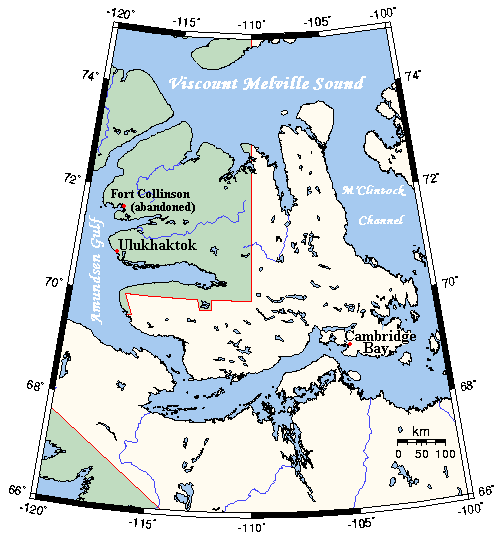
Viscount Melville Sound
Viscount Melville Sound is an arm of the Arctic Ocean in the Kitikmeot Region, Nunavut and the Inuvik Region, Northwest Territories, Canada. Forming part of the Parry Channel, it separates Victoria Island and Prince of Wales Island from the Queen Elizabeth Islands. East of the sound, via Barrow Strait, lies Lancaster Sound, leading into Baffin Bay; westward lies the M'Clure Strait and the Arctic Ocean/Beaufort Sea. The sound is a part of the Northwest Passage. In 1854, Edward Belcher abandoned his ship, HMS ''Resolute'', in the sound while searching for Sir John Franklin and his lost expedition. In 1855 HMS ''Resolute'' was found drifting off Baffin Island Baffin Island (formerly Baffin Land), in the Canadian territory of Nunavut, is the largest island in Canada and the fifth-largest island in the world. Its area is , slightly larger than Spain; its population was 13,039 as of the 2021 Canadia ..., and was later ceremonially returned to Queen Victoria. References ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Victoria Island (Canada)
Victoria Island ( ikt, Kitlineq, italic=yes) is a large island in the Arctic Archipelago that straddles the boundary between Nunavut and the Northwest Territories of Canada. It is the eighth-largest island in the world, and at in area, it is Canada's second-largest island. It is nearly double the size of Newfoundland (), and is slightly larger than the island of Great Britain () but smaller than Honshu (). The western third of the island lies in the Inuvik Region of the Northwest Territories; the remainder is part of Nunavut's Kitikmeot Region. The island is named after Queen Victoria, the Canadian sovereign from 1867 to 1901 (though she first became Queen in 1837). The features bearing the name "Prince Albert" are named after her consort, Albert. History In 1826 John Richardson saw the southwest coast and called it " Wollaston Land". In 1839 Peter Warren Dease and Thomas Simpson followed its southeast coast and called it "Victoria Land". A map published by John Barro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wellington Channel
The Wellington Channel () (not to be confused with Wellington Strait) is a natural waterway through the central Canadian Arctic Archipelago in Qikiqtaaluk Region, Nunavut. It runs north–south, separating Cornwallis Island and Devon Island. Queens Channel lies to the west, separated by Baillie-Hamilton Island, Dundas Island, and Margaret Island. Explorations In 1845, Sir John Franklin wintered at Beechey Island at the channel's southeast end. In winter 1848, Franklin's ships got trapped in sea ice further south in Victoria Strait, leading to the tragic end of what became known as Franklin's lost expedition. The First Grinnell expedition, an American effort to determine the fate of Franklin's lost expedition, covered the Wellington Channel. They identified there the remains of Franklin's Beechey Island winter camp, providing the first solid clues to Franklin's activities before becoming icebound themselves. In spring 1851, the channel was explored by William Penny, who went by s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baffin Bay
Baffin Bay ( Inuktitut: ''Saknirutiak Imanga''; kl, Avannaata Imaa; french: Baie de Baffin), located between Baffin Island and the west coast of Greenland, is defined by the International Hydrographic Organization as a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean. It is sometimes considered a sea of the North Atlantic Ocean. It is connected to the Atlantic via Davis Strait and the Labrador Sea. The narrower Nares Strait connects Baffin Bay with the Arctic Ocean. The bay is not navigable most of the year because of the ice cover and high density of floating ice and icebergs in the open areas. However, a polynya of about , known as the North Water, opens in summer on the north near Smith Sound. Most of the aquatic life of the bay is concentrated near that region. Extent The International Hydrographic Organization defines the limits of Baffin Bay as follows: History The area of the bay has been inhabited since BC. Around AD 1200, the initial Dorset settlers were replaced by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Depot Ship
A depot ship is an auxiliary ship used as a mobile or fixed base for submarines, destroyers, minesweepers, fast attack craft, landing craft, or other small ships with similarly limited space for maintenance equipment and crew dining, berthing and relaxation. Depot ships may be identified as tenders in American English. Depot ships may be specifically designed for their purpose or be converted from another purpose. Function Depot ships provide services unavailable from local naval base shore facilities. Industrialized countries may build naval bases with extensive workshops, warehouses, barracks, and medical and recreation facilities. Depot ships operating within such bases may provide little more than command staff offices,Lenton (1975) pp.391-394 while depot ships operating at remote bases may perform unusually diverse support functions. Some United States Navy submarine depot ships operating in the Pacific during World War II included sailors with Construction Battalion ratings ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward Belcher
Admiral Sir Edward Belcher (27 February 1799 – 18 March 1877) was a British naval officer, hydrographer, and explorer. Born in Nova Scotia, he was the great-grandson of Jonathan Belcher, who served as a colonial governor of Massachusetts, New Hampshire, and New Jersey. Biography Early life Belcher was born in Halifax, Nova Scotia, the second son of Andrew Belcher and entered the Royal Navy in 1812. Surveys In 1825, he accompanied Frederick William Beechey's expedition to the Pacific and Bering Strait as a surveyor. In 1835 he was surveying in the Irish Sea in , and in 1836 he commanded a surveying ship on the north and west coasts of Africa and in the British seas. Belcher took up the work which Beechey had left unfinished on the Pacific coast of South America. He was on board , which was ordered to return to England in 1839 via the Trans-Pacific route. Belcher made various observations at a number of islands which he visited, having been delayed by being despat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scott Polar Research Institute
The Scott Polar Research Institute (SPRI) is a centre for research into the polar regions and glaciology worldwide. It is a sub-department of the Department of Geography in the University of Cambridge, located on Lensfield Road in the south of Cambridge. SPRI was founded by Frank Debenham in 1920 as the national memorial to Captain Robert Falcon Scott and his companions, who died on their return journey from the South Pole in 1912. It investigates issues relevant to the Arctic and Antarctic in the environmental sciences, social sciences and humanities. The institute is home the Polar Museum and has some 60 personnel, consisting of academic, library and support staff plus postgraduate students, associates and fellows attached to research programmes. The institute also hosts the Scientific Committee on Antarctic Research. Research SPRI has several research groups. Notable researchers that have been based at the institute include Julian Dowdeswell, British diplomat Bryan Robert ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Museum
The British Museum is a public museum dedicated to human history, art and culture located in the Bloomsbury area of London. Its permanent collection of eight million works is among the largest and most comprehensive in existence. It documents the story of human culture from its beginnings to the present.Among the national museums in London, sculpture and decorative and applied art are in the Victoria and Albert Museum; the British Museum houses earlier art, non-Western art, prints and drawings. The National Gallery holds the national collection of Western European art to about 1900, while art of the 20th century on is at Tate Modern. Tate Britain holds British Art from 1500 onwards. Books, manuscripts and many works on paper are in the British Library. There are significant overlaps between the coverage of the various collections. The British Museum was the first public national museum to cover all fields of knowledge. The museum was established in 1753, largely b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sherard Osborn
Sherard Osborn (25 April 1822 – 6 May 1875) was a Royal Navy admiral and Arctic explorer. Biography Born in Madras, he was the son of an Indian army officer. Osborn entered the navy as a first-class volunteer in 1837, serving until 1844 on , , and . In 1838, he was entrusted with the command of a gunboat at the attack on Kedah in the Malay Peninsula, and was present at the Battle of Canton in 1841, and at the Battle of Woosung in 1842. From 1844 until 1848, he was gunnery mate and lieutenant on , the flagship of Sir George Seymour in the Pacific. He took a prominent part in 1849 in advocating a new search expedition for Sir John Franklin, and in 1850 was appointed to the command of the steam-tender HMS Pioneer (1850) in the Arctic expedition under Horatio Thomas Austin, in the course of which he performed a remarkable sledge-journey to the western extremity of Prince of Wales Island. He published an account of this voyage, entitled ''Stray Leaves from an Arctic Jo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)


.jpg)


