|
HMS Monmouth (1796)
HMS ''Monmouth'' was a 64-gun third rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, launched on 23 April 1796 at Rotherhithe. She had been designed and laid down for the East India Company, but the Navy purchased her after the start of the French Revolutionary War. She served at the Battle of Camperdown and during the Napoleonic Wars. Hulked in 1815, she was broken up in 1834. Construction and commissioning ''Monmouth'' was originally being built as an East Indiaman for the East India Company under the name ''Belmont''. In 1796 the Navy purchased five ships being built or serviced in commercial dockyards along the River Thames and had them completed as warships. Alongside ''Belmont'', then being built at Rotherhithe by Randall & Company, the Navy acquired the merchantmen ''Royal Admiral'', ''Princess Royal'', ''Earl Talbot'' and ''Pigot''; they became , , and respectively. ''Belmont'' was registered and named ''Monmouth'' on 14 July 1795 and was launched on 23 April 1796, be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
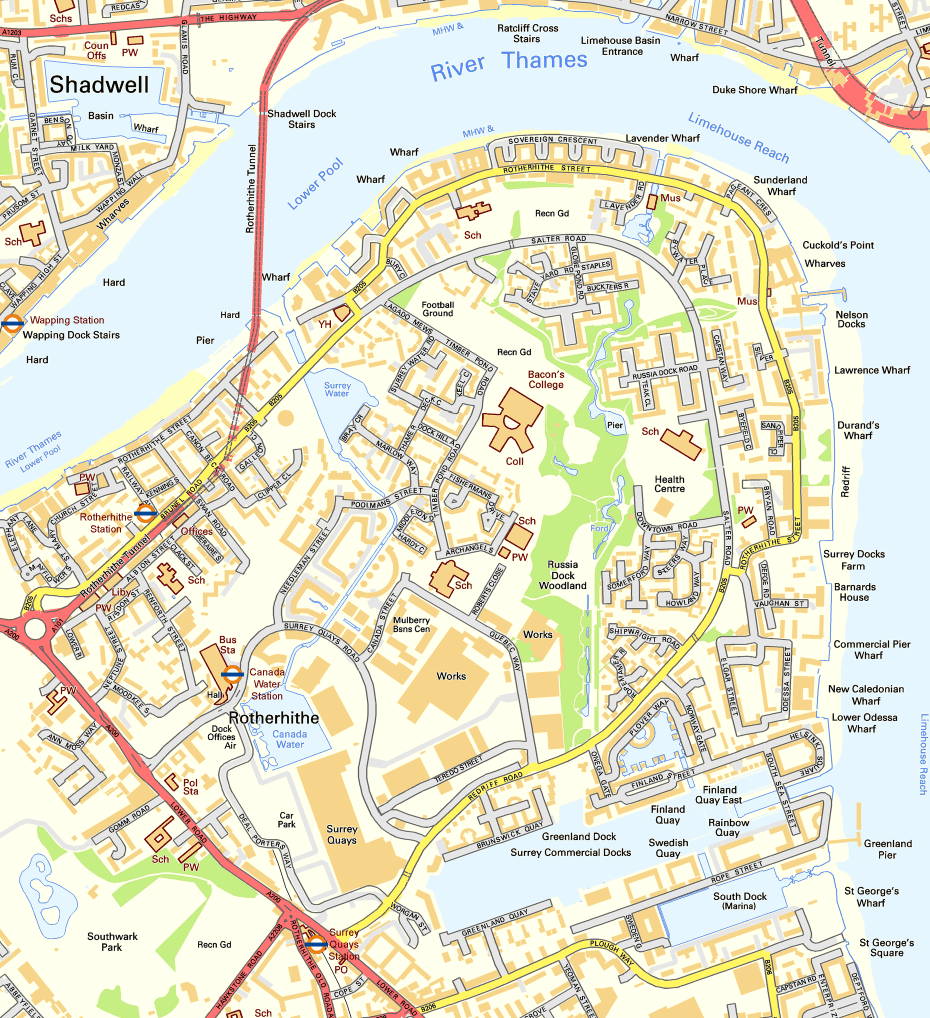
Rotherhithe
Rotherhithe () is a district of south-east London, England, and part of the London Borough of Southwark. It is on a peninsula on the south bank of the Thames, facing Wapping, Shadwell and Limehouse on the north bank, as well as the Isle of Dogs to the east of the Thames and is a part of the London Docklands, Docklands area. It borders Bermondsey to the west and Deptford to the south east. Rotherhithe has a long history as a port, with Elizabethan era, Elizabethan shipyards and working docks until the 1970s. In the 1980s, the area along the river was redeveloped as housing through a mix of warehouse conversions and new-build developments. Following the arrival of the Jubilee line in 1999 (giving quick connections to the West End of London, West End and to Canary Wharf) and the London Overground in 2010 (providing a quick route to the City of London), the rest of Rotherhithe is now a gentrification, gentrifying residential and commuter area, with urban regeneration progressing arou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Maritime Museum
The National Maritime Museum (NMM) is a maritime museum in Greenwich, London. It is part of Royal Museums Greenwich, a network of museums in the Maritime Greenwich World Heritage Site. Like other publicly funded national museums in the United Kingdom, it has no general admission charge; there are admission charges for most side-gallery temporary exhibitions, usually supplemented by many loaned works from other museums. Creation and official opening The museum was created by the National Maritime Museum Act 1934 under a Board of Trustees, appointed by HM Treasury. It is based on the generous donations of Sir James Caird (1864–1954). King George VI formally opened the museum on 27 April 1937 when his daughter Princess Elizabeth accompanied him for the journey along the Thames from London. The first director was Sir Geoffrey Callender. Collection Since the earliest times Greenwich has had associations with the sea and navigation. It was a landing place for the Romans, Henry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Batavian Republic
The Batavian Republic ( nl, Bataafse Republiek; french: République Batave) was the successor state to the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands. It was proclaimed on 19 January 1795 and ended on 5 June 1806, with the accession of Louis Bonaparte to the Dutch throne. From October 1801 onward, it was known as the Batavian Commonwealth ( nl, Bataafs Gemenebest). Both names refer to the Germanic tribe of the ''Batavi'', representing both the Dutch ancestry and their ancient quest for liberty in their nationalistic lore. In early 1795, intervention by the French Republic led to the downfall of the old Dutch Republic. The new Republic enjoyed widespread support from the Dutch populace and was the product of a genuine popular revolution. However, it was founded with the armed support of the French revolutionary forces. The Batavian Republic became a client state, the first of the " sister-republics", and later part of the French Empire of Napoleon. Its politics were deeply in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pence
A penny is a coin ( pennies) or a unit of currency (pl. pence) in various countries. Borrowed from the Carolingian denarius (hence its former abbreviation d.), it is usually the smallest denomination within a currency system. Presently, it is the formal name of the British penny ( p) and the ''de facto'' name of the American one-cent coin (abbr. ¢) as well as the informal Irish designation of the 1 cent euro coin (abbr. c). It is the informal name of the cent unit of account in Canada, although one-cent coins are no longer minted there. The name is used in reference to various historical currencies, also derived from the Carolingian system, such as the French denier and the German pfennig. It may also be informally used to refer to any similar smallest-denomination coin, such as the euro cent or Chinese fen. The Carolingian penny was originally a 0.940-fine silver coin, weighing pound. It was adopted by Offa of Mercia and other English kings and remained ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shilling
The shilling is a historical coin, and the name of a unit of modern currencies formerly used in the United Kingdom, Australia, New Zealand, other British Commonwealth countries and Ireland, where they were generally equivalent to 12 pence or one-twentieth of a pound before being phased out during the 20th century. Currently the shilling is used as a currency in five east African countries: Kenya, Tanzania, Uganda, Somalia, as well as the ''de facto'' country of Somaliland. The East African Community additionally plans to introduce an East African shilling. History The word ''shilling'' comes from Old English "Scilling", a monetary term meaning twentieth of a pound, from the Proto-Germanic root skiljaną meaning 'to separate, split, divide', from (s)kelH- meaning 'to cut, split.' The word "Scilling" is mentioned in the earliest recorded Germanic law codes, those of Æthelberht of Kent. There is evidence that it may alternatively be an early borrowing of Phoenician ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indiaman
East Indiaman was a general name for any sailing ship operating under charter or licence to any of the East India Company (other), East India trading companies of the major European trading powers of the 17th through the 19th centuries. The term is used to refer to vessels belonging to the Austrian East India Company, Austrian, Danish East India Company, Danish, Dutch East India Company, Dutch, English East India Company, English, French East India Company, French, Portuguese East India Company, Portuguese, or Swedish East India Company, Swedish companies. Some of the East Indiamen chartered by the British East India Company were known as Clipper, "tea clippers". In Britain, the East India Company held a monopoly granted to it by Queen Elizabeth I of England in 1600 for all English trade between the Cape of Good Hope and Cape Horn. This grant was progressively restricted during the late 18th and early 19th centuries, until the monopoly was lost in 1834. English (later ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andrew Mitchell (Royal Navy Officer)
Admiral Sir Andrew Mitchell, KB (1757 – 26 February 1806) was an admiral of the blue in the Royal Navy. He married Mary Uniacke (daughter of Richard John Uniacke) in Halifax, Nova Scotia on 3 May 1805. Career Mitchell entered service in 1771 as a midshipman on HMS ''Deal Castle''. He was promoted to lieutenant in 1776, while serving in the West Indies and again promoted to post-captain, skipping the rank of commander, after distinguishing himself in action in 1778. He distinguished himself again while serving with the 1782 expedition of Sir Edward Hughes in India. On 12 August 1782, Mitchell was captain of the frigate , when she encountered the French frigate ''Bellone'' off Friars Hood, Ceylon. After two-and-a-half hours, ''Bellone'' sailed away. ''Coventry'' had suffered 15 men killed and 29 wounded in the engagement. When Hughes returned to England, he left Mitchell in charge of the East Indies Station as commodore. Mitchell returned to England in 1786. In February, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anglo-Russian Invasion Of Holland
The Anglo-Russian invasion of Holland (or Anglo-Russian expedition to Holland, or Helder Expedition) was a military campaign from 27 August to 19 November 1799 during the War of the Second Coalition, in which an expeditionary force of British and Russian troops invaded the North Holland peninsula in the Batavian Republic. The campaign had two strategic objectives: to neutralize the Batavian fleet and to promote an uprising by followers of the former stadtholder William V against the Batavian government. The invasion was opposed by a slightly smaller joint Franco-Batavian army. Tactically, the Anglo-Russian forces were successful initially, defeating the defenders in the battles of Callantsoog and the Krabbendam, but subsequent battles went against the Anglo-Russian forces. Following a defeat at Castricum, the Duke of York, the British supreme commander, decided upon a strategic retreat to the original bridgehead in the extreme north of the peninsula. Subsequently, an agreement wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ship Of The Line
A ship of the line was a type of naval warship constructed during the Age of Sail from the 17th century to the mid-19th century. The ship of the line was designed for the naval tactic known as the line of battle, which depended on the two columns of opposing warships maneuvering to volley fire with the cannons along their broadsides. In conflicts where opposing ships were both able to fire from their broadsides, the opponent with more cannons firingand therefore more firepowertypically had an advantage. Since these engagements were almost invariably won by the heaviest ships carrying more of the most powerful guns, the natural progression was to build sailing vessels that were the largest and most powerful of their time. From the end of the 1840s, the introduction of steam power brought less dependence on the wind in battle and led to the construction of screw-driven wooden-hulled ships of the line; a number of purely sail-powered ships were converted to this propulsion mech ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dutch Ship Alkmaar
Dutch commonly refers to: * Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands * Dutch people () * Dutch language () Dutch may also refer to: Places * Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States * Pennsylvania Dutch Country People Ethnic groups * Germanic peoples, the original meaning of the term ''Dutch'' in English ** Pennsylvania Dutch, a group of early Germanic immigrants to Pennsylvania *Dutch people, the Germanic group native to the Netherlands Specific people * Dutch (nickname), a list of people * Johnny Dutch (born 1989), American hurdler * Dutch Schultz (1902–1935), American mobster born Arthur Simon Flegenheimer * Dutch Mantel, ring name of American retired professional wrestler Wayne Maurice Keown (born 1949) * Dutch Savage, ring name of professional wrestler and promoter Frank Stewart (1935–2013) Arts, entertainment, and media Fictional characters * Dutch (Black Lagoon), Dutch (''Black Lagoon''), an African-American character from the Japanese mang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dutch Ship Delft
Several ships of the Dutch Navy have borne the name ''Delft'': *''Delft'' (1658), a 36-gun ship, captured in 1665 during the Battle of Lowestoft and taken into service as HMS ''Delft''. She was sold in 1668. *''Delft'' (1664), a 36-gun ship, removed from Navy lists in 1667. *''Delft'' (1666), a 66-gun ship, removed from Navy lists in 1689. *''Delft'' (1691), a 60-gun ship, removed from Navy lists in 1697. *''Delft'' (1699), a 54-gun ship, removed from Navy lists in 1712. *''Delft'' (1731), a 56-gun ship, removed from Navy lists in 1778. *, a 54-gun ship, captured in 1797 during the Battle of Camperdown The Battle of Camperdown (known in Dutch as the ''Zeeslag bij Kamperduin'') was a major naval action fought on 11 October 1797, between the British North Sea Fleet under Admiral Adam Duncan and a Batavian Navy (Dutch) fleet under Vice-Admiral ..., she later sank due to damage received. {{DEFAULTSORT:Delft, Dutch Ship Naval ship names of the Netherlands ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adam Duncan, 1st Viscount Duncan
Admiral Adam Duncan, 1st Viscount Duncan, KB (1 July 17314 August 1804) was a British admiral who defeated the Dutch fleet off Camperdown on 11 October 1797. This victory is considered one of the most significant actions in naval history. Life Adam was the second son of Alexander Duncan, Baron of Lundie, Angus, (d. May 1777) Provost of Dundee, and his wife (and first cousin once removed) Helen, daughter of John Haldane of Gleneagles. He was born at Dundee. In 1746, after receiving his education in Dundee, he entered the Royal Navy on board the sloop ''Trial'', under Captain Robert Haldane, with whom, in and afterwards in , he continued until the peace in 1748. In 1749 he was appointed to , then commissioned for service in the Mediterranean, by the Hon. Augustus Keppel (afterwards Viscount Keppel), with whom he was afterwards in on the coast of North America, and was confirmed in the rank of lieutenant on 10 January 1755. Seven Years War In August 1755 he followed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
%2C_Monmouth_(1797).jpg)


.jpg)




