|
HMS Irresistible (1782)
HMS ''Irresistible'' was a 74-gun third rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, launched on 6 December 1782 at Harwich. Career ''Irresistible'' captured the French privateer ''Quatre frères'' in April 1797 in the Mediterranean. The Royal Navy took her into service as HMS ''Transfer''. ''Irresistible'' fought at the Battle of Groix in 1795, and at the Battle of Cape St Vincent in 1797 and captured two Spanish frigates at the action of 26 April 1797 The action of 26 April 1797 was a minor naval engagement during the French Revolutionary Wars in which a Spanish convoy of two frigates was trapped and defeated off the Spanish town of Conil de la Frontera by British ships of the Cadiz blocka .... Fate ''Irresistible'' was broken up in 1806. Citations and notes References *Lavery, Brian (2003) ''The Ship of the Line - Volume 1: The development of the battlefleet 1650-1850.'' Conway Maritime Press. . Ships of the line of the Royal Navy Albion-class ships of the l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Great Britain
The Kingdom of Great Britain (officially Great Britain) was a Sovereign state, sovereign country in Western Europe from 1 May 1707 to the end of 31 December 1800. The state was created by the 1706 Treaty of Union and ratified by the Acts of Union 1707, which united the kingdoms of Kingdom of England, England (which included Wales) and Kingdom of Scotland, Scotland to form a single kingdom encompassing the whole island of Great Britain and its outlying islands, with the exception of the Isle of Man and the Channel Islands. The unitary state was governed by a single Parliament of Great Britain, parliament at the Palace of Westminster, but distinct legal systems – English law and Scots law – remained in use. The formerly separate kingdoms had been in personal union since the 1603 "Union of the Crowns" when James VI of Scotland became King of England and King of Ireland. Since James's reign, who had been the first to refer to himself as "king of Great Britain", a political un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Third Rate
In the rating system of the Royal Navy, a third rate was a ship of the line which from the 1720s mounted between 64 and 80 guns, typically built with two gun decks (thus the related term two-decker). Years of experience proved that the third rate ships embodied the best compromise between sailing ability (speed, handling), firepower, and cost. So, while first-rates and second-rates were both larger and more powerful, third-rate ships were the optimal configuration. Rating When the rating system was first established in the 1620s, the third rate was defined as those ships having at least 200 but not more than 300 men; previous to this, the type had been classified as "middling ships". By the 1660s, the means of classification had shifted from the number of men to the number of carriage-mounted guns, and third rates at that time mounted between 48 and 60 guns. By the turn of the century, the criterion boundaries had increased and third rate carried more than 60 guns, with seco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ships Of The Line Of The Royal Navy
A ship is a large watercraft that travels the world's oceans and other sufficiently deep waterways, carrying cargo or passengers, or in support of specialized missions, such as defense, research, and fishing. Ships are generally distinguished from boats, based on size, shape, load capacity, and purpose. Ships have supported exploration, trade, warfare, migration, colonization, and science. After the 15th century, new crops that had come from and to the Americas via the European seafarers significantly contributed to world population growth. Ship transport is responsible for the largest portion of world commerce. The word ''ship'' has meant, depending on the era and the context, either just a large vessel or specifically a ship-rigged sailing ship with three or more masts, each of which is square-rigged. As of 2016, there were more than 49,000 merchant ships, totaling almost 1.8 billion dead weight tons. Of these 28% were oil tankers, 43% were bulk carriers, and 13% were con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Action Of 26 April 1797
The action of 26 April 1797 was a minor naval engagement during the French Revolutionary Wars in which a Spanish convoy of two frigates was trapped and defeated off the Spanish town of Conil de la Frontera by British ships of the Cadiz blockade. The British vessels, the ship of the line HMS ''Irresistible'' and the Fifth-rate frigate HMS ''Emerald'', were significantly more powerful than the Spanish frigates, which were on the last stage of a voyage carrying treasure from Havana, Cuba, to the Spanish fleet base of Cadiz. The British commander, Captain George Martin, succeeded in chasing the Spanish vessels into the rocky Conil Bay, where they surrendered after a brief engagement in which the Spanish suffered significantly higher casualties than the British. One of the Spanish ships, the ''Santa Elena'', was subsequently wrecked on the shore, while the other, the ''Ninfa'', was captured and later recommissioned into the Royal Navy. The treasure carried on board the frigate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cape St Vincent, 1797 RCIN 735050
A cape is a clothing accessory or a sleeveless outer garment which drapes the wearer's back, arms, and chest, and connects at the neck. History Capes were common in medieval Europe, especially when combined with a Hood (headgear), hood in the Chaperon (headgear), chaperon. They have had periodic returns to fashion - for example, in nineteenth-century Europe. Roman Catholic clergy wear a type of cape known as a ferraiolo, which is worn for formal events outside a ritualistic context. The cope is a liturgical vestment in the form of a cape. Capes are often highly decorated with elaborate embroidery. Capes remain in regular use as rainwear in various military units and police forces, in France for example. A gas cape was a voluminous military garment designed to give rain protection to someone wearing the bulky gas masks used in twentieth-century wars. Rich noblemen and elite warriors of the Aztec Empire would wear a tilmàtli; a Mesoamerican cloak/cape used as a symbol of thei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quatre Frères (1796 Ship)
''Quatre frères'' was either an American or Bermudian-built vessel. She was commissioned in 1796 at Bordeaux as a French privateer. The Royal Navy captured her in April 1797 and took her into service as HMS ''Transfer''. The Royal Navy sold her at Malta in 1802 to Ottoman Tripolitania. The U.S. Navy captured her in 1804 and took her into service as USS ''Scourge''. The U.S. Navy sold her in 1812. ''Quatre frères'' ''Quatre frères'' was commissioned in 1796 in Bordeaux under Martial Dupeyrat. Under his command she captured two prizes: ''Résolution'' and ''Frascara'', that she sent into Rochfort. ''Résolution'', of Lisbon and of 500 tons (French, "of load"), Dos Santos (or Roze de Sautort), master, was a Portuguese vessel carrying wheat and almonds from the Barbary Coast. ''Frascara'' was a Danish vessel carrying oranges and lemons.''Bulletin de la Société des sciences & arts de Bayonne'' (1998), p.39. The 74-gun captured ''Quatre frères'' in March 1797 in the Mediterran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harwich Dockyard
Harwich Dockyard (also known as The King's Yard, Harwich) was a Royal Navy Dockyard at Harwich in Essex, active in the 17th and early 18th century (after which it continued to operate under private ownership). Owing to its position on the East Coast of England, the yard was of strategic importance during the Anglo-Dutch Wars; however, due to a lack of deep-water access and the difficulty of setting off from Harwich against an easterly wind, its usefulness was somewhat limited and its facilities remained small-scale compared to the other Royal Dockyards over the same period. Nonetheless, it remained actively involved in repairing and refitting the nation's warships, as well as building them: of the eighty ships built for the Royal Navy in Britain between 1660 and 1688, fourteen were built at Harwich Dockyard. (Naval vessels had occasionally been built at Harwich in earlier times, but by private shipbuilders on or around the Town Quay). After the Royal Navy withdrew from the yard ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against France. The modern Royal Navy traces its origins to the early 16th century; the oldest of the UK's armed services, it is consequently known as the Senior Service. From the middle decades of the 17th century, and through the 18th century, the Royal Navy vied with the Dutch Navy and later with the French Navy for maritime supremacy. From the mid 18th century, it was the world's most powerful navy until the Second World War. The Royal Navy played a key part in establishing and defending the British Empire, and four Imperial fortress colonies and a string of imperial bases and coaling stations secured the Royal Navy's ability to assert naval superiority globally. Owing to this historical prominence, it is common, even among non-Britons, to ref ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forecastle
The forecastle ( ; contracted as fo'c'sle or fo'c's'le) is the upper deck of a sailing ship forward of the foremast, or, historically, the forward part of a ship with the sailors' living quarters. Related to the latter meaning is the phrase " before the mast" which denotes anything related to ordinary sailors, as opposed to a ship's officers. History and design In medieval shipbuilding, a ship of war was usually equipped with a tall, multi-deck castle-like structure in the bow of the ship. It served as a platform for archers to shoot down on enemy ships, or as a defensive stronghold if the ship were boarded. A similar but usually much larger structure, called the aftcastle, was at the aft end of the ship, often stretching all the way from the main mast to the stern. Having such tall upper works on the ship was detrimental to sailing performance. As cannons were introduced and gunfire replaced boarding as the primary means of naval combat during the 16th century, the medieval ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naval Ensign Of The United Kingdom
The White Ensign, at one time called the St George's Ensign due to the simultaneous existence of a cross-less version of the flag, is an ensign worn on British Royal Navy ships and shore establishments. It consists of a red St George's Cross on a white field, identical to the flag of England except with the Union Flag in the upper canton. The White Ensign is also worn by yachts of members of the Royal Yacht Squadron and by ships of Trinity House escorting the reigning monarch. In addition to the United Kingdom, several other nations have variants of the White Ensign with their own national flags in the canton, with the St George's Cross sometimes being replaced by a naval badge omitting the cross altogether. Yachts of the Royal Irish Yacht Club wear a white ensign with an Irish tricolour in the first quadrant and defaced by the crowned harp from the Heraldic Badge of Ireland. The Flag of the British Antarctic Territory and the Commissioners' flag of the Northern Lighthouse Bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
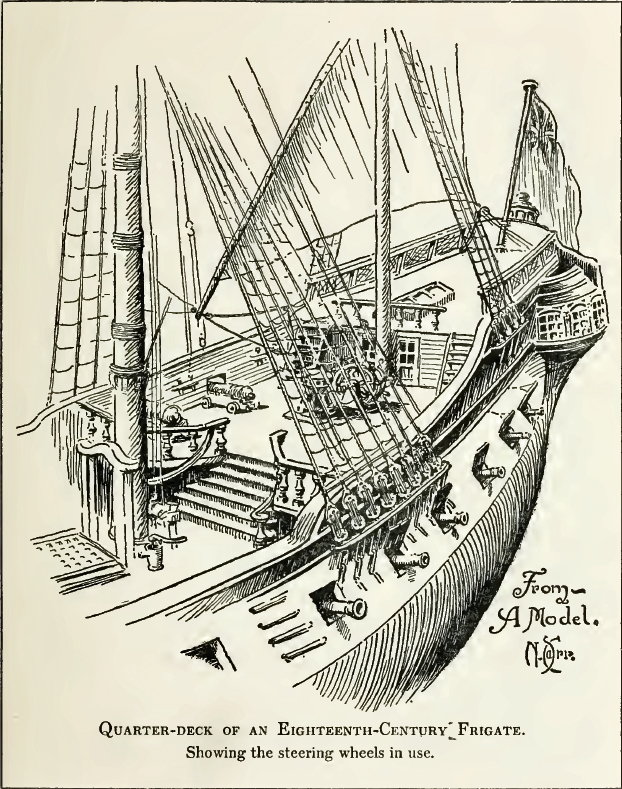
Quarterdeck
The quarterdeck is a raised deck behind the main mast of a sailing ship. Traditionally it was where the captain commanded his vessel and where the ship's colours were kept. This led to its use as the main ceremonial and reception area on board, and the word is still used to refer to such an area on a ship or even in naval establishments on land. Many such facilities have areas decorated like shipboard quarterdecks. In the 20th century the word came to be applied to the area at the stern of the ship, often (on naval vessels) used for secondary weapons and (on battleships) seaplane catapults. In modern military designs the stern has been roofed over by the helicopter deck but a large space remains underneath which is typically used for sonar equipment or small boats and which is still referred to as the quarterdeck in Commonwealth navies. Ceremonial use There are ancient traditions of offering special deference to the quarterdeck. Greek, Roman, and Carthaginian warships all c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |