|
HMS Ganges
Two ships and a shore establishment of the Royal Navy have been named HMS ''Ganges'' after the river Ganges in India. * was a 74-gun third-rate ship of the line launched in 1782 and broken up in 1816. * was an 84-gun second rate launched in 1821 and finally broken up in 1930. She was the last sailing ship of the Navy to serve as a flagship. * was a training establishment, originally aboard the second HMS ''Ganges''. She was in service between 1865 and 1976. During this period a number of other ships were renamed HMS ''Ganges'' whilst serving as the establishment: ** was ''Ganges'' between 1906 and 1908, and again between 1913 and 1919. She was also ''Ganges II'' between 1908 and 1912, and again between 1920 and 1922. ** was ''Ganges'' between 1908 and 1913. ** was ''Ganges II'' between 1906 and 1908. ** RNTE Shotley, a shore based training establishment set up in 1905 was ''Ganges II'' from 1913 to 1919, and ''Ganges'' from 1927 to 1976. See also * Ganges (disambiguat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shore Establishment
A stone frigate is a naval establishment on land. "Stone frigate" is an informal term that has its origin in Britain's Royal Navy after its use of Diamond Rock, an island off Martinique, as a 'sloop of war' to harass the First French Empire, French in 1803–04. The Royal Navy was prohibited from ruling over land, so the land was commissioned as a ship. The command of this first stone frigate was given to Sir Samuel Hood, 1st Baronet, Commodore Hood's first lieutenant, James Wilkes Maurice, who, with cannon taken off the Commodore's ship, manned it with a crew of 120 until its capture by the French in the Battle of Diamond Rock in 1805. Until the late 19th century, the Royal Navy housed training and other support facilities in Hulk (ship type), hulks—old wooden ships of the line—moored in ports as receiving ships, depot ships, or floating barracks. The British Admiralty, Admiralty regarded shore accommodation as expensive and liable to lead to indiscipline. These floating ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against France. The modern Royal Navy traces its origins to the early 16th century; the oldest of the UK's armed services, it is consequently known as the Senior Service. From the middle decades of the 17th century, and through the 18th century, the Royal Navy vied with the Dutch Navy and later with the French Navy for maritime supremacy. From the mid 18th century, it was the world's most powerful navy until the Second World War. The Royal Navy played a key part in establishing and defending the British Empire, and four Imperial fortress colonies and a string of imperial bases and coaling stations secured the Royal Navy's ability to assert naval superiority globally. Owing to this historical prominence, it is common, even among non-Britons, to ref ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ganges
The Ganges ( ) (in India: Ganga ( ); in Bangladesh: Padma ( )). "The Ganges Basin, known in India as the Ganga and in Bangladesh as the Padma, is an international river to which India, Bangladesh, Nepal and China are the riparian states." is a trans-boundary river of Asia which flows through India and Bangladesh. The river rises in the western Himalayas in the Indian state of Uttarakhand. It flows south and east through the Gangetic plain of North India, receiving the right-bank tributary, the Yamuna, which also rises in the western Indian Himalayas, and several left-bank tributaries from Nepal that account for the bulk of its flow. In West Bengal state, India, a feeder canal taking off from its right bank diverts 50% of its flow southwards, artificially connecting it to the Hooghly river. The Ganges continues into Bangladesh, its name changing to the Padma. It is then joined by the Jamuna, the lower stream of the Brahmaputra, and eventually the Meghna, forming the major ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the south, the Arabian Sea on the southwest, and the Bay of Bengal on the southeast, it shares land borders with Pakistan to the west; China, Nepal, and Bhutan to the north; and Bangladesh and Myanmar to the east. In the Indian Ocean, India is in the vicinity of Sri Lanka and the Maldives; its Andaman and Nicobar Islands share a maritime border with Thailand, Myanmar, and Indonesia. Modern humans arrived on the Indian subcontinent from Africa no later than 55,000 years ago., "Y-Chromosome and Mt-DNA data support the colonization of South Asia by modern humans originating in Africa. ... Coalescence dates for most non-European populations average to between 73–55 ka.", "Modern human beings—''Homo sapiens''—originated in Africa. Then, int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Third-rate
In the rating system of the Royal Navy, a third rate was a ship of the line which from the 1720s mounted between 64 and 80 guns, typically built with two gun decks (thus the related term two-decker). Years of experience proved that the third rate ships embodied the best compromise between sailing ability (speed, handling), firepower, and cost. So, while first-rates and second-rates were both larger and more powerful, third-rate ships were the optimal configuration. Rating When the rating system was first established in the 1620s, the third rate was defined as those ships having at least 200 but not more than 300 men; previous to this, the type had been classified as "middling ships". By the 1660s, the means of classification had shifted from the number of men to the number of carriage-mounted guns, and third rates at that time mounted between 48 and 60 guns. By the turn of the century, the criterion boundaries had increased and third rate carried more than 60 guns, with seco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ship Of The Line
A ship of the line was a type of naval warship constructed during the Age of Sail from the 17th century to the mid-19th century. The ship of the line was designed for the naval tactic known as the line of battle, which depended on the two columns of opposing warships maneuvering to volley fire with the cannons along their broadsides. In conflicts where opposing ships were both able to fire from their broadsides, the opponent with more cannons firingand therefore more firepowertypically had an advantage. Since these engagements were almost invariably won by the heaviest ships carrying more of the most powerful guns, the natural progression was to build sailing vessels that were the largest and most powerful of their time. From the end of the 1840s, the introduction of steam power brought less dependence on the wind in battle and led to the construction of screw-driven wooden-hulled ships of the line; a number of purely sail-powered ships were converted to this propulsion mech ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
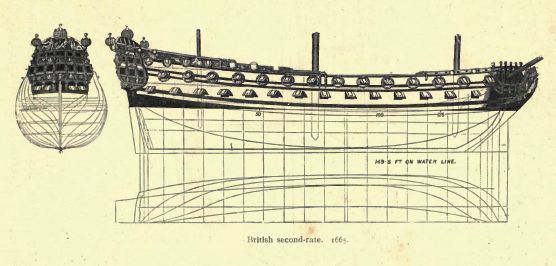
Second Rate
In the rating system of the Royal Navy used to categorise sailing warships, a second-rate was a ship of the line which by the start of the 18th century mounted 90 to 98 guns on three gun decks; earlier 17th-century second rates had fewer guns and were originally two-deckers or had only partially armed third gun decks. A "second rate" was the second largest class of warships in a hierarchical system of six "ratings" based on size and firepower. They were essentially smaller and hence cheaper versions of the three-decker first rates. Like the first rates, they fought in the line of battle, but unlike the first rates, which were considered too valuable to risk in distant stations, the second rates often served also in major overseas stations as flagships. They had a reputation for poor handling and slow sailing. They were popular as flagships of admirals commanding the Windward and/or Leeward Islands station, which was usually a Rear-admiral of the red. Rating Typically measuri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flagship
A flagship is a vessel used by the commanding officer of a group of naval ships, characteristically a flag officer entitled by custom to fly a distinguishing flag. Used more loosely, it is the lead ship in a fleet of vessels, typically the first, largest, fastest, most heavily armed, or best known. Over the years, the term "flagship" has become a metaphor used in industries such as broadcasting, automobiles, education, technology, airlines, and retail to refer to their highest profile or most expensive products and locations. Naval use In common naval use, the term ''flagship'' is fundamentally a temporary designation; the flagship is wherever the admiral's flag is being flown. However, admirals have always needed additional facilities, including a meeting room large enough to hold all the captains of the fleet and a place for the admiral's staff to make plans and draw up orders. Historically, only larger ships could accommodate such requirements. The term was also used by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RNTE Shotley
Royal Naval Training Establishment Shotley, known in the Royal Navy as , was a naval training establishment at Shotley, near Ipswich in Suffolk. Starting in 1905, it trained boys for naval service until 1973 (The school-leaving age was raised to 16 so ended the recruitment of 15-year-old boy sailors). In September 1973, HMS Ganges admitted adult entrants to the Royal Navy who only underwent 6 weeks training (6-week wonders) (the same as at HMS Raleigh near Plymouth) It finally closed in 1976. It had a mixed reputation in the Royal Navy, both for its reputed harsh methods of training boys in order to turn out professionally able, self-reliant ratings and for the professionalism of its former trainees. It is particularly famous for its 143-foot (44 m)-high mast which all boys under training were required to ascend, at least to the half-moon and for the mast manning ceremonies held whenever a dignitary visited the establishment. During the later 1980s and until 1999 RNTE Shotley ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ganges (other)
Ganges is a river in India. Ganges may also refer to: Places * Ganges, Hérault, a commune in the Hérault département in France * Ganges, British Columbia, a town on Saltspring Island in the province of British Columbia in Canada * Ganges, Ohio, a community in the United States * Ganges Township, Michigan, in the United States * Ganges Bank, a wholly submerged atoll structure in Indian Ocean southwest of the Chagos Archipelago * Ganges Chasma, a deep canyon at the eastern end of the vast Valles Marineris system on Mars * River Ganges is another name for Ping Yuen River The Ping Yuen River (also known as River Ganges) (; Hong Kong Chinese: ''Ap5li4 Ziu1''; Hong Kong Chinese: ''Pin2ngien2 Ho2'') is a river in the northern New Territories, Hong Kong. Its source lies near Cheung Shan in Ping Che. It flows along Ping ... in Hong Kong Ships Nourse Line ships * , the first Nourse Line ship (1861–1881) to bear the name * , the second Nourse Line ship (1882–1917) to bear the na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia), and later with East Asia. The company seized control of large parts of the Indian subcontinent, colonised parts of Southeast Asia and Hong Kong. At its peak, the company was the largest corporation in the world. The EIC had its own armed forces in the form of the company's three Presidency armies, totalling about 260,000 soldiers, twice the size of the British army at the time. The operations of the company had a profound effect on the global balance of trade, almost single-handedly reversing the trend of eastward drain of Western bullion, seen since Roman times. Originally chartered as the "Governor and Company of Merchants of London Trading into the East-Indies", the company rose to account for half of the world's trade duri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_-_geograph.org.uk_-_839260.jpg)
