|
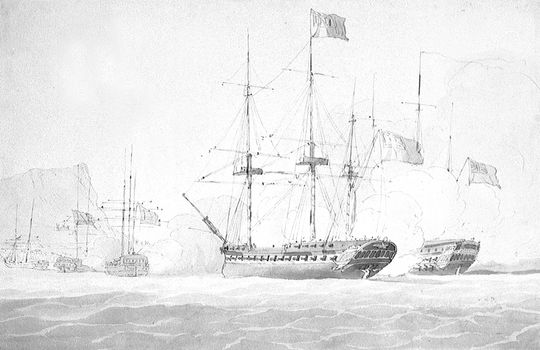
HMS Electra
Five ships of the Royal Navy have borne the name HMS ''Electra'', after the Greek mythological figure, Electra: * was a 16-gun brig-sloop launched in 1806 and wrecked in 1808. * was a 16-gun brig-sloop, previously the French ''Espiegle''. She was captured in 1808 by French frigate Sibylle (1792), HMS ''Sybille'' and was sold in 1816. * was an 18-gun sloop-of-war, sloop launched in 1837 and sold in 1862. * was a launched in 1896 and reclassified as a C-class destroyer (1913), C-class destroyer in 1913. She was sold for scrapping in 1920. * was an E and F-class destroyer, E-class destroyer launched in 1934 and sunk in 1942. {{DEFAULTSORT:Electra, Hms Royal Navy ship names ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against France. The modern Royal Navy traces its origins to the early 16th century; the oldest of the UK's armed services, it is consequently known as the Senior Service. From the middle decades of the 17th century, and through the 18th century, the Royal Navy vied with the Dutch Navy and later with the French Navy for maritime supremacy. From the mid 18th century, it was the world's most powerful navy until the Second World War. The Royal Navy played a key part in establishing and defending the British Empire, and four Imperial fortress colonies and a string of imperial bases and coaling stations secured the Royal Navy's ability to assert naval superiority globally. Owing to this historical prominence, it is common, even among non-Britons, to ref ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electra
Electra (; grc, Ήλέκτρα) is one of the most popular mythological characters in tragedies.Evans (1970), p. 79 She is the main character in two Greek tragedies, '' Electra'' by Sophocles and '' Electra'' by Euripides. She is also the central figure in plays by Aeschylus, Alfieri, Voltaire, Hofmannsthal, and Eugene O'Neill. She is a vengeful soul in '' The Libation Bearers'', the second play of Aeschylus' ''Oresteia'' trilogy. She plans out an attack with her brother to kill their mother, Clytemnestra. In psychology, the Electra complex is named after her. Family Electra's parents were King Agamemnon and Queen Clytemnestra. Her sisters were Iphigeneia and Chrysothemis, and her brother was Orestes. In the ''Iliad'', Homer is understood to be referring to Electra in mentioning "Laodice" as a daughter of Agamemnon. Murder of Agamemnon Electra was absent from Mycenae when her father, King Agamemnon, returned from the Trojan War. When he came back, he brought with him his w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brig-sloop
In the 18th century and most of the 19th, a sloop-of-war in the Royal Navy was a warship with a single gun deck that carried up to eighteen guns. The rating system covered all vessels with 20 guns and above; thus, the term ''sloop-of-war'' encompassed all the unrated combat vessels, including the very small gun-brigs and cutters. In technical terms, even the more specialised bomb vessels and fireships were classed as sloops-of-war, and in practice these were employed in the sloop role when not carrying out their specialised functions. In World War I and World War II, the Royal Navy reused the term "sloop" for specialised convoy-defence vessels, including the of World War I and the highly successful of World War II, with anti-aircraft and anti-submarine capability. They performed similar duties to the American destroyer escort class ships, and also performed similar duties to the smaller corvettes of the Royal Navy. Rigging A sloop-of-war was quite different from a civilian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Frigate Sibylle (1792)
''Sibylle'' was a 38-gun of the French Navy. She was launched in 1791 at the dockyards in Toulon and placed in service in 1792. After the 50-gun Fourth-rate, fourth rate captured her in 1794, the British took her into service as HMS ''Sybille''. She served in the Royal Navy until disposed of in 1833. While in British service ''Sybille'' participated in three notable single ship actions, in each case capturing a French vessel. On anti-slavery duties off West Africa from July 1827 to June 1830, ''Sybille'' captured numerous slavers and freed some 3,500 slaves. She was finally sold in 1833 in Portsmouth. French service From 23 April 1790 to October–December 1792, ''Sibylle'' escorted a convoy and transferred funds from Toulon to Smyrna, first under Capitaine de vaisseau (CV) Grasse-Briançon and then CV de Venel. From March 1793 to January 1794, under CV Rondeau, she escorted convoys between Toulon and Marseilles and then she moved to the Levant station. She cruised the Aegea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sloop-of-war
In the 18th century and most of the 19th, a sloop-of-war in the Royal Navy was a warship with a single gun deck that carried up to eighteen guns. The rating system covered all vessels with 20 guns and above; thus, the term ''sloop-of-war'' encompassed all the unrated combat vessels, including the very small gun-brigs and cutters. In technical terms, even the more specialised bomb vessels and fireships were classed as sloops-of-war, and in practice these were employed in the sloop role when not carrying out their specialised functions. In World War I and World War II, the Royal Navy reused the term "sloop" for specialised convoy-defence vessels, including the of World War I and the highly successful of World War II, with anti-aircraft and anti-submarine capability. They performed similar duties to the American destroyer escort class ships, and also performed similar duties to the smaller corvettes of the Royal Navy. Rigging A sloop-of-war was quite different from a civilian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C-class Destroyer (1913)
The C class as designated in 1913 was a heterogeneous group of torpedo boat destroyers (TBDs) built for the Royal Navy in the late-1890s. They were constructed to the individual designs of their builders to meet Admiralty specifications. The uniting feature of the class was a top speed of 30 knots, a "turtleback" forecastle and that they all had three funnels. The funnels were spaced equidistantly and were of equal height, but the central one was thicker. In 1913 all "30 knotter" vessels with 3 funnels were classified by the Admiralty as the "C" class to provide some system to the naming of HM destroyers (at the same time, the 4-funnelled, "30 knotters" became the "B" class and the 2-funnelled ships the "D" class). All vessels had the distinctive turtleback that was intended to clear water from the bows but actually tended to dig the bow in to anything of a sea, resulting in a very wet conning position and poor seaboats that were unable to reach top speed in anything but perf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
E And F-class Destroyer
The E and F-class destroyers were a group of 18 destroyers built for the Royal Navy during the 1930s. The ships were initially assigned to the Home Fleet, although they reinforced the Mediterranean Fleet during the Italian invasion of Abyssinia of 1935–36 and enforced the Non-Intervention Agreement during the Spanish Civil War of 1936–1939. After the beginning of the Second World War in August 1939, the E-class ships were mostly assigned to escort duties under the Western Approaches Command, while the Fs were assigned to escort the ships of the Home Fleet. Between them they sank four German submarines through March 1940 while losing only one ship to a submarine. Most of the sisters were committed to the Norwegian Campaign in April–June where they helped to sink one German destroyer and a submarine. The two E-class minelayer-destroyers helped to evacuate Allied troops from Dunkirk in May–June. Most of the Fs were sent to Gibraltar around the end of June and formed pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |