|
HMS Circe (1785)
HMS ''Circe'' was a 28-gun sixth-rate frigate of the Royal Navy. She was launched in 1785 but not completed or commissioned until 1790. She then served in the English Channel on the blockade of French ports before she was wrecked in 1803. Career ''Circe'' was first commissioned in September 1790 under the command of Captain George Oakes. She was paid off in October 1791. Captain A. H. Gardiner commissioned her in April 1792. French Revolutionary Wars Joseph Sydney Yorke was promoted to post-captain on 4 February 1793 and given command of ''Circe'', then part of a squadron under Admiral Richard Howe. He patrolled off the French port of Brest. In March ''Circe'' took the French ships ''Diane'', ''Vaudreuil'' and ''Jeune Felix''. ''Circe'' shared the prize money for ''Diane'' and ''Vaudreuil'' with . On 18 March ''Circe'' captured the Danish brig ''Pelican''. Then in May ''Circe'' took the French privateers ''Didon'' (or ''Dido'') and ''Auguste'' (or ''1 Auguste''). ''Didon'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naval Ensign Of Great Britain (1707-1800)
A navy, naval force, or maritime force is the branch of a nation's armed forces principally designated for naval warfare, naval and amphibious warfare; namely, lake-borne, riverine, littoral zone, littoral, or ocean-borne combat operations and related functions. It includes anything conducted by surface Naval ship, ships, amphibious warfare, amphibious ships, submarines, and seaborne naval aviation, aviation, as well as ancillary support, communications, training, and other fields. The strategic offensive role of a navy is Power projection, projection of force into areas beyond a country's shores (for example, to protect Sea lane, sea-lanes, deter or confront piracy, ferry troops, or attack other navies, ports, or shore installations). The strategic defensive purpose of a navy is to frustrate seaborne projection-of-force by enemies. The strategic task of the navy also may incorporate nuclear deterrence by use of submarine-launched ballistic missiles. Naval operations can be broa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brest, France
Brest (; ) is a port city in the Finistère department, Brittany. Located in a sheltered bay not far from the western tip of the peninsula, and the western extremity of metropolitan France, Brest is an important harbour and the second French military port after Toulon. The city is located on the western edge of continental France. With 142,722 inhabitants in a 2007 census, Brest forms Western Brittany's largest metropolitan area (with a population of 300,300 in total), ranking third behind only Nantes and Rennes in the whole of historic Brittany, and the 19th most populous city in France; moreover, Brest provides services to the one million inhabitants of Western Brittany. Although Brest is by far the largest city in Finistère, the ''préfecture'' (regional capital) of the department is the much smaller Quimper. During the Middle Ages, the history of Brest was the history of its castle. Then Richelieu made it a military harbour in 1631. Brest grew around its arsenal unti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Winthrop (1764 - 1832)
Robert Winthrop (7 DecemberThis date is from Winthrop, p. 13; Ward gives 7 September as birth date. 1764, New London, Connecticut – 10 May 1832, Dover) was a scion of the New England Winthrop family of high colonial civil servants, and a Vice-Admiral of the Blue in the Royal Navy. Among his many feats of arms was taking possession of admiral Samuel Story's squadron of the Batavian Navy after its surrender in the Vlieter Incident.Even in reputable contemporary and historical sources his name is often misspelled Winthorp, but after cross-checking with his postings there should be no doubt Personal life Winthrop was the youngest son of John S. Winthrop of New London, Conn. and Elizabeth Sheriffe Hay. He was a lineal descendant of governors John Winthrop of Massachusetts and John Winthrop the Younger of Connecticut, Chief Justice Wait Winthrop of Massachusetts, and John Winthrop (1681–1747) FRS, his grandfather. His family evidently had Loyalist sympathies as he was ent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
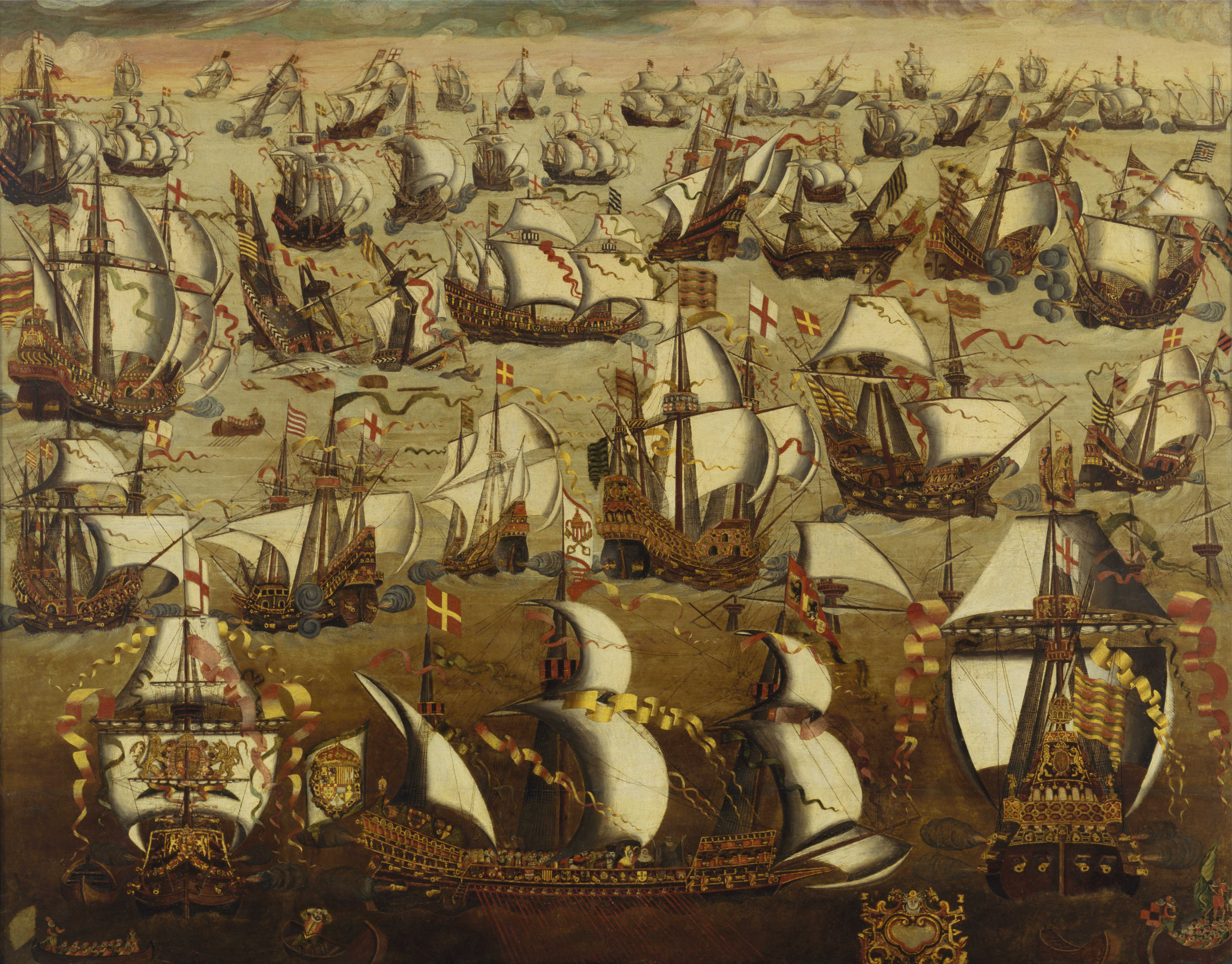
Battle Of Camperdown
The Battle of Camperdown (known in Dutch as the ''Zeeslag bij Kamperduin'') was a major naval action fought on 11 October 1797, between the British North Sea Fleet under Admiral Adam Duncan and a Batavian Navy (Dutch) fleet under Vice-Admiral Jan de Winter. The battle was the most significant action between British and Dutch forces during the French Revolutionary Wars and resulted in a complete victory for the British, who captured eleven Dutch ships without losing any of their own. In 1795, the Dutch Republic had been overrun by the army of the French Republic and had been reorganised into the Batavian Republic, a French client state. In early 1797, after the French Atlantic Fleet had suffered heavy losses in a disastrous winter campaign, the Dutch fleet was ordered to reinforce the French at Brest. The rendezvous never occurred; the continental allies failed to capitalise on the Spithead and Nore mutinies that paralysed the British Channel forces and North Sea fleets during th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adam Duncan, 1st Viscount Duncan
Admiral Adam Duncan, 1st Viscount Duncan, KB (1 July 17314 August 1804) was a British admiral who defeated the Dutch fleet off Camperdown on 11 October 1797. This victory is considered one of the most significant actions in naval history. Life Adam was the second son of Alexander Duncan, Baron of Lundie, Angus, (d. May 1777) Provost of Dundee, and his wife (and first cousin once removed) Helen, daughter of John Haldane of Gleneagles. He was born at Dundee. In 1746, after receiving his education in Dundee, he entered the Royal Navy on board the sloop ''Trial'', under Captain Robert Haldane, with whom, in and afterwards in , he continued until the peace in 1748. In 1749 he was appointed to , then commissioned for service in the Mediterranean, by the Hon. Augustus Keppel (afterwards Viscount Keppel), with whom he was afterwards in on the coast of North America, and was confirmed in the rank of lieutenant on 10 January 1755. Seven Years War In August 1755 he followed K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
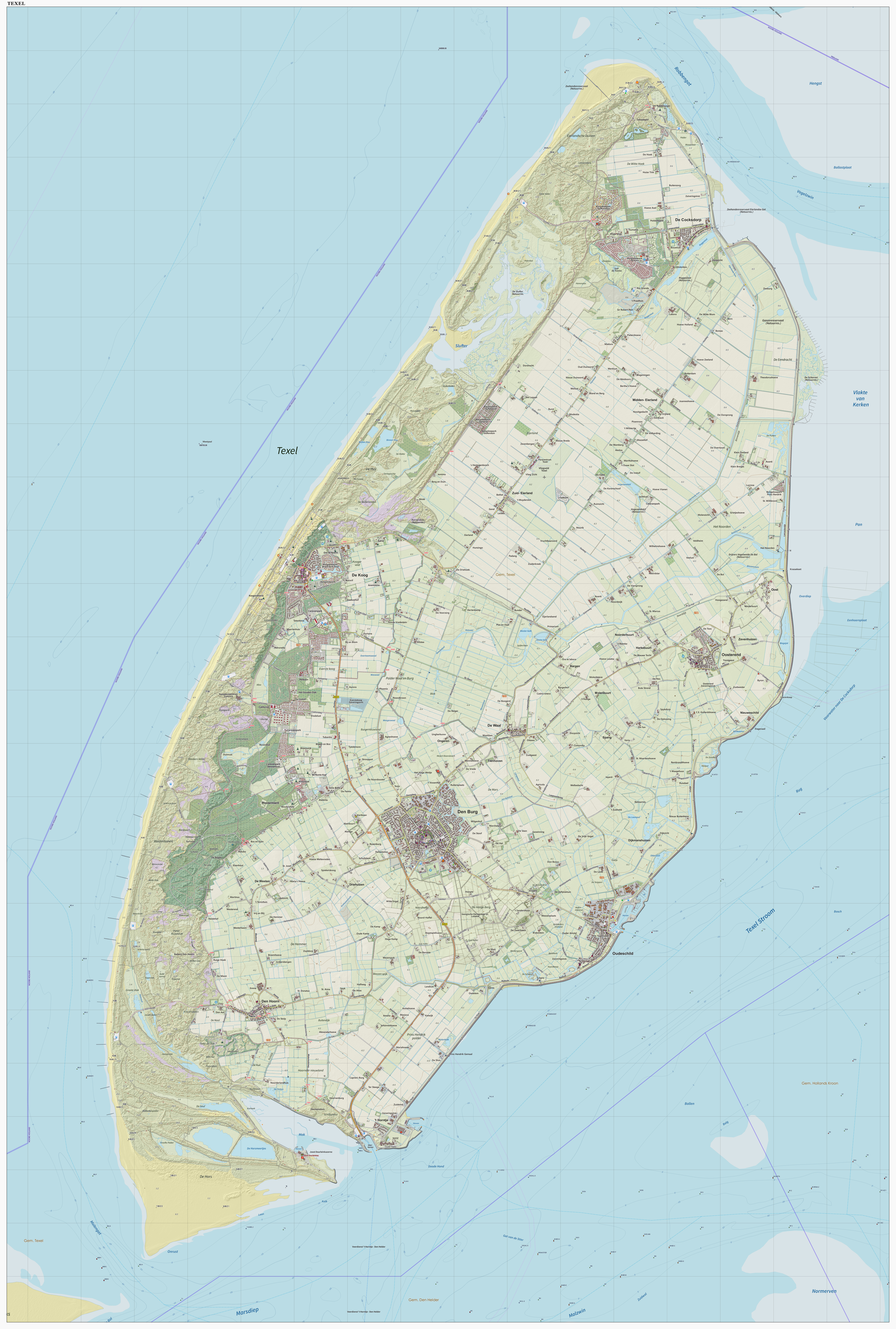
Texel
Texel (; Texels dialect: ) is a municipality and an island with a population of 13,643 in North Holland, Netherlands. It is the largest and most populated island of the West Frisian Islands in the Wadden Sea. The island is situated north of Den Helder, northeast of Noorderhaaks, and southwest of Vlieland. Name The name ''Texel'' is Frisian, but because of historical sound-changes in Dutch, where all -x- sounds have been replaced with -s- sounds (compare for instance English ''fox'', Frisian ''fokse'', German ''Fuchs'' with Dutch ''vos''), the name is typically pronounced ''Tessel'' in Dutch. History The All Saints' Flood (1170) created the islands of Texel and Wieringen from North Holland. In the 13th century Ada, Countess of Holland was held prisoner on Texel by her uncle, William I, Count of Holland. Texel received city rights in 1415. The first Dutch expedition to the Northwest Passage departed from the island on the 5th of June, 1594. Texel was involved in the Battl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Trollope
Admiral Sir Henry Trollope, GCB (20 April 1756 – 2 November 1839) was an officer of the British Royal Navy. Early life Henry Trollope was born the son of the Reverend John Trollope of Bucklebury on 20 April 1756. His paternal grandfather, also named Henry, was the brother of Sir Thomas Trollope, 4th Baronet. Early career Trollope entered the Royal Navy at the age of fourteen in April 1771. He joined the ship of the line HMS ''Captain'', flagship of Rear-Admiral John Montagu, which subsequently sailed to the North America Station. While on board ''Captain'' Trollope rose from captain's servant to able seaman and then to midshipman. The ship returned to England in 1774 and Trollope then transferred to the ship of the line HMS ''Asia'', also on the North America Station, to serve in the American Revolutionary War. As such he fought at the Battle of Lexington on 19 April 1775 and at the Battle of Bunker Hill on 17 June. At both battles he served in ''Asia''s small boats, cove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingston Upon Hull
Kingston upon Hull, usually abbreviated to Hull, is a port city and unitary authority in the East Riding of Yorkshire, England. It lies upon the River Hull at its confluence with the Humber Estuary, inland from the North Sea and south-east of York, the historic county town. With a population of (), it is the fourth-largest city in the Yorkshire and the Humber region after Leeds, Sheffield and Bradford. The town of Wyke on Hull was founded late in the 12th century by the monks of Meaux Abbey as a port from which to export their wool. Renamed ''Kings-town upon Hull'' in 1299, Hull had been a market town, military supply port, trading centre, fishing and whaling centre and industrial metropolis. Hull was an early theatre of battle in the English Civil Wars. Its 18th-century Member of Parliament, William Wilberforce, took a prominent part in the abolition of the slave trade in Britain. More than 95% of the city was damaged or destroyed in the blitz and suffered a perio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
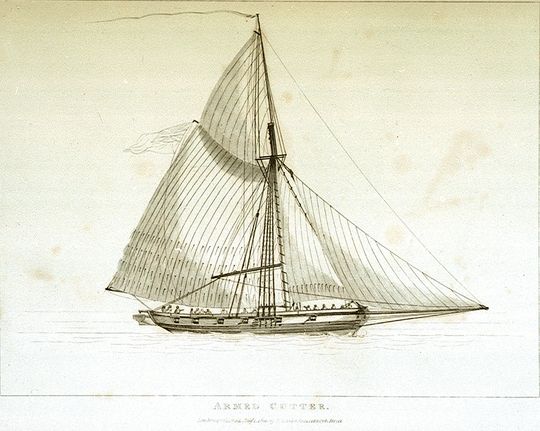
Hired Armed Vessels
During the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries the Royal Navy made use of a considerable number of hired armed vessels. These were generally smaller vessels, often cutters and luggers, that the Navy used for duties ranging from carrying and passengers to convoy escort, particularly in British coastal waters, and reconnaissance.Winfield (2008), p.387. Doctrine The Navy Board usually hired the vessel complete with master and crew rather than bareboat. Contracts were for a specified time or on an open-ended monthly hire basis. During periods of peace, such as the period between the Treaty of Amiens and the commencement of the Napoleonic Wars, the Admiralty returned the vessels to their owners, only to rehire many on the outbreak of war. The Admiralty provided a regular naval officer, usually a lieutenant for the small vessels, to be the commander. The civilian master then served as the sailing master. For purposes of prize money or salvage, hired armed vessels received the same ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spithead And Nore Mutinies
The Spithead and Nore mutinies were two major mutinies by sailors of the Royal Navy in 1797. They were the first in an increasing series of outbreaks of maritime radicalism in the Atlantic World. Despite their temporal proximity, the mutinies differed in character. The Spithead mutiny was a simple, peaceful, successful strike action to address economic grievances, while the Nore mutiny was a more radical action, articulating political ideals as well, which failed. The mutinies were extremely problematic for Britain, because at the time the country was at war with Revolutionary France, and the Navy was the main component of the war effort. There were also concerns among the government that the mutinies might be part of wider attempts at revolutionary sedition instigated by societies such as the London Corresponding Society and the United Irishmen. Spithead The mutiny at Spithead (an anchorage near Portsmouth) lasted from 16 April to 15 May 1797. Sailors on 16 ships in the Ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sir Peter Halkett, 6th Baronet
Admiral Sir Peter Halkett, 6th Baronet (''c.'' 1765 – 7 October 1839) was a senior Royal Navy officer of the early nineteenth century who is best known for his service in the French Revolutionary Wars. The younger son a Scottish baronet, Halkett joined the Navy and by 1793 was a lieutenant, becoming a post captain after service at the Siege of Williamstadt in the Netherlands. He later commanded the frigate HMS ''Circe'' during the Battle of Camperdown in 1797 and later achieved success in the Caribbean in command of HMS ''Apollo''. He was made a rear-admiral in 1812, but his first major command was in the West Indies in 1836, lasting two years. Shortly before his death he inherited the Halkett Baronetcy from his brother Charles, later passing it to his son John. Life Peter Halkett was born in 1765, the second son of Sir John Halkett, the 4th Halkett Baronet of Pitfirrane in Fife. At a young age, Halkett entered the Royal Navy and as a lieutenant achieved his first comm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Montagu (Royal Navy Officer)
Admiral Sir George Montagu (12 December 1750 – 24 December 1829) was a Royal Navy officer, the second son of Admiral John Montagu, and the brother of Captain James Montagu and Lieutenant-Colonel Edward Montagu. Early career In 1763 Montagu entered the Royal Academy at Portsmouth, and was then appointed to with Captain Alan Gardner (afterwards Admiral Lord Gardner), going out to the Jamaica station with the flag of Rear Admiral William Parry. He served in ''Preston'' for three years, before following Captain Gardner to HMS ''Levant''. He finally returned to England in 1770. He passed his lieutenant's examination on 2 October 1770, and on 14 January 1771 was appointed lieutenant of HMS ''Marlborough''. In February he was moved into HMS ''Captain'', going out to North America as the flagship of his father. On 9 April 1773 he was appointed commander in the 18 gun sloop , and on 15 April 1774 (Pay-book of the ''Fowey'') he was posted to . In her he continued on the North A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |