|
HMS Caledonia (1808)
HMS ''Caledonia'' was a 120-gun first-rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, launched on 25 June 1808 at Plymouth. She was Admiral Pellew's flagship in the Mediterranean. Construction The Admiralty orders for ''Caledonia''s construction were issued in November 1794, for a 100-gun vessel measuring approximately 2,600 tons burthen. There were considerable delays in obtaining dockyard facilities and in assembling a workforce, and actual building did not commence until 1805 when the keel was laid down at Plymouth Dockyard. By this time the designs had also been amended to stipulate construction of a 120-gun vessel of 2,616 tons. When completed to this new design in 1808, ''Caledonia'' entered Royal Navy service as the largest and most heavily armed vessel of the time.Winfield 2010, p.77 Active service ''Caledonia'' proved to be a very successful ship, and it was said that 'This fine three-decker rides easy at her anchors, carries her lee ports well, rolls and pitches quite e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Kingdom Of Great Britain And Ireland
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland was a sovereign state in the British Isles that existed between 1801 and 1922, when it included all of Ireland. It was established by the Acts of Union 1800, which merged the Kingdom of Great Britain and the Kingdom of Ireland into a unified state. The establishment of the Irish Free State in 1922 led to the remainder later being renamed the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland in 1927. The United Kingdom, having financed the European coalition that defeated France during the Napoleonic Wars, developed a large Royal Navy that enabled the British Empire to become the foremost world power for the next century. For nearly a century from the final defeat of Napoleon following the Battle of Waterloo to the outbreak of World War I, Britain was almost continuously at peace with Great Powers. The most notable exception was the Crimean War with the Russian Empire, in which actual hostilities were relatively limited. How ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Boyne (1810)
HMS ''Boyne'' was a 98-gun second rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, built by Nicholas Diddams at Portsmouth Dockyard and launched on 3 July 1810 at Portsmouth. On 12 February 1814 she took part with HMS ''Caledonia'' in a hot action against the French line-of-battle ship ''Romulus'' off Toulon; the French 74 managed to escape to Toulon by sailing close to the coast to avoid being surrounded. With the 1817 changes to the rating system ''Boyne'' was rerated as a 104-gun first rate ship. On 23 November 1824, ''Boyne'' was driven ashore at Portsmouth during a gale. In 1826 she was cut down (razeed) to become a two-deck, 76-gun third-rate In the rating system of the Royal Navy, a third rate was a ship of the line which from the 1720s mounted between 64 and 80 guns, typically built with two gun decks (thus the related term two-decker). Years of experience proved that the third r ... ship of the line. On 1 December 1834 she was renamed HMS '' Excellent'' and becam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ships Of The Line Of The Royal Navy
A ship is a large watercraft that travels the world's oceans and other sufficiently deep waterways, carrying cargo or passengers, or in support of specialized missions, such as defense, research, and fishing. Ships are generally distinguished from boats, based on size, shape, load capacity, and purpose. Ships have supported exploration, trade, warfare, migration, colonization, and science. After the 15th century, new crops that had come from and to the Americas via the European seafarers significantly contributed to world population growth. Ship transport is responsible for the largest portion of world commerce. The word ''ship'' has meant, depending on the era and the context, either just a large vessel or specifically a ship-rigged sailing ship with three or more masts, each of which is square-rigged. As of 2016, there were more than 49,000 merchant ships, totaling almost 1.8 billion dead weight tons. Of these 28% were oil tankers, 43% were bulk carriers, and 13% were con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epidemic
An epidemic (from Ancient Greek, Greek ἐπί ''epi'' "upon or above" and δῆμος ''demos'' "people") is the rapid spread of disease to a large number of patients among a given population within an area in a short period of time. Epidemics of infectious diseases are generally caused by several factors including a significant change in the ecology of the areal population (e.g., increased stress maybe additional reason or increase in the density of a vector species), the introduction of an emerging pathogen to an areal population (by movement of pathogen or host) or an unexpected genetic change that is in the pathogen reservoir. Generally, epidemics concerns with the patterns of infectious disease spread. An epidemic may occur when host immunity to either an established pathogen or newly emerging novel pathogen is suddenly reduced below that found in the endemic equilibrium and the transmission threshold is exceeded. For example, in meningococcal infections, an attack rate in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smallpox
Smallpox was an infectious disease caused by variola virus (often called smallpox virus) which belongs to the genus Orthopoxvirus. The last naturally occurring case was diagnosed in October 1977, and the World Health Organization (WHO) certified the global eradication of the disease in 1980, making it the only human disease to be eradicated. The initial symptoms of the disease included fever and vomiting. This was followed by formation of ulcers in the mouth and a skin rash. Over a number of days, the skin rash turned into the characteristic fluid-filled blisters with a dent in the center. The bumps then scabbed over and fell off, leaving scars. The disease was spread between people or via contaminated objects. Prevention was achieved mainly through the smallpox vaccine. Once the disease had developed, certain antiviral medication may have helped. The risk of death was about 30%, with higher rates among babies. Often, those who survived had extensive scarring of their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lazaretto
A lazaretto or lazaret (from it, lazzaretto a diminutive form of the Italian word for beggar cf. lazzaro) is a quarantine station for maritime travellers. Lazarets can be ships permanently at anchor, isolated islands, or mainland buildings. In some lazarets, postal items were also disinfected, usually by fumigation. This practice was still being done as late as 1936, albeit in rare cases. A leper colony administered by a Christian religious order was often called a lazar house, after the parable of Lazarus the beggar. Throughout history In 1592, a lazaretto made of wooden huts was built on Manoel Island in Malta during a plague epidemic. It was pulled down in 1593 after the disease had subsided. In 1643, Grandmaster Lascaris built a permanent Lazzaretto in the same place to control the periodic influx of plague and cholera on board visiting ships. The hospital was subsequently improved over time, and was enlarged during the governorship of Sir Henry Bouverie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greenwich
Greenwich ( , ,) is a town in south-east London, England, within the ceremonial county of Greater London. It is situated east-southeast of Charing Cross. Greenwich is notable for its maritime history and for giving its name to the Greenwich Meridian (0° longitude) and Greenwich Mean Time. The town became the site of a royal palace, the Palace of Placentia from the 15th century, and was the birthplace of many Tudors, including Henry VIII and Elizabeth I. The palace fell into disrepair during the English Civil War and was demolished to be replaced by the Royal Naval Hospital for Sailors, designed by Sir Christopher Wren and his assistant Nicholas Hawksmoor. These buildings became the Royal Naval College in 1873, and they remained a military education establishment until 1998 when they passed into the hands of the Greenwich Foundation. The historic rooms within these buildings remain open to the public; other buildings are used by University of Greenwich and Trinity Laban C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
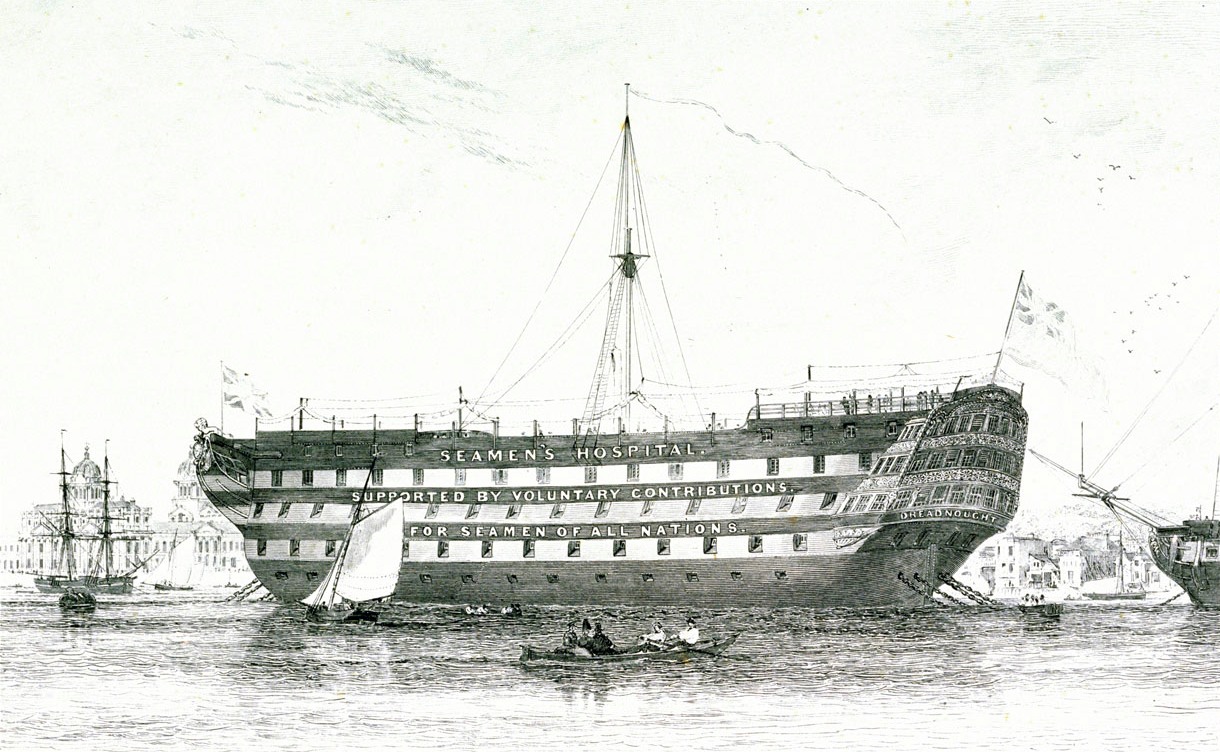
Dreadnought Seamen's Hospital
The Seafarers Hospital Society, formerly the Seamen's Hospital Society, is a charity for people currently or previously employed by the British Merchant Navy and fishing fleets, and their families. It was established in 1821. Current activities The Dreadnought Seamen's Hospital continues to the present day under the NHS as the 'Dreadnought Unit' at St Thomas's Hospital and the dedicated Hospital for Tropical Diseases, part of the University College Hospitals London NHS Trust. The society currently part-funds the ''Seafarers' Advice and Information Line'', a national advice service operated by the Greenwich Citizens Advice Bureau. In addition it provides funds to nursing and residential care units for seafarers, and helps those in need by providing hardship grants.UK Statutory Instrument1999 No. 73- "The Charities (Seamen's Hospital Society) Order 1999". An order amending the Seaman's Hospital Society Act 1833, removing impractical or anachronistic measures and extending benefi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hospital Ship
A hospital ship is a ship designated for primary function as a floating medical treatment facility or hospital. Most are operated by the military forces (mostly navies) of various countries, as they are intended to be used in or near war zones. In the 19th century, redundant warships were used as moored hospitals for seamen. The Second Geneva Convention prohibits military attacks on hospital ships that meet specified requirements, though belligerent forces have right of inspection and may take patients, but not staff, as prisoners of war. History Early examples Hospital ships possibly existed in ancient times. The Athenian Navy had a ship named ''Therapia'', and the Roman Navy had a ship named ''Aesculapius'', their names indicating that they may have been hospital ships. The earliest British hospital ship may have been the vessel ''Goodwill'', which accompanied a Royal Navy squadron in the Mediterranean in 1608 and was used to house the sick sent aboard from other ships. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Galatea (1810)
HMS ''Galatea'' was an fifth rate of the Royal Navy. The frigate was built at Deptford Dockyard, London, England and launched on 31 August 1810. In 1811 she participated in the Battle of Tamatave, which battle confirmed British dominance of the seas east of the Cape of Good Hope for the rest of the Napoleonic Wars. She was hulked in 1836 and broken up in 1849. Napoleonic Wars ''Galatea'' was commissioned in September 1810 under Captain Woodley Losack, who would remain her captain until 1815. He sailed her to the Cape of Good Hope on 31 December 1810. On 6 May 1811, a French squadron of frigates under the command of Commodore François Roquebert in '' Renommée'' approached Grand Port, not realizing that Isle de France (now Mauritius) had fallen to the British. The French squadron escaped an encounter with an equivalent British squadron under Captain Charles Marsh Schomberg of . Between 7 and 9 May the frigates ''Galatea'' and , under James Hillyar, and the brig-sloop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward Codrington
Sir Edward Codrington, (27 April 1770 – 28 April 1851) was a British admiral, who took part in the Battle of Trafalgar and the Battle of Navarino. Early life and career The youngest of three brothers born to Edward Codrington the elder (1732–1775) and Rebecca Lestourgeon (Sturgeon) (1736–1770), Codrington came from a long military tradition. Edward the elder was the youngest son of William Codrington, 1st Baronet. Their aristocratic, landowning family, was descended from John Codrington, reputed to be standard-bearer to Henry V at Agincourt, and related to the Codrington baronets, Codrington was educated by an uncle named Mr Bethell. He was sent for a short time to Harrow, and entered the Royal Navy in July 1783. He served off the Eastern Seaboard of the United States, in the Mediterranean and in home waters, until he was promoted to lieutenant on 28 May 1793, when Lord Howe selected him to be signal lieutenant on the flagship of the Channel fleet at the beginning of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Channel Fleet
The Channel Fleet and originally known as the Channel Squadron was the Royal Navy formation of warships that defended the waters of the English Channel from 1854 to 1909 and 1914 to 1915. History Throughout the course of Royal Navy's history there had been different squadrons stationed in home waters. One of the earliest known naval formations to be based at Plymouth was called the Western Squadron which was the forerunner of the Channel Squadron that was later known as the Channel Fleet. In 1650 Captain William Penn, Commander-in-Chief, was charged with guarding the Channel from Beachy Head to Lands End with six ships. This system continued following the Restoration. It was the start of what was to become a Western Squadron. From 1690 the squadron operated out of Plymouth Dockyard during wartime periods, which was for most of the 18th century and early 19th century. In 1854 The Channel Squadron, sometimes known as the Particular Service Squadron, was established. The Channel Squ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)

