|
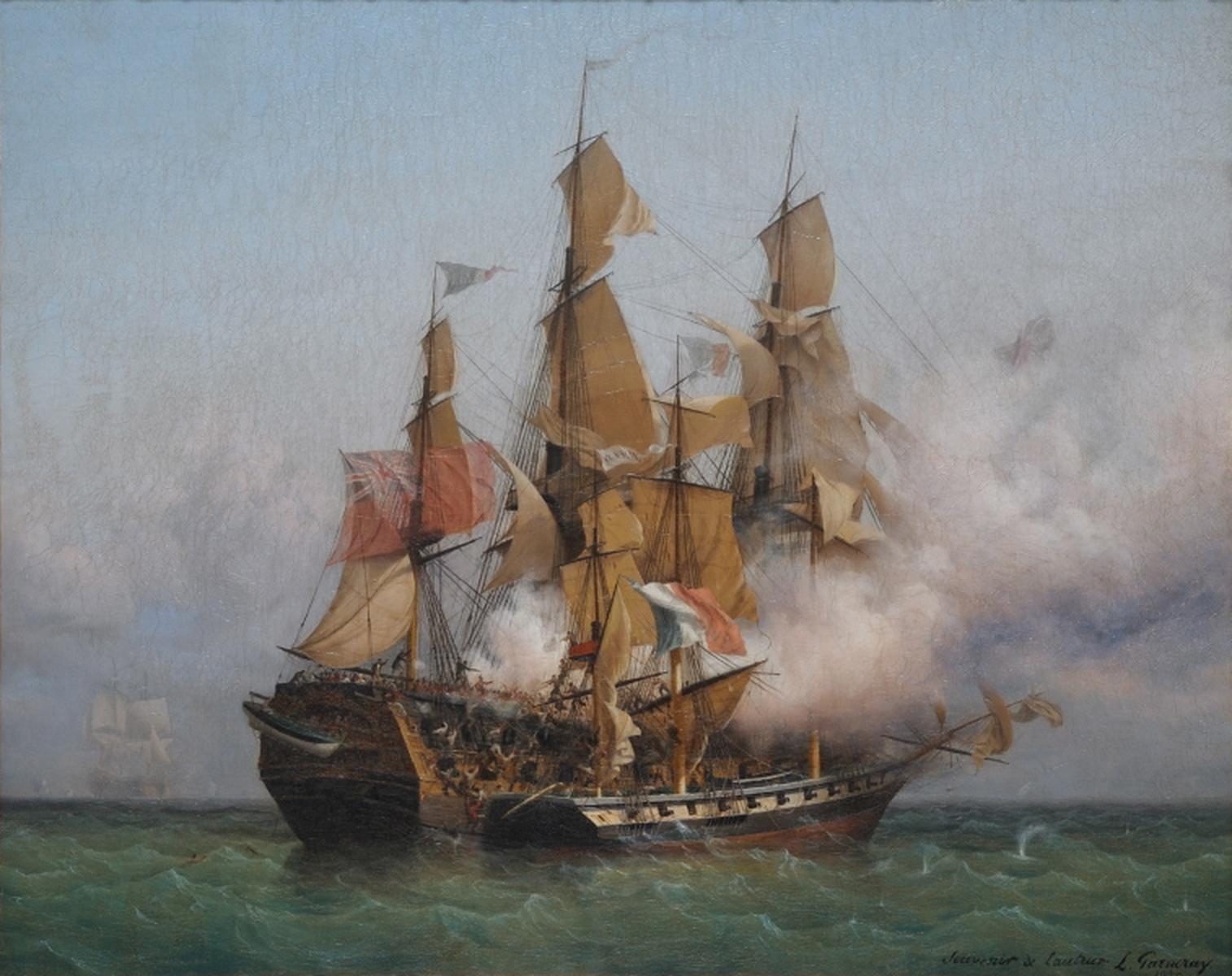
HMS Barrosa (1812)
HMS ''Barrosa'' was launched in 1812 for the Royal Navy and served during the War of 1812 during which she captured several prices. After the war she spent a decade or so (1823–1833) on harbour duties. The navy sold ''Barrosa'' in 1841. Career Captain William Henry Shirreff commissioned ''Barrosa'' on 25 October 1812. He sailed her for North America on 31 January 1813. She was serving as an escort to a convoy for the West Indies and the Brazils. War of 1812 On 22 May 1813 ''Barrosa'' captured the American schooner ''William and Thomas'', of 25 tons (bm). ''Barrosa'' kept her prize as a ship's tender. ''Barrosa'' was among the British naval vessels that shared in the capture of a number of merchant vessels in mid-January 1813: *11 June: Spanish brig ''St. Iago'' *12 June: American schooner ''Surveyor'', ''Governor Strong'', and ''Emily'' *14 June: ''Star'' *21 June: American ship ''Herman'' ''Surveyor'' was a United States revenue schooner of six 12-pounder carronades, 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Builder's Old Measurement
Builder's Old Measurement (BOM, bm, OM, and o.m.) is the method used in England from approximately 1650 to 1849 for calculating the cargo capacity of a ship. It is a volumetric measurement of cubic capacity. It estimated the tonnage of a ship based on length and maximum beam (nautical), beam. It is expressed in "tons burden" ( en-em , burthen , enm , byrthen ), and abbreviated "tons bm". The formula is: : \text = \frac where: * ''Length'' is the length, in foot (length), feet, from the stem (ship), stem to the sternpost; * ''Beam (nautical), Beam'' is the maximum beam, in feet. The Builder's Old Measurement formula remained in effect until the advent of steam propulsion. Steamships required a different method of estimating tonnage, because the ratio of length to beam was larger and a significant volume of internal space was used for boilers and machinery. In 1849, the Moorsom System was created in the United Kingdom. The Moorsom system calculates the cargo-carrying capaci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halifax, Nova Scotia
Halifax is the capital and largest municipality of the Canadian province of Nova Scotia, and the largest municipality in Atlantic Canada. As of the 2021 Census, the municipal population was 439,819, with 348,634 people in its urban area. The regional municipality consists of four former municipalities that were amalgamated in 1996: Halifax, Dartmouth, Bedford, and Halifax County. Halifax is a major economic centre in Atlantic Canada, with a large concentration of government services and private sector companies. Major employers and economic generators include the Department of National Defence, Dalhousie University, Nova Scotia Health Authority, Saint Mary's University, the Halifax Shipyard, various levels of government, and the Port of Halifax. Agriculture, fishing, mining, forestry, and natural gas extraction are major resource industries found in the rural areas of the municipality. History Halifax is located within ''Miꞌkmaꞌki'' the traditional ancestral lands ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reserve Fleet
A reserve fleet is a collection of naval vessels of all types that are fully equipped for service but are not currently needed; they are partially or fully decommissioned. A reserve fleet is informally said to be "in mothballs" or "mothballed"; an equivalent expression in unofficial modern US naval usage is "ghost fleet". In earlier times, especially in British usage, the ships were said to be "laid up in ordinary". Overview Such ships are held in reserve against a time when it may be necessary to call them back into service. They are usually tied up in backwater areas near naval bases or shipyards in order to speed the reactivation process. They may be modified for storage during such a period, for instance by having rust-prone areas sealed off or wrapped in plastic or, in the case of sailing warships, the masts removed. While being held in the reserve fleet, ships typically have a minimal crew (known informally as a skeleton crew) to ensure that they stay in somewhat usable co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Privateering
A privateer is a private person or ship that engages in maritime warfare under a commission of war. Since robbery under arms was a common aspect of seaborne trade, until the early 19th century all merchant ships carried arms. A sovereign or delegated authority issued commissions, also referred to as a letter of marque, during wartime. The commission empowered the holder to carry on all forms of hostility permissible at sea by the usages of war. This included attacking foreign vessels and taking them as prizes, and taking prize crews as prisoners for exchange. Captured ships were subject to condemnation and sale under prize law, with the proceeds divided by percentage between the privateer's sponsors, shipowners, captains and crew. A percentage share usually went to the issuer of the commission (i.e. the sovereign). Privateering allowed sovereigns to raise revenue for war by mobilizing privately owned armed ships and sailors to supplement state power. For participants, privateeri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sperm Oil
Sperm oil is a waxy liquid obtained from sperm whales. It is a clear, yellowish liquid with a very faint odor. Sperm oil has a different composition from common whale oil, obtained from rendered blubber. Although it is traditionally called an "oil", it is technically a liquid wax. It is composed of wax esters with a small proportion of triglycerides, an ester of an unsaturated fatty acid, and a branched-chain fatty alcohol. ransmission Digest, Volume 26, No. 2, October 2006, "The Science of Synthetic Sperm Whale Oil"/ref> It is a natural antioxidant and heat-transfer agent. In the late-18th and early-19th centuries, sperm oil was prized as an illuminant for its bright, odorless flame and as a lubricant for its low viscosity and stability. It was supplanted in the late 19th century by less expensive alternatives such as kerosene and petroleum-based lubricants. With the 1987 international ban on whaling, sperm oil is no longer legally sold. The oil from bottlenose whales was som ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Frigate Bellone (1807)
''Bellone'' was a 44-gun ''Consolante''-class frigate of the French Navy. French service ''Bellone'', under the command of Guy-Victor Duperré, departed Saint-Malo on 18 January 1809, bound for the Indian Ocean. She sailed from La Réunion for a combat patrol in August. On 2 November she captured HMS ''Victor''. Twenty days later, she captured the 48-gun Portuguese ''Minerva'' after a 2-hour battle. ''Bellone'' sailed back to La Réunion with her prize, arriving on 2 January 1810. In April 1810, the squadron comprising ''Bellone'', ''Minerve'' and ''Victor'' departed for another patrol, during which they fought the action of 3 July 1810 and the Battle of Grand Port. ''Bellone'' was surrendered to the British when Île de France fell, on 4 December 1810. British service ''Bellone'' was recommissioned in the Royal Navy as HMS ''Junon''. In June 1812, ''Junon'' escorted a convoy from Portsmouth to India. On 8 February 1813, nine boats and 200 men of the squadron of which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Laura (1806)
HMS ''Laura'' was an of the Royal Navy, launched in 1806 at Bermuda. ''Laura'' served during the Napoleonic Wars before a French privateer captured her at the beginning of the War of 1812. She was briefly an American letter of marque before the British recaptured her in 1813. Despite having recaptured her, the British did not return ''Laura'' to service. Adonis-class schooners ''Laura'' was built at Bermuda of the pencil cedar . The ''Adonis''-class schooners were a little larger and much better armed than the ''Ballahoo''- and ''Cuckoo''-class schooners that they followed. The Admiralty's intent was to improve survivability of these dispatch boats. Service In March 1806 ''Laura'' was commissioned under Lieutenant Joseph R.R. Webb, for the Channel. In 1807 Lieutenant Robert Yetts took command and on 28 March he sailed ''Laura'' for the Leeward Islands. On 4 August 1807, ''Laura'' was in company with the schooner ''Ballahoo'', of four guns, when they encountered the Frenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ship's Tender
A ship's tender, usually referred to as a tender, is a boat, or a larger ship, used to service or support other boats or ships. This is generally done by transporting people or supplies to and from shore or another ship. A second and distinctly different meaning for ''tender'' is small boats carried by larger vessels, to be used either as lifeboats, or as transport to shore, or both. Tenders as smaller craft For a variety of reasons, it is not always advisable to try to tie a ship up at a dock; the weather or the sea might be rough, the time might be short, or the ship too large to fit. In such cases tenders provide the link from ship to shore, and may have a very busy schedule of back-and-forth trips while the ship is in port. On cruise ships, lifeboat tenders do double duty, serving as tenders in day-to-day activities, but fully equipped to act as lifeboats in an emergency. They are generally carried on davits just above the promenade deck, and may at first glance appear to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
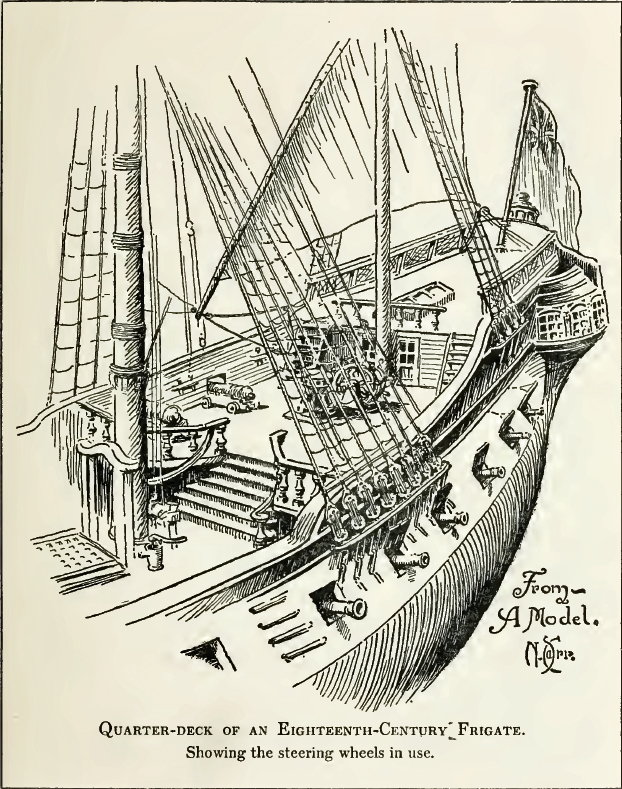
Quarterdeck
The quarterdeck is a raised deck behind the main mast of a sailing ship. Traditionally it was where the captain commanded his vessel and where the ship's colours were kept. This led to its use as the main ceremonial and reception area on board, and the word is still used to refer to such an area on a ship or even in naval establishments on land. Many such facilities have areas decorated like shipboard quarterdecks. In the 20th century the word came to be applied to the area at the stern of the ship, often (on naval vessels) used for secondary weapons and (on battleships) seaplane catapults. In modern military designs the stern has been roofed over by the helicopter deck but a large space remains underneath which is typically used for sonar equipment or small boats and which is still referred to as the quarterdeck in Commonwealth navies. Ceremonial use There are ancient traditions of offering special deference to the quarterdeck. Greek, Roman, and Carthaginian warships all c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Henry Shirreff
William Henry Shirreff (baptised 4 April 1785 – 1 December 1847) was a British Royal Navy officer, captain of , , , and . He had six children four of whom were daughters. He had two notable daughters, Maria Georgina Grey and Emily Anne Eliza Shirreff, who transformed the education of British women. He retired as Rear-Admiral of the Blue. Biography Shirreff was born in 1785 and he joined the Royal Navy on 1 January 1796. In 1810, he married Elizabeth Murray, the oldest daughter of the lawyer and Member of Parliament David Murray, a brother of Alexander Murray, 7th Lord Elibank. From October 1812 until he invalided in July 1814, Shirreff commanded the frigate ''Barrosa'' on the coast of North America and in the West Indies. From 10 September 1817 until September 1821 he commanded ''Andromache''. When patrolling the west coast of South America in protection of the British interests in the region and in support of local independence movement against Spanish authority in the earl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
War Of 1812
The War of 1812 (18 June 1812 – 17 February 1815) was fought by the United States of America and its indigenous allies against the United Kingdom and its allies in British North America, with limited participation by Spain in Florida. It began when the United States declared war on 18 June 1812 and, although peace terms were agreed upon in the December 1814 Treaty of Ghent, did not officially end until the peace treaty was ratified by Congress on 17 February 1815. Tensions originated in long-standing differences over territorial expansion in North America and British support for Native American tribes who opposed US colonial settlement in the Northwest Territory. These escalated in 1807 after the Royal Navy began enforcing tighter restrictions on American trade with France and press-ganged men they claimed as British subjects, even those with American citizenship certificates. Opinion in the US was split on how to respond, and although majorities in both the House and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_underway_c1947.jpg)