|
HMR 1883
HMR 1883 (1- sodium salt HMR 1098, are experimental anti-arrhythmic drugs classified as sulfonylthiourea">Antiarrhythmic agent">anti-arrhythmic drugs classified as sulfonylthiourea compounds.Heinrich C. Englert, Uwe Gerlach, Heinz Goegelein, Jens Hartung, Holger Heitsch, Dieter Mania, and Sabine Scheidler. 2001. Cardioselective KATP Channel Blockers Derived from a New Series of m-Anisamidoethylbenzenesulfonylthioureas J. Med. Chem. 44 (7):1085–1098 Their main purpose is to treat ventricular fibrillation caused by myocardial ischemia. They were synthesized via structural modifications to glibenclamide, an Anti-diabetic medication, antidiabetic drug. Both HMR 1883 and glibenclamide act by inactivating the ATP-sensitive potassium channels (KATP) responsible for potassium efflux. Billman, G. E., Englert, H. C., & Schoelkens, B. A. (1998) HMR 1883, a novel cardioselective inhibitor of the ATP- sensitive potassium channel; Part II: effects on susceptibility to ventricular fibrillatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salt (chemistry)
In chemistry, a salt is a chemical compound consisting of an ionic assembly of positively charged cations and negatively charged anions, which results in a compound with no net electric charge. A common example is table salt, with positively charged sodium ions and negatively charged chloride ions. The component ions in a salt compound can be either inorganic, such as chloride (Cl−), or organic, such as acetate (). Each ion can be either monatomic, such as fluoride (F−), or polyatomic, such as sulfate (). Types of salt Salts can be classified in a variety of ways. Salts that produce hydroxide ions when dissolved in water are called ''alkali salts'' and salts that produce hydrogen ions when dissolved in water are called ''acid salts''. ''Neutral salts'' are those salts that are neither acidic nor basic. Zwitterions contain an anionic and a cationic centre in the same molecule, but are not considered salts. Examples of zwitterions are amino acids, many metabolites, peptid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antiarrhythmic Agent
Antiarrhythmic agents, also known as cardiac dysrhythmia medications, are a group of pharmaceuticals that are used to suppress abnormally fast rhythms ( tachycardias), such as atrial fibrillation, supraventricular tachycardia and ventricular tachycardia. Many attempts have been made to classify antiarrhythmic agents. Many of the antiarrhythmic agents have multiple modes of action, which makes any classification imprecise. Vaughan Williams classification The Vaughan Williams classification was introduced in 1970 by Miles Vaughan Williams.Vaughan Williams, EM (1970) "Classification of antiarrhythmic drugs". In ''Symposium on Cardiac Arrhythmias'' (Eds. Sandoe E; Flensted-Jensen E; Olsen KH). Astra, Elsinore. Denmark (1970) Vaughan Williams was a pharmacology tutor at Hertford College, Oxford. One of his students, Bramah N. Singh, contributed to the development of the classification system. The system is therefore sometimes known as the Singh-Vaughan Williams classification. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
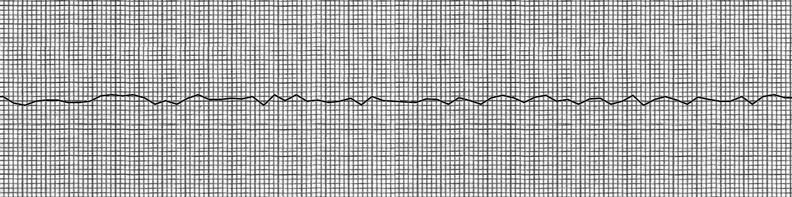
Ventricular Fibrillation
Ventricular fibrillation (V-fib or VF) is an abnormal heart rhythm in which the ventricles of the heart quiver. It is due to disorganized electrical activity. Ventricular fibrillation results in cardiac arrest with loss of consciousness and no pulse. This is followed by sudden cardiac death in the absence of treatment. Ventricular fibrillation is initially found in about 10% of people with cardiac arrest. Ventricular fibrillation can occur due to coronary heart disease, valvular heart disease, cardiomyopathy, Brugada syndrome, long QT syndrome, electric shock, or intracranial hemorrhage. Diagnosis is by an electrocardiogram (ECG) showing irregular unformed QRS complexes without any clear P waves. An important differential diagnosis is torsades de pointes. Treatment is with cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) and defibrillation. Biphasic defibrillation may be better than monophasic. The medication epinephrine or amiodarone may be given if initial treatments are not effect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
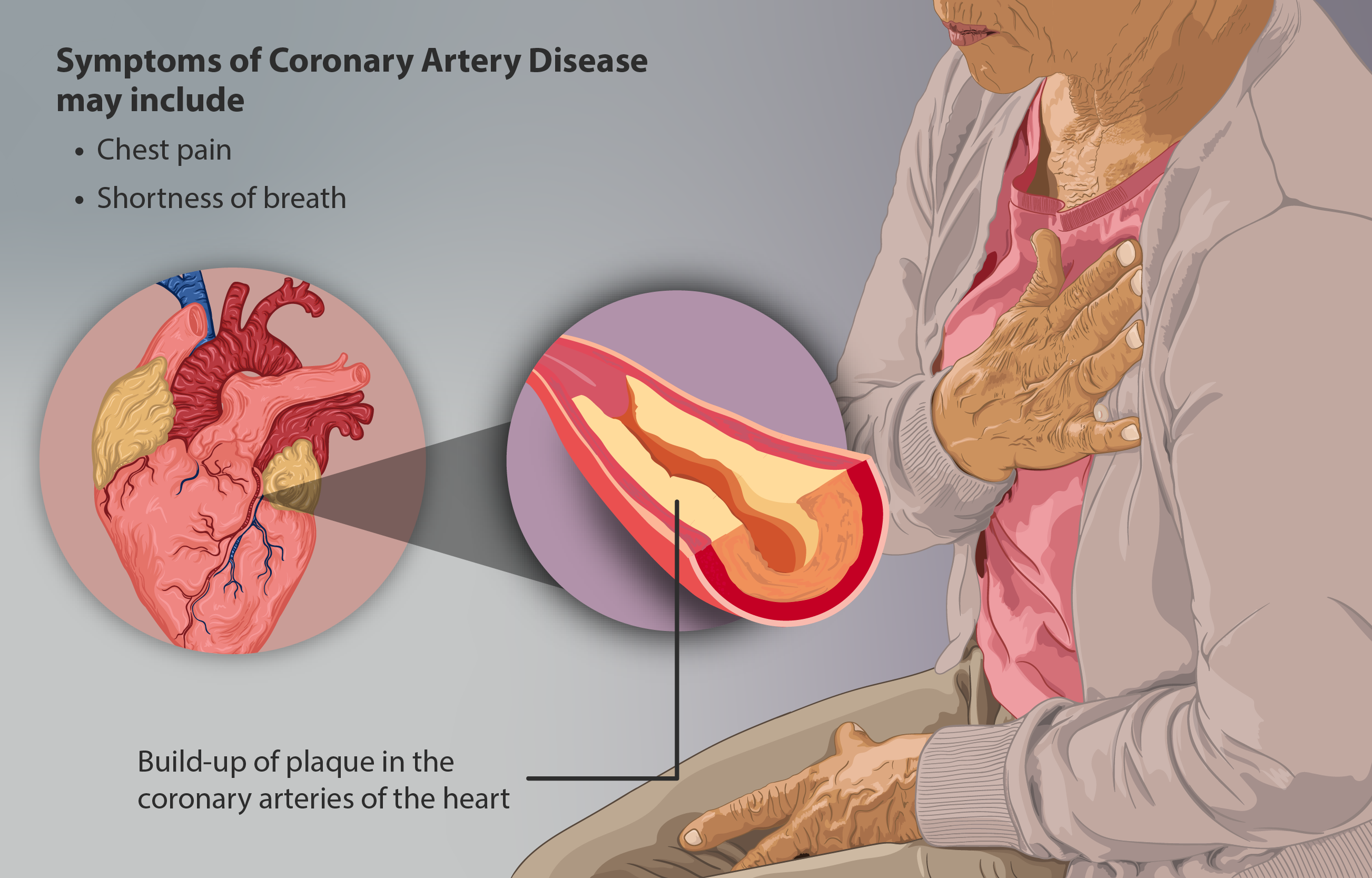
Myocardial Ischemia
Coronary artery disease (CAD), also called coronary heart disease (CHD), ischemic heart disease (IHD), myocardial ischemia, or simply heart disease, involves the reduction of blood flow to the heart muscle due to build-up of atherosclerotic plaque in the arteries of the heart. It is the most common of the cardiovascular diseases. Types include stable angina, unstable angina, myocardial infarction, and sudden cardiac death. A common symptom is chest pain or discomfort which may travel into the shoulder, arm, back, neck, or jaw. Occasionally it may feel like heartburn. Usually symptoms occur with exercise or emotional stress, last less than a few minutes, and improve with rest. Shortness of breath may also occur and sometimes no symptoms are present. In many cases, the first sign is a heart attack. Other complications include heart failure or an abnormal heartbeat. Risk factors include high blood pressure, smoking, diabetes, lack of exercise, obesity, high blood cholesterol, po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glibenclamide
Glibenclamide, also known as glyburide, is an antidiabetic medication used to treat type 2 diabetes. It is recommended that it be taken together with diet and exercise. It may be used with other antidiabetic medication. It is not recommended for use by itself in type 1 diabetes. It is taken by mouth. Common side effects include nausea and heartburn. Serious side effects may include angioedema and low blood sugar. It is generally not recommended during pregnancy but can be used during breastfeeding. It is in the sulfonylureas class of medications and works by increasing the release of insulin from the pancreas. Glibenclamide was discovered in 1969 and approved for medical use in the United States in 1984. It is available as a generic medication. In 2022, it was the 200th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 2million prescriptions. Medical uses Glibenclamide is indicated as an adjunct to diet and exercise to improve glycemic control in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti-diabetic Medication
Drugs used in diabetes treat diabetes mellitus by altering the glucose level in the blood. With the exceptions of insulin, most GLP receptor agonists ( liraglutide, exenatide, and others), and pramlintide, all are administered orally and are thus also called oral hypoglycemic agents or oral antihyperglycemic agents. There are different classes of anti-diabetic drugs, and their selection depends on the nature of the diabetes, age and situation of the person, as well as other factors. Diabetes mellitus type 1 is a disease caused by the lack of insulin. Insulin must be used in type 1, which must be injected. Diabetes mellitus type 2 is a disease of insulin resistance by cells. Type 2 diabetes mellitus is the most common type of diabetes. Treatments include agents that (1) increase the amount of insulin secreted by the pancreas, (2) increase the sensitivity of target organs to insulin, (3) decrease the rate at which glucose is absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, and (4) inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adenosine Triphosphate
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is an organic compound that provides energy to drive many processes in living cells, such as muscle contraction, nerve impulse propagation, condensate dissolution, and chemical synthesis. Found in all known forms of life, ATP is often referred to as the "molecular unit of currency" of intracellular energy transfer. When consumed in metabolic processes, it converts either to adenosine diphosphate (ADP) or to adenosine monophosphate (AMP). Other processes regenerate ATP. The human body recycles its own body weight equivalent in ATP each day. It is also a precursor to DNA and RNA, and is used as a coenzyme. From the perspective of biochemistry, ATP is classified as a nucleoside triphosphate, which indicates that it consists of three components: a nitrogenous base (adenine), the sugar ribose, and the Polyphosphate, triphosphate. Structure ATP consists of an adenine attached by the 9-nitrogen atom to the 1′ carbon atom of a sugar (ribose), which i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Efflux (microbiology)
In microbiology, efflux is the moving of a variety of different compounds out of cells, such as antibiotics, heavy metals, organic pollutants, plant-produced compounds, quorum sensing signals, bacterial metabolites and neurotransmitters. All microorganisms, with a few exceptions, have highly conserved DNA sequences in their genome that are transcribed and translated to efflux pumps. Efflux pumps actively move substances out of a microorganism, in a process known as active efflux, which is a vital part of xenobiotic metabolism. This active efflux mechanism is responsible for various types of resistance to bacterial pathogens within bacterial species - the most concerning being antibiotic resistance because microorganisms can have adapted efflux pumps to divert toxins out of the cytoplasm and into extracellular media. Efflux systems function via an energy-dependent mechanism (active transport) to pump out unwanted toxic substances through specific efflux pumps. Some efflux systems ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Billman
George Edward Billman (born July 23, 1954) is an American physiologist and professor at Ohio State University. After receiving a Ph.D from the University of Kentucky in 1980, Billman began his professional career at the University of Oklahoma. In 1984, he joined the Ohio State staff, where he became an associate professor in 1990 and a full professor in 1996. Billman's research has focused on cardiovascular function, in particular its role in the induction of ventricular fibrillation (VF). He developed non-invasive methods to study autonomic neural regulation of the heart, using a canine model of sudden cardiac death (SCD). These techniques have subsequently been used in human patients to identify people at high risk for VF. Billman has used his sudden cardiac death models to study the effects of exercise training on susceptibility to SCD and the effects of omega-3 fatty acids, among other things. Due to his use of live animals in experiments, Billman has been criticized by anim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
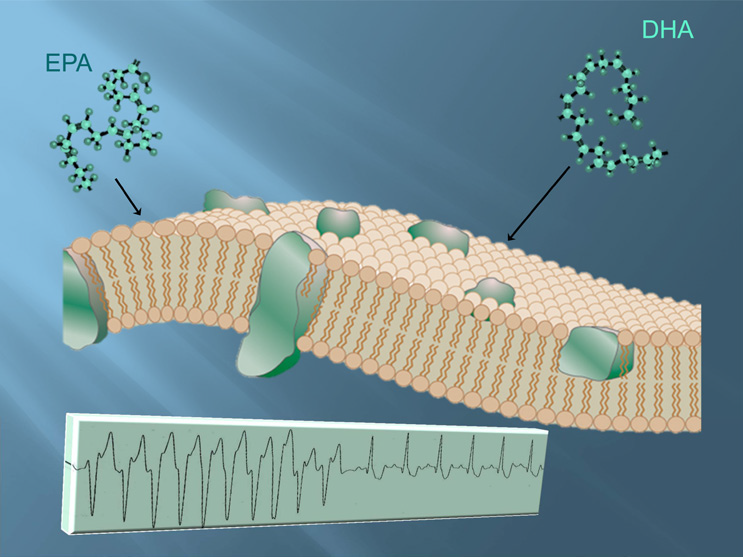
Cell Membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane (PM) or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of all cells from the outside environment (the extracellular space). The cell membrane consists of a lipid bilayer, made up of two layers of phospholipids with cholesterols (a lipid component) interspersed between them, maintaining appropriate membrane fluidity at various temperatures. The membrane also contains membrane proteins, including integral proteins that span the membrane and serve as membrane transporters, and peripheral proteins that loosely attach to the outer (peripheral) side of the cell membrane, acting as enzymes to facilitate interaction with the cell's environment. Glycolipids embedded in the outer lipid layer serve a similar purpose. The cell membrane controls the movement of substances in and out of cells and organelles, being selectively permeable to ions a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
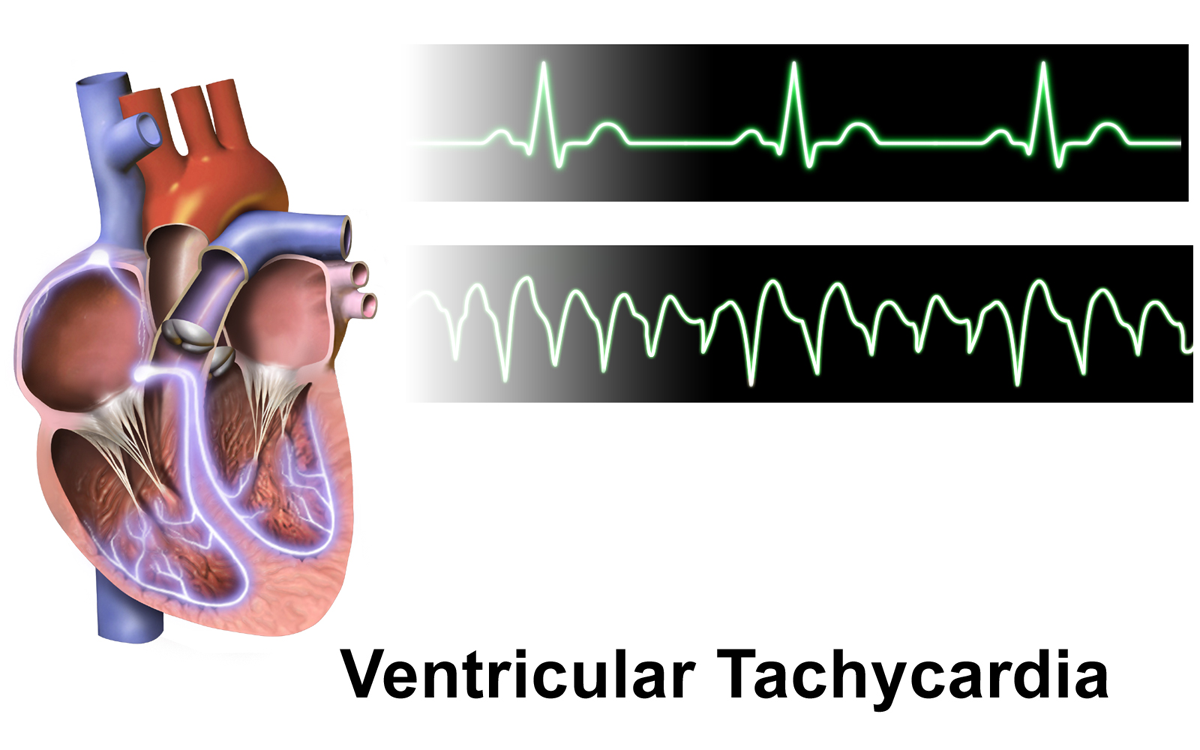
Ventricular Tachycardia
Ventricular tachycardia (V-tach or VT) is a fast heart rate arising from the lower chambers of the heart. Although a few seconds of VT may not result in permanent problems, longer periods are dangerous; and multiple episodes over a short period of time are referred to as an electrical storm. Short periods may occur without symptoms, or present with lightheadedness, palpitations, or chest pain. Ventricular tachycardia may result in ventricular fibrillation (VF) and turn into cardiac arrest. This conversion of the VT into VF is called the degeneration of the VT. It is found initially in about 7% of people in cardiac arrest. Ventricular tachycardia can occur due to coronary heart disease, aortic stenosis, cardiomyopathy, electrolyte problems, or a heart attack. Diagnosis is by an electrocardiogram (ECG) showing a rate of greater than 120 beats per minute and at least three wide QRS complexes in a row. It is classified as non-sustained versus sustained based on whether it lasts le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |