|
HHV Infected Cell Polypeptide 0 (ICP0)
Human Herpes Virus (HHV) Infected Cell Polypeptide 0 (ICP0) is a protein, encoded by the DNA of herpes viruses. It is produced by herpes viruses during the earliest stage of infection, when the virus has recently entered the host cell; this stage is known as the '' immediate-early'' or ''α'' ("alpha") phase of viral gene expression. During these early stages of infection, ICP0 protein is synthesized and transported to the nucleus of the infected host cell. Here, ICP0 promotes transcription from viral genes, disrupts structures in the nucleus known as nuclear dots or promyelocytic leukemia (PML) nuclear bodies, and alters the expression of host and viral genes in combination with a neuron specific protein. At later stages of cellular infection, ICP0 relocates to the cell cytoplasm to be incorporated into new virion particles. History and background ICP0 was identified as an immediate-early polypeptide product of Herpes simplex virus-1 (HSV-1) infection in 1976. The gene, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3D Protein Structure Of The Ring Finger Domain Of Equine Herpes Virus-1 ICP0
3-D, 3D, or 3d may refer to: Science, technology, and mathematics Relating to three-dimensionality * Three-dimensional space ** 3D computer graphics, computer graphics that use a three-dimensional representation of geometric data ** 3D film, a motion picture that gives the illusion of three-dimensional perception ** 3D modeling, developing a representation of any three-dimensional surface or object ** 3D printing, making a three-dimensional solid object of a shape from a digital model ** 3D display, a type of information display that conveys depth to the viewer ** 3D television, television that conveys depth perception to the viewer ** Stereoscopy, any technique capable of recording three-dimensional visual information or creating the illusion of depth in an image Other uses in science and technology or commercial products * 3D projection * 3D rendering * 3D scanning, making a digital representation of three-dimensional objects * 3D video game (other) * 3-D Secure, a se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphorylation
In chemistry, phosphorylation is the attachment of a phosphate group to a molecule or an ion. This process and its inverse, dephosphorylation, are common in biology and could be driven by natural selection. Text was copied from this source, which is available under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Protein phosphorylation often activates (or deactivates) many enzymes. Glucose Phosphorylation of sugars is often the first stage in their catabolism. Phosphorylation allows cells to accumulate sugars because the phosphate group prevents the molecules from diffusing back across their transporter. Phosphorylation of glucose is a key reaction in sugar metabolism. The chemical equation for the conversion of D-glucose to D-glucose-6-phosphate in the first step of glycolysis is given by :D-glucose + ATP → D-glucose-6-phosphate + ADP : ΔG° = −16.7 kJ/mol (° indicates measurement at standard condition) Hepatic cells are freely permeable to glucose, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RCOR1
REST corepressor 1 also known as CoREST is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''RCOR1'' gene. Function This gene encodes a protein that is well-conserved, downregulated at birth, and with a specific role in determining neural cell differentiation. The encoded protein binds to the C-terminal domain of REST (repressor element-1 silencing transcription factor). Interactions RCOR1 has been shown to interact with * HDAC1, * HDAC2, * HMG20B, * REST and * PHF21A PHD finger protein 21A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''PHF21A'' gene. Function BHC80 is a component of a BRAF35 (MIM 605535)/histone deacetylase (HDAC; see MIM 601241) complex (BHC) that mediates repression of neuron-specific g .... References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * {{Gene-14-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Differentiation
Cellular differentiation is the process in which a stem cell alters from one type to a differentiated one. Usually, the cell changes to a more specialized type. Differentiation happens multiple times during the development of a multicellular organism as it changes from a simple zygote to a complex system of tissues and cell types. Differentiation continues in adulthood as adult stem cells divide and create fully differentiated daughter cells during tissue repair and during normal cell turnover. Some differentiation occurs in response to antigen exposure. Differentiation dramatically changes a cell's size, shape, membrane potential, metabolic activity, and responsiveness to signals. These changes are largely due to highly controlled modifications in gene expression and are the study of epigenetics. With a few exceptions, cellular differentiation almost never involves a change in the DNA sequence itself. Although metabolic composition does get altered quite dramatica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
REST (gene)
RE1-Silencing Transcription factor (REST), also known as Neuron-Restrictive Silencer Factor (NRSF), is a protein which in humans is encoded by the ''REST'' gene, and acts as a transcriptional repressor. REST is expressly involved in the repression of neural genes in non-neuronal cells. Many genetic disorders have been tied to alterations in the REST expression pattern, including colon and small-cell lung carcinomas found with truncated versions of REST. In addition to these cancers, defects in REST have also been attributed a role in Huntington Disease, neuroblastomas, and the effects of epileptic seizures and ischemia. Function This gene encodes a transcriptional repressor which represses neuronal genes in non-neuronal tissues. It is a member of the Kruppel-type zinc finger transcription factor family. It represses transcription by binding a DNA sequence element called the neuron-restrictive silencer element (NRSE, also known as RE1). The protein is also found in undifferent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endogeny
Endogenous substances and processes are those that originate from within a living system such as an organism, tissue, or cell. In contrast, exogenous substances and processes are those that originate from outside of an organism. For example, estradiol is an endogenous estrogen hormone produced within the body, whereas ethinylestradiol Ethinylestradiol (EE) is an estrogen medication which is used widely in birth control pills in combination with progestins. In the past, EE was widely used for various indications such as the treatment of menopausal symptoms, gynecological disord ... is an exogenous synthetic estrogen, commonly used in birth control pills. References External links *{{Wiktionary-inline, endogeny Biology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Small Ubiquitin-related Modifier 1
Small ubiquitin-related modifier 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SUMO1'' gene. Function This gene encodes a protein that is a member of the SUMO (small ubiquitin-like modifier) protein family. It is a ubiquitin-like protein and functions in a manner similar to ubiquitin in that it is bound to target proteins as part of a post-translational modification system. However, unlike ubiquitin, which is primarily associated with targeting proteins for proteasomal degradation, SUMO1 is involved in a variety of cellular processes, such as nuclear transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, and protein stability. It is not active until the last four amino acids of the carboxy-terminus have been cleaved off. Several pseudogenes have been reported for this gene. Alternate transcriptional splice variants encoding different isoforms have been characterized. Most cleft genes have a sumoylation component. Analysis of chromosomal anomalies in patients has led to the iden ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apoptosis
Apoptosis (from grc, ἀπόπτωσις, apóptōsis, 'falling off') is a form of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms. Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes (morphology) and death. These changes include blebbing, cell shrinkage, nuclear fragmentation, chromatin condensation, DNA fragmentation, and mRNA decay. The average adult human loses between 50 and 70 billion cells each day due to apoptosis. For an average human child between eight and fourteen years old, approximately twenty to thirty billion cells die per day. In contrast to necrosis, which is a form of traumatic cell death that results from acute cellular injury, apoptosis is a highly regulated and controlled process that confers advantages during an organism's life cycle. For example, the separation of fingers and toes in a developing human embryo occurs because cells between the digits undergo apoptosis. Unlike necrosis, apoptosis produces cell fragments called apoptotic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
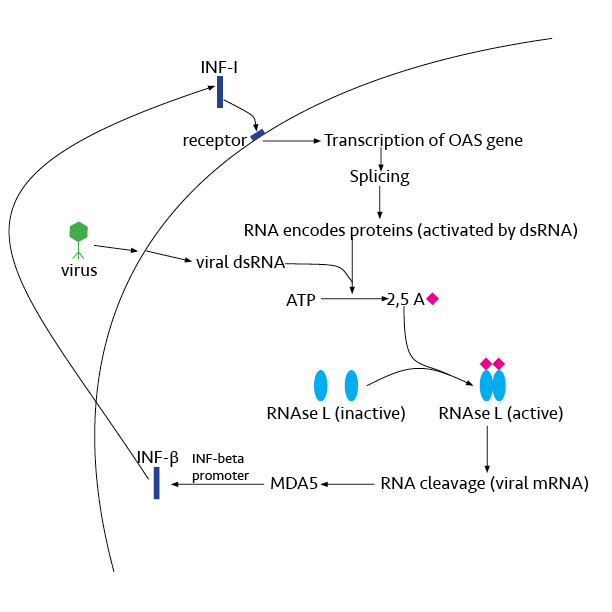
RNase L
Ribonuclease L or RNase L (for ''latent''), known sometimes as ribonuclease 4 or 2'-5' oligoadenylate synthetase-dependent ribonuclease — is an interferon (IFN)-induced ribonuclease which, upon activation, destroys all RNA within the cell (both cellular and viral). RNase L is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''RNASEL'' gene. This gene encodes a component of the interferon-regulated 2'-5'oligoadenylate (2'-5'A) system that functions in the antiviral and antiproliferative roles of interferons. RNase L is activated by dimerization, which occurs upon 2'-5'A binding, and results in cleavage of all RNA in the cell. This can lead to activation of MDA5, an RNA helicase involved in the production of interferons. Synthesis and activation RNase L is present in very minute quantities during the normal cell cycle. When interferon binds to cell receptors, it activates transcription of around 300 genes to bring about the antiviral state. Among the enzymes produced is RNase L, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interferon
Interferons (IFNs, ) are a group of signaling proteins made and released by host cells in response to the presence of several viruses. In a typical scenario, a virus-infected cell will release interferons causing nearby cells to heighten their anti-viral defenses. IFNs belong to the large class of proteins known as cytokines, molecules used for communication between cells to trigger the protective defenses of the immune system that help eradicate pathogens. Interferons are named for their ability to "interfere" with viral replication by protecting cells from virus infections. However, virus-encoded genetic elements have the ability to antagonize the IFN response contributing to viral pathogenesis and viral diseases. IFNs also have various other functions: they activate immune cells, such as natural killer cells and macrophages, and they increase host defenses by up-regulating antigen presentation by virtue of increasing the expression of major histocompatibility complex (M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytokine
Cytokines are a broad and loose category of small proteins (~5–25 kDa) important in cell signaling. Cytokines are peptides and cannot cross the lipid bilayer of cells to enter the cytoplasm. Cytokines have been shown to be involved in autocrine, paracrine and endocrine signaling as immunomodulating agents. Cytokines include chemokines, interferons, interleukins, lymphokines, and tumour necrosis factors, but generally not hormones or growth factors (despite some overlap in the terminology). Cytokines are produced by a broad range of cells, including immune cells like macrophages, B lymphocytes, T lymphocytes and mast cells, as well as endothelial cells, fibroblasts, and various stromal cells; a given cytokine may be produced by more than one type of cell. They act through cell surface receptors and are especially important in the immune system; cytokines modulate the balance between humoral and cell-based immune responses, and they regulate the maturation, growth, and res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transcription Factor
In molecular biology, a transcription factor (TF) (or sequence-specific DNA-binding factor) is a protein that controls the rate of transcription of genetic information from DNA to messenger RNA, by binding to a specific DNA sequence. The function of TFs is to regulate—turn on and off—genes in order to make sure that they are expressed in the desired cells at the right time and in the right amount throughout the life of the cell and the organism. Groups of TFs function in a coordinated fashion to direct cell division, cell growth, and cell death throughout life; cell migration and organization (body plan) during embryonic development; and intermittently in response to signals from outside the cell, such as a hormone. There are up to 1600 TFs in the human genome. Transcription factors are members of the proteome as well as regulome. TFs work alone or with other proteins in a complex, by promoting (as an activator), or blocking (as a repressor) the recruitment of RNA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |