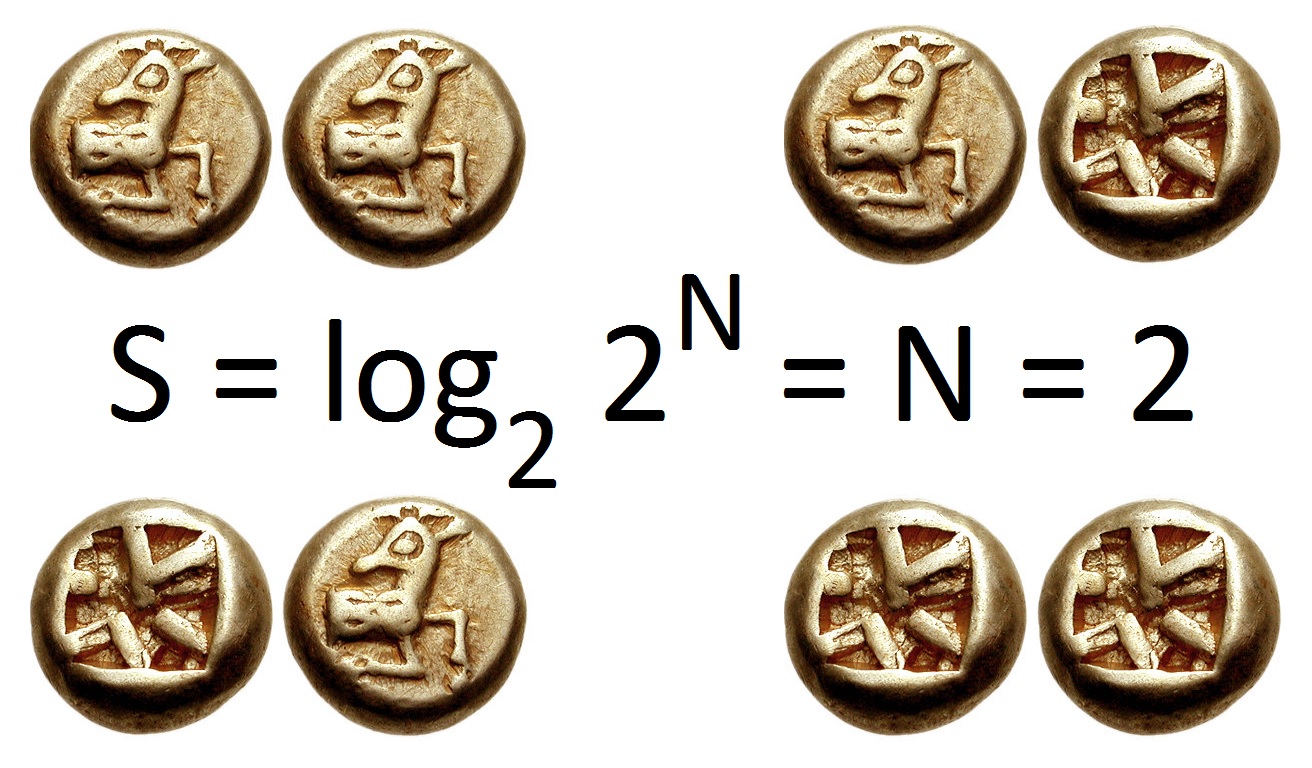|
H-theorem
In classical statistical mechanics, the ''H''-theorem, introduced by Ludwig Boltzmann in 1872, describes the tendency to decrease in the quantity ''H'' (defined below) in a nearly-ideal gas of molecules. L. Boltzmann,Weitere Studien über das Wärmegleichgewicht unter Gasmolekülen" Sitzungsberichte Akademie der Wissenschaften 66 (1872): 275-370. English translation: As this quantity ''H'' was meant to represent the entropy of thermodynamics, the ''H''-theorem was an early demonstration of the power of statistical mechanics as it claimed to derive the second law of thermodynamics—a statement about fundamentally irreversible processes—from reversible microscopic mechanics. It is thought to prove the second law of thermodynamics, albeit under the assumption of low-entropy initial conditions. The ''H''-theorem is a natural consequence of the kinetic equation derived by Boltzmann that has come to be known as Boltzmann's equation. The ''H''-theorem has led to considerable discuss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ludwig Boltzmann
Ludwig Eduard Boltzmann (; 20 February 1844 – 5 September 1906) was an Austrian physicist and philosopher. His greatest achievements were the development of statistical mechanics, and the statistical explanation of the second law of thermodynamics. In 1877 he provided the current definition of entropy, S = k_ \ln \Omega \!, where Ω is the number of microstates whose energy equals the system's energy, interpreted as a measure of statistical disorder of a system. Max Planck named the constant the Boltzmann constant. Statistical mechanics is one of the pillars of modern physics. It describes how macroscopic observations (such as temperature and pressure) are related to microscopic parameters that fluctuate around an average. It connects thermodynamic quantities (such as heat capacity) to microscopic behavior, whereas, in classical thermodynamics, the only available option would be to measure and tabulate such quantities for various materials. Biography Childhood and educatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statistical Mechanics
In physics, statistical mechanics is a mathematical framework that applies statistical methods and probability theory to large assemblies of microscopic entities. It does not assume or postulate any natural laws, but explains the macroscopic behavior of nature from the behavior of such ensembles. Statistical mechanics arose out of the development of classical thermodynamics, a field for which it was successful in explaining macroscopic physical properties—such as temperature, pressure, and heat capacity—in terms of microscopic parameters that fluctuate about average values and are characterized by probability distributions. This established the fields of statistical thermodynamics and statistical physics. The founding of the field of statistical mechanics is generally credited to three physicists: *Ludwig Boltzmann, who developed the fundamental interpretation of entropy in terms of a collection of microstates *James Clerk Maxwell, who developed models of probability distr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
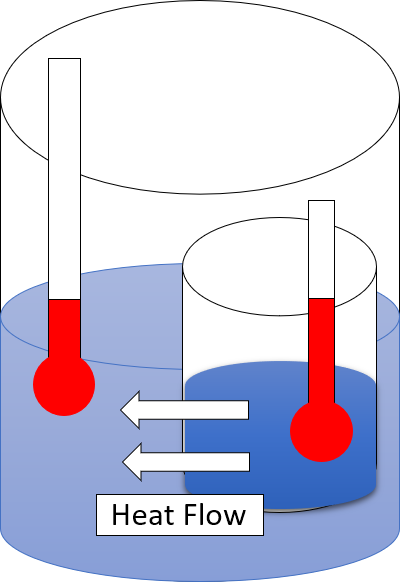
Second Law Of Thermodynamics
The second law of thermodynamics is a physical law based on universal experience concerning heat and Energy transformation, energy interconversions. One simple statement of the law is that heat always moves from hotter objects to colder objects (or "downhill"), unless energy in some form is supplied to reverse the direction of heat flow. Another definition is: "Not all heat energy can be converted into Work (thermodynamics), work in a cyclic process."Young, H. D; Freedman, R. A. (2004). ''University Physics'', 11th edition. Pearson. p. 764. The second law of thermodynamics in other versions establishes the concept of entropy as a physical property of a thermodynamic system. It can be used to predict whether processes are forbidden despite obeying the requirement of conservation of energy as expressed in the first law of thermodynamics and provides necessary criteria for spontaneous processes. The second law may be formulated by the observation that the entropy of isolated systems ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Josiah Willard Gibbs
Josiah Willard Gibbs (; February 11, 1839 – April 28, 1903) was an American scientist who made significant theoretical contributions to physics, chemistry, and mathematics. His work on the applications of thermodynamics was instrumental in transforming physical chemistry into a rigorous inductive science. Together with James Clerk Maxwell and Ludwig Boltzmann, he created statistical mechanics (a term that he coined), explaining the laws of thermodynamics as consequences of the statistical properties of Statistical ensemble (mathematical physics), ensembles of the possible states of a physical system composed of many particles. Gibbs also worked on the application of Maxwell's equations to problems in physical optics. As a mathematician, he invented modern vector calculus (independently of the British scientist Oliver Heaviside, who carried out similar work during the same period). In 1863, Yale University, Yale awarded Gibbs the first American Doctor of Philosophy, doctorate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maxwell–Boltzmann Distribution
In physics (in particular in statistical mechanics), the Maxwell–Boltzmann distribution, or Maxwell(ian) distribution, is a particular probability distribution named after James Clerk Maxwell and Ludwig Boltzmann. It was first defined and used for describing particle speeds in idealized gases, where the particles move freely inside a stationary container without interacting with one another, except for very brief collisions in which they exchange energy and momentum with each other or with their thermal environment. The term "particle" in this context refers to gaseous particles only (atoms or molecules), and the system of particles is assumed to have reached thermodynamic equilibrium.''Statistical Physics'' (2nd Edition), F. Mandl, Manchester Physics, John Wiley & Sons, 2008, The energies of such particles follow what is known as Maxwell–Boltzmann statistics, and the statistical distribution of speeds is derived by equating particle energies with kinetic energy. Mathematica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Information Entropy
In information theory, the entropy of a random variable is the average level of "information", "surprise", or "uncertainty" inherent to the variable's possible outcomes. Given a discrete random variable X, which takes values in the alphabet \mathcal and is distributed according to p: \mathcal\to , 1/math>: \Eta(X) := -\sum_ p(x) \log p(x) = \mathbb \log p(X), where \Sigma denotes the sum over the variable's possible values. The choice of base for \log, the logarithm, varies for different applications. Base 2 gives the unit of bits (or " shannons"), while base ''e'' gives "natural units" nat, and base 10 gives units of "dits", "bans", or " hartleys". An equivalent definition of entropy is the expected value of the self-information of a variable. The concept of information entropy was introduced by Claude Shannon in his 1948 paper " A Mathematical Theory of Communication",PDF archived froherePDF archived frohere and is also referred to as Shannon entropy. Shannon's theory d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermalisation
In physics, thermalisation is the process of physical bodies reaching thermal equilibrium through mutual interaction. In general the natural tendency of a system is towards a state of equipartition of energy and uniform temperature that maximizes the system's entropy. Thermalisation, thermal equilibrium, and temperature are therefore important fundamental concepts within statistical physics, statistical mechanics, and thermodynamics; all of which are a basis for many other specific fields of scientific understanding and engineering application. Examples of thermalisation include: * the achievement of equilibrium in a plasma. * the process undergone by high-energy neutrons as they lose energy by collision with a moderator. The hypothesis, foundational to most introductory textbooks treating quantum statistical mechanics, assumes that systems go to thermal equilibrium (thermalisation). The process of thermalisation erases local memory of the initial conditions. The eigenstate th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Chaos
In the kinetic theory of gases in physics, the molecular chaos hypothesis (also called ''Stosszahlansatz'' in the writings of Paul Ehrenfest) is the assumption that the velocities of colliding particles are uncorrelated, and independent of position. This means the probability that a pair of particles with given velocities will collide can be calculated by considering each particle separately and ignoring any correlation between the probability for finding one particle with velocity and probability for finding another velocity in a small region . James Clerk Maxwell introduced this approximation in 1867 although its origins can be traced back to his first work on the kinetic theory in 1860. The assumption of molecular chaos is the key ingredient that allows proceeding from the BBGKY hierarchy to Boltzmann's equation, by reducing the 2-particle distribution function showing up in the collision term to a product of 1-particle distributions. This in turn leads to Boltzmann's H-theo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boltzmann Equation
The Boltzmann equation or Boltzmann transport equation (BTE) describes the statistical behaviour of a thermodynamic system not in a state of equilibrium, devised by Ludwig Boltzmann in 1872.Encyclopaedia of Physics (2nd Edition), R. G. Lerner, G. L. Trigg, VHC publishers, 1991, ISBN (Verlagsgesellschaft) 3-527-26954-1, ISBN (VHC Inc.) 0-89573-752-3. The classic example of such a system is a fluid with temperature gradients in space causing heat to flow from hotter regions to colder ones, by the random but biased transport of the particles making up that fluid. In the modern literature the term Boltzmann equation is often used in a more general sense, referring to any kinetic equation that describes the change of a macroscopic quantity in a thermodynamic system, such as energy, charge or particle number. The equation arises not by analyzing the individual positions and momenta of each particle in the fluid but rather by considering a probability distribution for the positio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laws Of Thermodynamics
The laws of thermodynamics are a set of scientific laws which define a group of physical quantities, such as temperature, energy, and entropy, that characterize thermodynamic systems in thermodynamic equilibrium. The laws also use various parameters for thermodynamic processes, such as thermodynamic work and heat, and establish relationships between them. They state empirical facts that form a basis of precluding the possibility of certain phenomena, such as perpetual motion. In addition to their use in thermodynamics, they are important fundamental laws of physics in general, and are applicable in other natural sciences. Traditionally, thermodynamics has recognized three fundamental laws, simply named by an ordinal identification, the first law, the second law, and the third law.Guggenheim, E.A. (1985). ''Thermodynamics. An Advanced Treatment for Chemists and Physicists'', seventh edition, North Holland, Amsterdam, .Kittel, C. Kroemer, H. (1980). ''Thermal Physics'', second edit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boltzmann's Equation
The Boltzmann equation or Boltzmann transport equation (BTE) describes the statistical behaviour of a thermodynamic system not in a state of equilibrium, devised by Ludwig Boltzmann in 1872.Encyclopaedia of Physics (2nd Edition), R. G. Lerner, G. L. Trigg, VHC publishers, 1991, ISBN (Verlagsgesellschaft) 3-527-26954-1, ISBN (VHC Inc.) 0-89573-752-3. The classic example of such a system is a fluid with temperature gradients in space causing heat to flow from hotter regions to colder ones, by the random but biased transport of the particles making up that fluid. In the modern literature the term Boltzmann equation is often used in a more general sense, referring to any kinetic equation that describes the change of a macroscopic quantity in a thermodynamic system, such as energy, charge or particle number. The equation arises not by analyzing the individual positions and momenta of each particle in the fluid but rather by considering a probability distribution for the positi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isolated System
In physical science, an isolated system is either of the following: # a physical system so far removed from other systems that it does not interact with them. # a thermodynamic system enclosed by rigid immovable walls through which neither mass nor energy can pass. Though subject internally to its own gravity, an isolated system is usually taken to be outside the reach of external gravitational and other long-range forces. This can be contrasted with what (in the more common terminology used in thermodynamics) is called a closed system, being enclosed by selective walls through which energy can pass as heat or work, but not matter; and with an open system, which both matter and energy can enter or exit, though it may have variously impermeable walls in parts of its boundaries. An isolated system obeys the conservation law that its total energy–mass stays constant. Most often, in thermodynamics, mass and energy are treated as separately conserved. Because of the require ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |