|
Gül Baba
Gül Baba (died 1541), also known as Jafer, was an Ottoman Bektashi dervish poet and companion of Sultan Suleiman the Magnificent who took part in a number of campaigns in Europe from the reign of Mehmed II onwards. Biography A native of Merzifon (''Marsiwān'', in the vilāyet of Sivas, Anatolia), he was the son of Kutb’ül Arifin Veli’üddin İbn Yalınkılıç. In Hungary, Gül Baba is known as the "Father of Roses," a literal translation of the meaning of his names in Turkish; he is said to have introduced the flower to the country. However, this is likely a misunderstanding of the metaphorical meaning of the Turkish name, which referred to the dervish's status derived from his deep mystical knowledge of Allah. Roses, wild and domesticated, were already in Hungary by the time of the Ottoman invasion. The name could also be a corruption of ''Kel Baba'', meaning "Bald Father". Gül Baba is thought to have died in Buda during the first Muslim religious ceremony hel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) // CITED: p. 36 (PDF p. 38/338) also known as the Turkish Empire, was an empire that controlled much of Southeast Europe, Western Asia, and Northern Africa between the 14th and early 20th centuries. It was founded at the end of the 13th century in northwestern Anatolia in the town of Söğüt (modern-day Bilecik Province) by the Turkoman tribal leader Osman I. After 1354, the Ottomans crossed into Europe and, with the conquest of the Balkans, the Ottoman beylik was transformed into a transcontinental empire. The Ottomans ended the Byzantine Empire with the conquest of Constantinople in 1453 by Mehmed the Conqueror. Under the reign of Suleiman the Magnificent, the Ottoman Empire marked the peak of its power and prosperity, as well a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Islam In Hungary
Islam in Hungary has a long history that dates back to at least the 10th century. The influence of Sunni Islam was especially pronounced in the 16th century during the Ottoman period in Hungary. History Early history In the old form of the Hungarian language, Muslims were called ''Böszörmény'', cognates with ''Turkish'' Bozulmamış, which in turn descends from ar, مسلم, ''Muslim'', a term preserved as both a family name, and as that of the town Hajdúböszörmény. The first Islamic author to speak of this Muslim community was Yaqut al-Hamawi (575-626 AH/1179-1229 CE), he writes about a famous Hungarian student who studied in Aleppo, according to the student there were 30 Muslim villages in Hungary. Yaqut writes in his famous geographical dictionary, "Mu'ajam al-Buldan", about his meeting with a Hungarian Muslim youth in Syria who was studying Islam there and brought some details of the history and life of their people in Hungary. The Spaniard Muslim traveler Abu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pilgrim
A pilgrim (from the Latin ''peregrinus'') is a traveler (literally one who has come from afar) who is on Pilgrimage, a journey to a holy place. Typically, this is a physical journey (often on foot) to some place of special significance to the adherent of a particular religious belief system. In the spiritual literature of Christianity, the concept of pilgrim and pilgrimage may refer to the experience of life in World (theology), the world (considered as a period of exile) or to the inner path of the spiritual aspirant from a state of wretchedness to a state of beatitude. History Pilgrims and the making of pilgrimages are common in many religions, including the faiths of ancient Egypt, Persia in the Mithraism, Mithraic period, India, China, and Japan. The ancient Greece, Greek and Ancient Rome, Roman customs of consulting the Deity, gods at local oracles, such as those at Dodona or Delphi, both in Greece, are widely known. In Greece, pilgrimages could either be personal or state ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jesuits
The Society of Jesus ( la, Societas Iesu; abbreviation: SJ), also known as the Jesuits (; la, Iesuitæ), is a religious order (Catholic), religious order of clerics regular of pontifical right for men in the Catholic Church headquartered in Rome. It was founded in 1540 by Ignatius of Loyola and six companions, with the approval of Pope Paul III. The society is engaged in evangelization and apostolic ministry in 112 nations. Jesuits work in education, research, and cultural pursuits. Jesuits also give retreats, minister in hospitals and parishes, sponsor direct social and humanitarian ministries, and promote Ecumenism, ecumenical dialogue. The Society of Jesus is consecrated under the patron saint, patronage of Madonna della Strada, a title of the Blessed Virgin Mary, and it is led by a Superior General of the Society of Jesus, Superior General. The headquarters of the society, its Curia, General Curia, is in Rome. The historic curia of Ignatius is now part of the attached to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Catholicism In Hungary
The Catholic Church in Hungary or Hungarian Catholic Church ( hu, Magyar Katolikus Egyház) is part of the worldwide Catholic Church, under the spiritual leadership of the Pope in Rome. According to a 2019 survey by Eurobarometer, 62% of Hungarians consider themselves Catholics. The country is divided into 12 dioceses including 4 archdioceses. In addition, there is a territorial abbey and a separate sui juris particular Church for those who adhere to the Byzantine Rite known as the Hungarian Greek Catholic Church. History From early times to the accession of St. Stephen (997) Since the early times the territory of the former Kingdom of Hungary were inhabited by many peoples followed by several waves of migrations until the Hungarian conquest of the Carpathian Basin. At about the same time, under their leader Árpád ( 845 – 907), they began once more expeditions to the countries west of them in order to recon the neighboring environments and secure their newly fou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Buda (1686)
The siege of Buda (1686) ( hu, Buda visszafoglalása, lit=Recapture of Buda) was fought between the Holy League and the Ottoman Empire, as part of the follow-up campaign in Hungary after the Battle of Vienna. The Holy League retook Buda (modern day Budapest) after 78 days, ending almost 150 years of Ottoman rule. Background Ottoman Buda In 1541, Buda was conquered by the Turks in the siege of Buda, and was under Ottoman rule for the next 145 years. Under Ottoman rule the economic decline of Buda, the capital city of Hungary, was characterized by the stagnation of population. The population of Buda was not larger in 1686, than the population of the city two centuries earlier in the 15th century. The Ottomans allowed the Hungarian royal palace to fall into ruins. The amortized palace was later transformed into a gunpowder storage and magazine by the Ottomans, which caused its detonation during the siege in 1686. The original Christian Hungarian population did not feel secure d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Habsburg Monarchy
The Habsburg monarchy (german: Habsburgermonarchie, ), also known as the Danubian monarchy (german: Donaumonarchie, ), or Habsburg Empire (german: Habsburgerreich, ), was the collection of empires, kingdoms, duchies, counties and other polities that were ruled by the House of Habsburg, especially the dynasty's Austrian branch. The history of the Habsburg monarchy can be traced back to the election of Rudolf I as King of Germany in 1273 and his acquisition of the Duchy of Austria for the Habsburg in 1282. In 1482, Maximilian I acquired the Netherlands through marriage. Both realms passed to his grandson and successor, Charles V, who also inherited the Spanish throne and its colonial possessions, and thus came to rule the Habsburg empire at its greatest territorial extent. The abdication of Charles V in 1556 led to a division within the dynasty between his son Philip II of Spain and his brother Ferdinand I, who had served as his lieutenant and the elected king of Hungary and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pasha
Pasha, Pacha or Paşa ( ota, پاشا; tr, paşa; sq, Pashë; ar, باشا), in older works sometimes anglicized as bashaw, was a higher rank in the Ottoman Empire, Ottoman political and military system, typically granted to governors, generals, dignitary, dignitaries, and others. As an honorific, honorary title, ''Pasha'', in one of its various ranks, is similar to a British Peerage of the United Kingdom, peerage or knighthood, and was also one of the highest titles in the 20th-century Kingdom of Egypt. The title was also used in Morocco in the 20th century, where it denoted a regional official or governor of a district. Etymology The English word "pasha" comes from Turkish language, Turkish ('; also ()). The Oxford Dictionaries (website), Oxford Dictionaries attributes the origin of the English borrowing to the mid-17th century. The etymology of the Turkish word itself has been a matter of debate. Contrary to titles like emir (''amīr'') and bey (''beg''), which were es ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
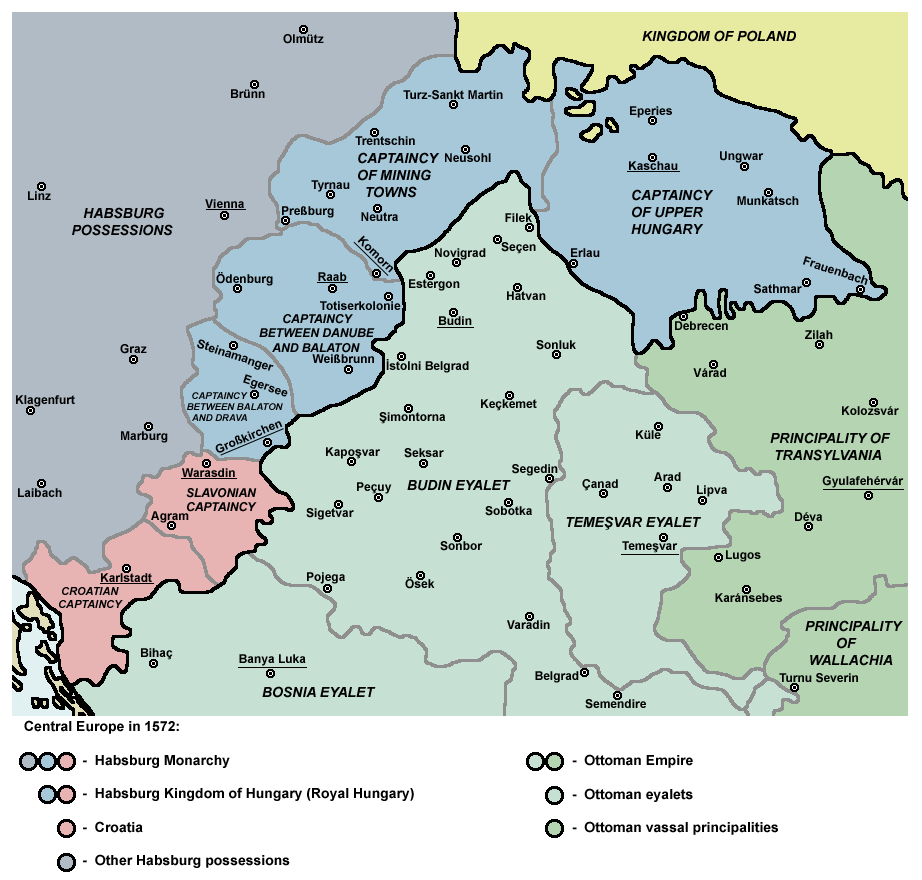
Ottoman Hungary
Ottoman Hungary ( hu, Török hódoltság) was the southern and central parts of what had been the Kingdom of Hungary in the late medieval period, which were conquered and ruled by the Ottoman Empire from 1541 to 1699. The Ottoman rule covered almost the entire region of the Great Hungarian Plain (except the northeastern parts) and Southern Transdanubia. The territory was invaded and annexed to the Ottoman Empire by Sultan Suleiman the Magnificent between 1521 and 1541. The north-western rim of the Hungarian kingdom remained unconquered and recognised members of the House of Habsburg as Kings of Hungary, giving it the name " Royal Hungary". The boundary between the two thereupon became the frontline in the Ottoman–Habsburg wars over the next 150 years. Following the defeat of the Ottomans in the Great Turkish War, most of Ottoman Hungary was ceded to the Habsburgs under the Treaty of Karlowitz in 1699. During the period of Ottoman rule, Hungary was divided for administrati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rózsadomb
The area known as Rózsadomb (, tr, Gültepe, lit.:"Rose Hill") is a wealthy area in the 2nd district of Budapest, the capital of Hungary. It is a member of the Buda Hills. Background Rózsadomb is part of the 2nd district of Budapest, in the Buda Hills, one of the most prestigious areas in Hungary. Most of the city's wealthiest and most famous residents live here (e.g. former prime minister Gordon Bajnai). House prices are amongst the highest in Hungary. The area has easy access to local parks and the forests and hills around the Buda area, while also reasonably near the downtown area. Although it is mostly covered with exclusive villas, many old, dilapidated buildings can also be found here, remaining from the pre-war era. Although Rózsadomb officially refers only to a relatively small part of the city, in broader sense other hilly and prominent parts of the 2nd district such as Vérhalom, Zöldmál, Rézmál, Csatárka, Szemlőhegy, Törökvész, Felhévíz or Nyék are v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Margaret Bridge
Margaret Bridge or Margit híd (sometimes ''Margit Bridge'') is a three-way bridge in Budapest, Hungary, connecting Buda and Pest across the Danube and linking Margaret Island to the banks. It is the second-northernmost and second-oldest public bridge in Budapest. It was designed by French engineer Ernest Goüin and built by the construction company Maison Ernest Goüin et Cie. between 1872 and 1876, the engineer in charge being Émile Nouguier. Margaret Bridge was the second permanent bridge in Budapest after Széchenyi Chain Bridge. This bridge leads up to Margaret Island, its two parts enclosing 165 degrees with each other at the embranchment towards the island. The reason for this unusual geometry is that the small extension to connect to Margaret Island was hastily inserted into the original design but not built until two decades later due to lack of funds. The bridge's two ends are * Jászai Mari tér (northern end of Grand Boulevard) and * Germanus Gyula park (stop of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |