|
Gödel, Escher, Bach
''Gödel, Escher, Bach: an Eternal Golden Braid'', also known as ''GEB'', is a 1979 book by Douglas Hofstadter. By exploring common themes in the lives and works of logician Kurt Gödel, artist M. C. Escher, and composer Johann Sebastian Bach, the book expounds concepts fundamental to mathematics, symmetry, and intelligence. Through short stories, illustrations, and analysis, the book discusses how systems can acquire meaningful context despite being made of "meaningless" elements. It also discusses self-reference and formal rules, isomorphism, what it means to communicate, how knowledge can be represented and stored, the methods and limitations of symbolic representation, and even the fundamental notion of "meaning" itself. In response to confusion over the book's theme, Hofstadter emphasized that ''Gödel, Escher, Bach'' is not about the relationships of mathematics, art, and music—but rather about how cognition emerges from hidden neurological mechanisms. One point in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Douglas Hofstadter
Douglas Richard Hofstadter (born February 15, 1945) is an American scholar of cognitive science, physics, and comparative literature whose research includes concepts such as the sense of self in relation to the external world, consciousness, analogy-making, artistic creation, literary translation, and discovery in mathematics and physics. His 1979 book '' Gödel, Escher, Bach: An Eternal Golden Braid'' won both the Pulitzer Prize for general nonfiction"General Nonfiction" . ''Past winners and finalists by category''. The Pulitzer Prizes. Retrieved March 17, 2012. and a (at that time called The American Book Award) for Science. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ant Colony
An ant colony is a population of a single ant species capable to maintain its complete lifecycle. Ant colonies are eusocial, communal, and efficiently organized and are very much like those found in other social Hymenoptera, though the various groups of these developed sociality independently through convergent evolution. The typical colony consists of one or more egg-laying queens, numerous sterile females (workers, soldiers) and, seasonally, many winged sexual males and females. In order to establish new colonies, ants undertake flights that occur at species-characteristic times of the day. Swarms of the winged sexuals (known as alates) depart the nest in search of other nests. The males die shortly thereafter, along with most of the females. A small percentage of the females survive to initiate new nests. Names The term "ant colony" refers to a population of workers, reproductive individuals, and brood that live together, cooperate, and treat one another non-aggressively ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jesu, Joy Of Man's Desiring
"Jesu, Joy of Man's Desiring" (or simply "Joy"; German: ''Jesus bleibet meine Freude'') is the most common English title of a piece of music derived from a chorale setting from the cantata ''Herz und Mund und Tat und Leben'', BWV 147 ("Heart and Mouth and Deed and Life"), composed by Johann Sebastian Bach in 1723. The same music on different stanzas of a chorale closes both parts of the cantata. A transcription by the English pianist Myra Hess (1890–1965) was published in 1926 for piano solo and in 1934 for piano duet. It is often performed slowly and reverently at wedding ceremonies, as well as during Christian festive seasons like Christmas and Easter. Background Bach composed a four-part setting with independent orchestral accompaniment of two stanzas of the hymn "", written by Martin Janus in 1661, which was sung to a melody by the violinist and composer Johann Schop, "". The movements conclude the two parts of the cantata. Bach scored the chorale movements (6 and 10) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SHRDLU
SHRDLU was an early natural-language understanding computer program, developed by Terry Winograd at MIT in 1968–1970. In the program, the user carries on a conversation with the computer, moving objects, naming collections and querying the state of a simplified " blocks world", essentially a virtual box filled with different blocks. SHRDLU was written in the Micro Planner and Lisp programming language on the DEC PDP-6 computer and a DEC graphics terminal. Later additions were made at the computer graphics labs at the University of Utah, adding a full 3D rendering of SHRDLU's "world". The name SHRDLU was derived from ETAOIN SHRDLU, the arrangement of the letter keys on a Linotype machine, arranged in descending order of usage frequency in English. Functionality SHRDLU was primarily a language parser that allowed user interaction using English terms. The user instructed SHRDLU to move various objects around in the "blocks world" containing various basic objects: blocks ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Word Play
Word play or wordplay (also: play-on-words) is a literary technique and a form of wit in which words used become the main subject of the work, primarily for the purpose of intended effect or amusement. Examples of word play include puns, phonetic mix-ups such as spoonerisms, obscure words and meanings, clever rhetorical excursions, oddly formed sentences, double entendres, and telling character names (such as in the play '' The Importance of Being Earnest'', ''Ernest'' being a given name that sounds exactly like the adjective ''earnest''). Word play is quite common in oral cultures as a method of reinforcing meaning. Examples of text-based ( orthographic) word play are found in languages with or without alphabet-based scripts, such as homophonic puns in Mandarin Chinese. Techniques Some techniques often used in word play include interpreting idioms literally and creating contradictions and redundancies, as in Tom Swifties: :"Hurry up and get to the back of the ship," To ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metafiction
Metafiction is a form of fiction which emphasises its own narrative structure in a way that continually reminds the audience that they are reading or viewing a fictional work. Metafiction is self-conscious about language, literary form, and story-telling, and works of metafiction directly or indirectly draw attention to their status as artifacts. Metafiction is frequently used as a form of parody or a tool to undermine literary conventions and explore the relationship between literature and reality, life, and art. Although metafiction is most commonly associated with postmodern literature that developed in the mid-20th century, its use can be traced back to much earlier works of fiction, such as '' The Canterbury Tales'' ( Geoffrey Chaucer, 1387), '' Don Quixote'' ( Miguel de Cervantes, 1605), '' The Life and Opinions of Tristram Shandy, Gentleman'' ( Laurence Sterne, 1759), and ''Vanity Fair'' ( William Makepeace Thackeray, 1847). Metafiction became particularly prominent in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lewis Carroll
Charles Lutwidge Dodgson (; 27 January 1832 – 14 January 1898), better known by his pen name Lewis Carroll, was an English author, poet and mathematician. His most notable works are '' Alice's Adventures in Wonderland'' (1865) and its sequel ''Through the Looking-Glass'' (1871). He was noted for his facility with word play, logic, and fantasy. His poems '' Jabberwocky'' (1871) and ''The Hunting of the Snark'' (1876) are classified in the genre of literary nonsense. Carroll came from a family of high-church Anglicans, and developed a long relationship with Christ Church, Oxford, where he lived for most of his life as a scholar and teacher. Alice Liddell, the daughter of Christ Church's dean Henry Liddell, is widely identified as the original inspiration for ''Alice in Wonderland'', though Carroll always denied this. An avid puzzler, Carroll created the word ladder puzzle (which he then called "Doublets"), which he published in his weekly column for ''Vanity Fair'' ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zeno Of Elea
Zeno of Elea (; grc, Ζήνων ὁ Ἐλεᾱ́της; ) was a pre-Socratic Greek philosopher of Magna Graecia and a member of the Eleatic School founded by Parmenides. Aristotle called him the inventor of the dialectic. He is best known for his paradoxes, which Bertrand Russell described as "immeasurably subtle and profound". Life Little is known for certain about Zeno's life. Although written nearly a century after Zeno's death, the primary source of biographical information about Zeno is Plato's '' Parmenides'' and he is also mentioned in Aristotle's ''Physics''. In the dialogue of ''Parmenides'', Plato describes a visit to Athens by Zeno and Parmenides, at a time when Parmenides is "about 65", Zeno is "nearly 40", and Socrates is "a very young man".Plato, ''Parmenides'127b–e (at footnote n. 2) Assuming an age for Socrates of around 20 and taking the date of Socrates' birth as 469 BC gives an approximate date of birth for Zeno of 490 BC. Plato says that Zeno was " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
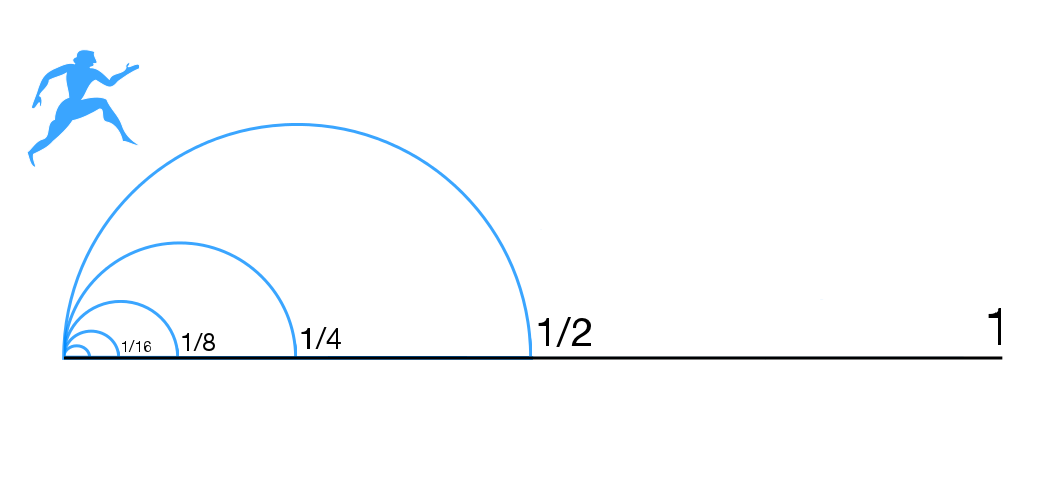
Achilles And The Tortoise
Zeno's paradoxes are a set of philosophical problems generally thought to have been devised by Greek philosopher Zeno of Elea (c. 490–430 BC) to support Parmenides' doctrine that contrary to the evidence of one's senses, the belief in plurality and change is mistaken, and in particular that motion is nothing but an illusion. It is usually assumed, based on Plato's ''Parmenides'' (128a–d), that Zeno took on the project of creating these paradoxes because other philosophers had created paradoxes against Parmenides' view. Thus Plato has Zeno say the purpose of the paradoxes "is to show that their hypothesis that existences are many, if properly followed up, leads to still more absurd results than the hypothesis that they are one." Plato has Socrates claim that Zeno and Parmenides were essentially arguing exactly the same point. Some of Zeno's nine surviving paradoxes (preserved in Aristotle's ''Physics'' [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Book Award For Nonfiction
The National Book Award for Nonfiction is one of five U.S. annual National Book Awards, which are given by the National Book Foundation to recognize outstanding literary work by U.S. citizens. They are awards "by writers to writers". The panelists are five "writers who are known to be doing great work in their genre or field". The original National Book Awards recognized the "Most Distinguished" biography and nonfiction books (two) of 1935 and 1936, and the "Favorite" nonfiction books of 1937 to 1940. The "Bookseller Discovery" and the "Most Original Book" sometimes recognized nonfiction. (See below.) The general "Nonfiction" award was one of three when the National Book Awards were re-established in 1950 for 1949 publications, which the National Book Foundation considers the origin of its current Awards series. From 1964 to 1983, under different administrators, there were multiple nonfiction categories. The current Nonfiction award recognizes one book written by a U.S. citizen a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Winners Of The National Book Award
These authors and books have won the annual National Book Awards, awarded to American authors by the National Book Foundation based in the United States. History of categories The National Book Awards were first awarded to four 1935 publications in May 1936. Contrary to that historical fact, the National Book Foundation currently recognizes only a history of purely literary awards that begins in 1950. The pre-war awards and the 1980 to 1983 graphics awards are covered below following the main list of current award categories. There have been four award categories since 1996, Fiction, Non-fiction, Poetry, and Young People's Literature. The main list below is organized by the current award categories and by year. The four categories' winners are selected from hundreds of preliminary nominees. For example, in the 2010 cycle the preliminary phase nominees ranged from 148 in the Poetry category to 435 in the Nonfiction category. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)