 |
Gwanghwamun
Gwanghwamun () is the main and largest gate of Gyeongbokgung, Gyeongbok Palace, in Jongno-gu, Seoul, South Korea. It is located at a three-way intersection at the northern end of Sejongno. As a landmark and symbol of History of Seoul, Seoul's long history as the capital city during the Joseon Dynasty, the gate has gone through multiple periods of destruction and disrepair. The most recent large-scale restoration work on the gate was finished and it was opened to the public on August 15, 2010. History Gwanghwamun was first constructed in 1395 as the main gate to Gyeongbokgung, Gyeongbok Palace, the main and most important royal palace during the Joseon Dynasty. During the Japanese invasions of Korea (1592–1598), 1592 Japanese invasion, it was destroyed by fire and left in ruins for over 250 years. Gwanghwamun was reconstructed in 1867 along with the rest of Gyeongbokgung Palace by the order of regent Daewongun during the reign of Gojong of Korea, Emperor Gojong. The gate stood ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Gwanghwamun Name Plate
Gwanghwamun () is the main and largest gate of Gyeongbok Palace, in Jongno-gu, Seoul, South Korea. It is located at a three-way intersection at the northern end of Sejongno. As a landmark and symbol of Seoul's long history as the capital city during the Joseon Dynasty, the gate has gone through multiple periods of destruction and disrepair. The most recent large-scale restoration work on the gate was finished and it was opened to the public on August 15, 2010. History Gwanghwamun was first constructed in 1395 as the main gate to Gyeongbok Palace, the main and most important royal palace during the Joseon Dynasty. During the 1592 Japanese invasion, it was destroyed by fire and left in ruins for over 250 years. Gwanghwamun was reconstructed in 1867 along with the rest of Gyeongbokgung Palace by the order of regent Daewongun during the reign of Emperor Gojong. The gate stood until 1926, when the Japanese government had it deconstructed and moved it just to the southeast of the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Gyeongbokgung
Gyeongbokgung (), also known as Gyeongbokgung Palace or Gyeongbok Palace, was the main royal palace of the Joseon dynasty. Built in 1395, it is located in northern Seoul, South Korea. The largest of the '' Five Grand Palaces'' built by the Joseon dynasty, Gyeongbokgung served as the home of Kings of the Joseon dynasty, the Kings' households, as well as the government of Joseon. Gyeongbokgung continued to serve as the main palace of the Joseon dynasty until the premises were destroyed by fire during the Imjin War (1592–1598) and abandoned for two centuries. However, in the 19th century, all of the palace's 7,700 rooms were later restored under the leadership of Prince Regent Heungseon during the reign of King Gojong. Some 500 buildings were restored on a site of over 40 hectares. The architectural principles of ancient Korea were incorporated into the tradition and appearance of the Joseon royal court. In the early 20th century, much of the palace was systematically destroye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Sejongno
Sejongno (), also known as Sejong-daero, is a street that runs through Jongno-gu in downtown Seoul. It is named after King Sejong the Great of Joseon. The street is 600 meters in length, but due to its central location it is of great symbolic importance. It points north to Gwanaksan and Bukhansan (Mountains), and the Joseon Dynasty palace, Gyeongbokgung. It is also of historical significance as the location for royal administrative buildings and features statues of the Admiral Yi Sun-sin of Joseon Dynasty and King Sejong the Great of Joseon. Characteristic At the crossroads, stands the statue of the Admiral Yi Sun-sin, the naval war hero of Korea. At the northern end of Sejongno sits Gwanghwamun, the gate at the entrance to Gyeongbokgung. To either side of the street rests the Public Prosecutors Office, Sejong Center, U.S. Embassy, Kyobo Life Insurance, Kyobo Book Centre and Donga Ilbo headquarters. It was customary for the Korean Marines who are about to graduate t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Jongno-gu
Bosingak bell pavilion Jongno District () is a district () in central Seoul, South Korea. It takes its name from a major local street, Jongno, which means "Bell Road". Characteristics Jongno District has been the center of the city for 600 years, since it is where the Joseon dynasty established its capital city. Jongno District is commonly referred to as the face and heart of Korea because of its important roles in the politics, economics, culture, and history as the capital city. Jongno District is home to palaces in which the kings used to reside and work, such as Gyeongbok Palace, Changdeok Palace, Changgyeonggung and Unhyeon Palace. The South Korean president's former residence, the Cheongwadae, is also located in the Jongno District. Due to its rich history, Jongno District attracts visitors and tourists, especially those interested in Korean history and culture. These include the restored Cheonggyecheon stream, the traditional neighborhood of Insa-dong, and the Jo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Cultural Heritage Administration Of Korea
The Cultural Heritage Administration () or CHA, formerly the Cultural Properties Administration, is the agency of the South Korean government charged with preserving and promoting Korean cultural heritage. It is headquartered in the city of Daejeon at the Daejeon Government Complex. Previously part of the Ministry of Culture and Tourism, it was elevated to a sub-ministerial agency in 1999. History The Cultural Properties Administration was formally established in October 1961, but descends from the Former Royal Properties Administration to the Office created in November 1945 at the beginning of American military rule to replace the Office of the Yi Dynasty. The 1962 Cultural Property Protection Law was modelled on the Japanese 1950 Law for the Protection of Cultural Properties. Administration In accordance with Article 2 of the 1962 Cultural Property Protection Law, cultural heritage is classified in four main categories: Tangible Cultural Heritage (including National Trea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Japanese General Government Building, Seoul
The Japanese General Government Building ( ko, 조선총독부 청사, ''Joseon-chongdokbu Cheongsa''), also known as the Government-General Building and the Seoul Capitol, was a building located in Jongno District of Seoul, South Korea, from 1926 to 1996. The Government-General Building was constructed by the Empire of Japan on the site of the Gyeongbokgung complex, the royal palace of the Joseon, and was the largest government building in East Asia. The Government-General Building served as the chief administrative building of Chōsen and the seat of its Governor-General in Keijō from 1926 until 1945. The Government-General Building was the scene of numerous important events after South Korean independence in 1948, becoming the seat of the National Assembly of South Korea and housing offices of the Government of South Korea until 1950 when it was damaged during the Korean War and intentionally left derelict. President Park Chung-hee restored the Government-General Building ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Korea Under Japanese Rule
Between 1910 and 1945, Korea was ruled as a part of the Empire of Japan. Joseon Korea had come into the Japanese sphere of influence with the Japan–Korea Treaty of 1876; a complex coalition of the Meiji government, military, and business officials began a process of integrating Korea's politics and economy with Japan. The Korean Empire, proclaimed in 1897, became a protectorate of Japan with the Japan–Korea Treaty of 1905; thereafter Japan ruled the country indirectly through the Japanese Resident-General of Korea. Japan formally annexed the Korean Empire with the Japan–Korea Treaty of 1910, without the consent of the former Korean Emperor Gojong, the regent of the Emperor Sunjong. Upon its annexation, Japan declared that Korea would henceforth be officially named Chōsen. This name was recognized internationally until the end of Japanese colonial rule. The territory was administered by the Governor-General of Chōsen based in Keijō (Seoul). Japanese rule prior ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
South Korean Government
The Government of South Korea is the union government of the Republic of Korea, created by the Constitution of South Korea as the executive, legislative and judicial authority of the republic. The president acts as the head of state and is the highest figure of executive authority in the country, followed by the prime minister and government ministers in decreasing order. The Executive and Legislative branches operate primarily at the national level, although various ministries in the executive branch also carry out local functions. Local governments are semi-autonomous and contain executive and legislative bodies of their own. The judicial branch operates at both the national and local levels. The South Korean government's structure is determined by the Constitution of the Republic of Korea. This document has been revised several times since its first promulgation in 1948 (for details, see History of South Korea). However, it has retained many broad characteristics; with the e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
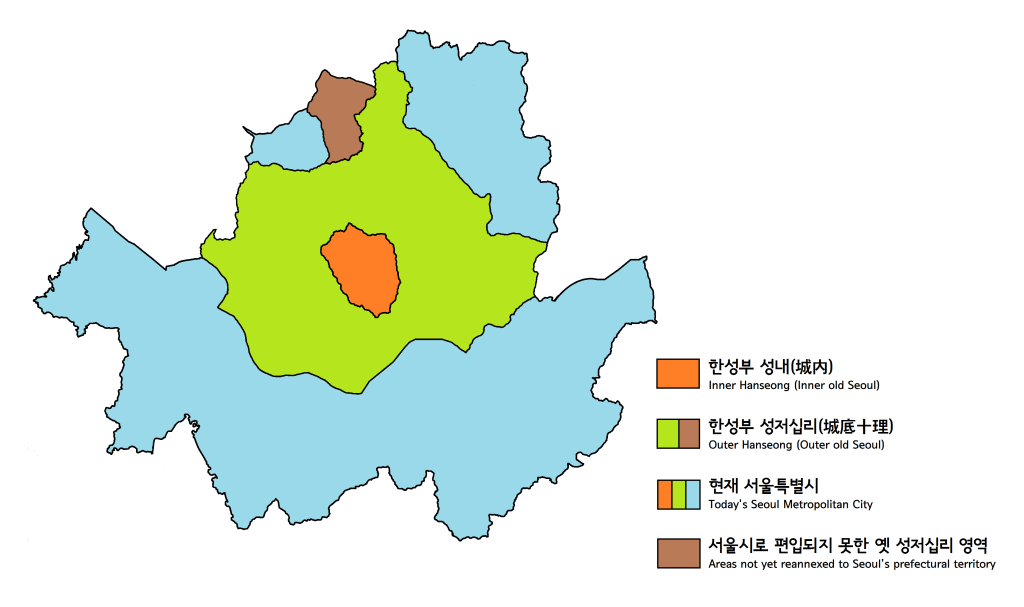 |
History Of Seoul
The history of Seoul can be traced back as far as 18 BC, although humans have occupied the area now known as Seoul since the Paleolithic Age. It has been the capital of numerous kingdoms on the Korean Peninsula since it was established. Early history Prehistoric It is believed that humans were living in the area that is now Seoul along the lower reaches of the Han River during the Paleolithic Age and archaeological research shows that people began to lead settled lives starting in the Neolithic Age. Prehistoric remains that are unearthed in the Amsa Prehistoric Site (암사선사유적지, ''Amsa Seonsa Yujeokji''), located in Amsa-dong, Gangdong District, date back to about 3,000 to 7,000 years ago. With the introduction of bronze ware from about 700 BC, settlements gradually began to spread from the river basin toward inland areas. Three Kingdoms and Unified Silla period In 18 BC, the kingdom of Baekje founded its capital city, Wiryeseong (위례성), which is believ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
South Korea
South Korea, officially the Republic of Korea (ROK), is a country in East Asia, constituting the southern part of the Korea, Korean Peninsula and sharing a Korean Demilitarized Zone, land border with North Korea. Its western border is formed by the Yellow Sea, while its eastern border is defined by the Sea of Japan. South Korea claims to be the sole legitimate government of the entire peninsula and List of islands of South Korea, adjacent islands. It has a Demographics of South Korea, population of 51.75 million, of which roughly half live in the Seoul Capital Area, the List of metropolitan areas by population, fourth most populous metropolitan area in the world. Other major cities include Incheon, Busan, and Daegu. The Korean Peninsula was inhabited as early as the Lower Paleolithic period. Its Gojoseon, first kingdom was noted in Chinese records in the early 7th century BCE. Following the unification of the Three Kingdoms of Korea into Unified Silla, Silla and Balhae in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Dancheong
''Dancheong'' ( ko, 단청; 丹青) refers to Korean traditional decorative colouring on wooden buildings and artifacts for the purpose of style. It literally means "cinnabar and blue-green" in Korean, and is sometimes translated as "red and blue" in English. Along with its decorations and the choice of paint colours, Dancheong carries various symbolic meanings. It is based on five basic colours; blue (east), white (west), red (south), black (north), and yellow (center). The use of those five colours reflected the use of the yin and yang principle and the Philosophy of the five elements. The Dancheong is usually used in important places, such as temples and palaces, and can even be found on the eaves of temple's roofs with patterns of animals (e.g. dragons, lions, cranes). Dancheong also functions not only as decoration, but also for practical purposes such as to protect building surfaces against temperature and to make the crudeness of materials less conspicuous. It also protec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |