|
Guortepir
Vortiporius or Vortipor ( owl, Guortepir, Middle Welsh ''Gwrdeber'' or ''Gwerthefyr'') was a king of Dyfed in the early to mid-6th century. He ruled over an area approximately corresponding to modern Pembrokeshire, Wales. Records from this era are scant, and virtually nothing is known of him or his kingdom. The only contemporary information about Vortiporius comes from the Welsh ecclesiastic Gildas, in a highly allegorical condemnation from his ''De Excidio et Conquestu Britanniae'' ( en, "On the Ruin and Conquest of Britain"). At the time the work was written (c. 540), Gildas says that Vortiporius was king of Dyfed, that he was grey with age, that his wife had died, and that he had at least one daughter., ''De Excidio'', section 31 (in English), ''De Excidio'', section 31 (in Latin) As a legendary king in Geoffrey of Monmouth's 12th-century treatment of the Matter of Britain, the ''Historia Regum Britanniae'', Vortiporius was the successor of Aurelius Conanus and was succeed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
De Excidio Et Conquestu Britanniae
''De Excidio et Conquestu Britanniae'' ( la, On the Ruin and Conquest of Britain, sometimes just ''On the Ruin of Britain'') is a work written in Latin by the 6th-century AD British cleric St Gildas. It is a sermon in three parts condemning the acts of Gildas' contemporaries, both secular and religious, whom he blames for the dire state of affairs in sub-Roman Britain. It is one of the most important sources for the history of Britain in the 5th and 6th centuries, as it is the only significant source for the period written by a near contemporary of the people and events described. Part I contains a narrative of British history from the Roman conquest to Gildas' time; it includes references to Ambrosius Aurelianus and the Britons' victory against the Saxons at the Battle of Mons Badonicus. Part II is a condemnation of five kings for their various sins, including both obscure figures and relatively well-documented ones such as Maelgwn Gwynedd. Part III is a similar attack upo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eochaid Allmuir
Eochaid or Eochaidh (earlier Eochu or Eocho, sometimes Anglicised as Eochy, Achaius or Haughey) is a popular medieval Irish and Scottish Gaelic name deriving from Old Irish ''ech'', horse, borne by a variety of historical and legendary figures. Variations List *Eochaid mac Eirc, mythological king of the Fir Bolg in the 16th or 20th century BC *Eochaid Ollathair, also known as The Dagda, mythical king of the Tuatha Dé Danann, said to have ruled Ireland in the 15th or 18th century BC *Eochaid Faebar Glas, legendary High King of Ireland of the 13th or 15th century BC *Eochaid Étgudach, legendary High King of Ireland of the 12th or 15th century BC *Eochaid Mumho, legendary High King of Ireland of the 12th or 15th century BC *Eochaid Apthach, legendary High King of Ireland of the 9th or 10th century BC *Eochaid Uaircheas, legendary High King of Ireland of the 8th or 9th century BC *Eochaid Fiadmuine, legendary High King of Ireland of the 8th or 9th century BC *Eochaid mac Ailella, l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gododdin
The Gododdin () were a Brittonic people of north-eastern Britannia, the area known as the Hen Ogledd or Old North (modern south-east Scotland and north-east England), in the sub-Roman period. Descendants of the Votadini, they are best known as the subject of the 6th-century Welsh poem ''Y Gododdin'', which memorialises the Battle of Catraeth and is attributed to Aneirin. The name ''Gododdin'' is the Modern Welsh form, but the name appeared in Old Welsh as ''Guotodin'' and derived from the tribal name '' Votadini'' recorded in Classical sources, such as in Greek texts from the Roman period. Kingdom It is not known exactly how far the kingdom of the Gododdin extended, possibly from the Stirling area to the kingdom of '' Bryneich'' (Bernicia), and including what are now the Lothian and Borders regions of eastern Scotland. It was bounded to the west by the Brittonic Kingdom of Strathclyde, and to the north by the Picts. Those living around Clackmannanshire were known as the Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rheged
Rheged () was one of the kingdoms of the ''Hen Ogledd'' ("Old North"), the Brittonic-speaking region of what is now Northern England and southern Scotland, during the post-Roman era and Early Middle Ages. It is recorded in several poetic and bardic sources, although its borders are not described in any of them. A recent archaeological discovery suggests that its stronghold was located in what is now Galloway in Scotland rather than, as was previously speculated, being in Cumbria. Rheged possibly extended into Lancashire and other parts of northern England. In some sources, Rheged is intimately associated with the king Urien Rheged and his family. Its inhabitants spoke Cumbric, a Brittonic dialect closely related to Old Welsh. Etymology The origin of the name ''Rheged'' has been described as "problematic". One Brittonic-language solution is that the name may be a compound of ''rö-'', a prefix meaning "great", and ''cę:d'' meaning "wood, forest" (c.f. Welsh ''coed'') although ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Strathclyde
Strathclyde (lit. "Strath of the River Clyde", and Strað-Clota in Old English), was a Brittonic successor state of the Roman Empire and one of the early medieval kingdoms of the Britons, located in the region the Welsh tribes referred to as Yr Hen Ogledd (“the Old North"), which comprised the Brythonic-speaking parts of what is now southern Scotland and northern England. The kingdom developed during Britain's post-Roman period. It is also known as ''Alt Clut'', a Brittonic term for Dumbarton Castle, the medieval capital of the region. It may have had its origins with the Damnonii people of Ptolemy's ''Geography''. The language of Strathclyde is known as Cumbric, a language that is closely related to Old Welsh, and, among modern languages, is most closely related to Welsh, Cornish, and Breton. Scottish toponymy and archaeology points to some later settlement by Vikings or Norse–Gaels (see Scandinavian Scotland), although to a lesser degree than in neighbouring Galloway. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Damnonii
The Damnonii (also referred to as Damnii) were a Brittonic people of the late 2nd century who lived in what became the Kingdom of Strathclyde by the Early Middle Ages, and is now southern Scotland. They are mentioned briefly in Ptolemy's ''Geography'', where he uses both of the terms "Damnonii" and "Damnii" to describe them, and there is no other historical record of them, except arguably by Gildas three centuries later. Their cultural and linguistic affinity is presumed to be Brythonic. However, there is no unbroken historical record, and a partly Pictish origin is not precluded. The Romans under Agricola had campaigned in the area in 81, and it was Roman-occupied (at least nominally) between the time that Hadrian's Wall was built (c. 122), through the building of the Antonine Wall (c. 142), until the pullback to Hadrian's Wall in 164. Ptolemy's ''Geography'' was written within this timeframe, so his account is contemporary. Etymology The tribe's name is nearly identical t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
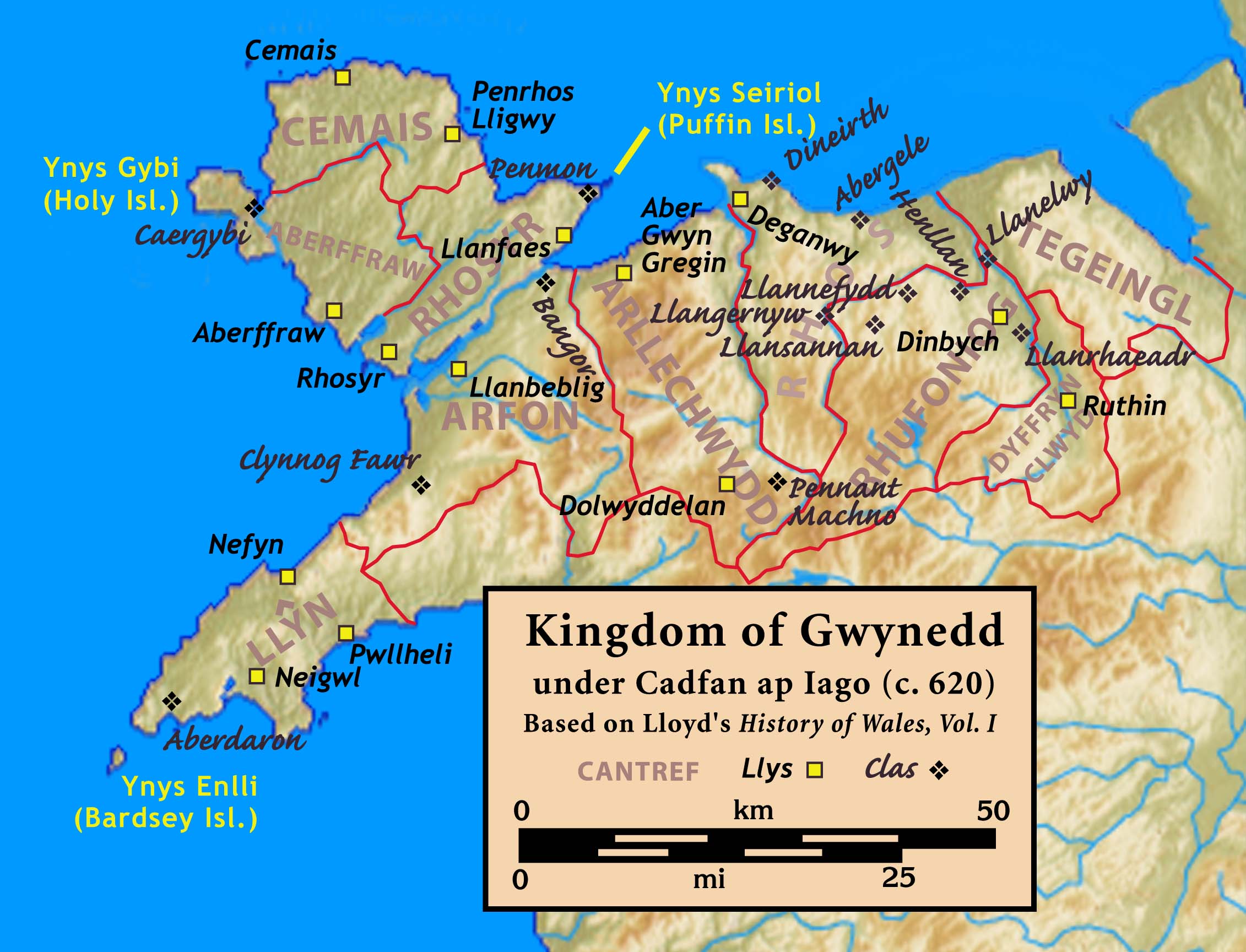
Kingdom Of Gwynedd
The Kingdom of Gwynedd (Medieval Latin: ; Middle Welsh: ) was a Welsh kingdom and a Roman Empire successor state that emerged in sub-Roman Britain in the 5th century during the Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain. Based in northwest Wales, the rulers of Gwynedd repeatedly rose to dominance and were acclaimed as " King of the Britons" before losing their power in civil wars or invasions. The kingdom of Gruffydd ap Llywelynthe King of Wales from 1055 to 1063was shattered by a Saxon invasion in 1063 just prior to the Norman invasion of Wales, but the House of Aberffraw restored by Gruffudd ap Cynan slowly recovered and Llywelyn the Great of Gwynedd was able to proclaim the Principality of Wales at the Aberdyfi gathering of Welsh princes in 1216. In 1277, the Treaty of Aberconwy between Edward I of England and Llewelyn's grandson Llywelyn ap Gruffudd granted peace between the two but would also guarantee that Welsh self-rule would end upon Llewelyn's death, and so it represented ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apocalypse
Apocalypse () is a literary genre in which a supernatural being reveals cosmic mysteries or the future to a human intermediary. The means of mediation include dreams, visions and heavenly journeys, and they typically feature symbolic imagery drawn from the Hebrew Bible, cosmological and (pessimistic) historical surveys, the division of time into periods, esoteric numerology, and claims of ecstasy and inspiration. Almost all are written under pseudonyms (false names), claiming as author a venerated hero from previous centuries, as with Book of Daniel, composed during the 2nd century BCE but bearing the name of the legendary Daniel. Eschatology, from Greek ''eschatos'', last, concerns expectations of the end of the present age, and apocalyptic eschatology is the application of the apocalyptic world-view to the end of the world, when God will punish the wicked and reward the faithful. An apocalypse will often contain much eschatological material, but need not: the baptism of J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global population. Its adherents, known as Christians, are estimated to make up a majority of the population in 157 countries and territories, and believe that Jesus is the Son of God, whose coming as the messiah was prophesied in the Hebrew Bible (called the Old Testament in Christianity) and chronicled in the New Testament. Christianity began as a Second Temple Judaic sect in the 1st century Hellenistic Judaism in the Roman province of Judea. Jesus' apostles and their followers spread around the Levant, Europe, Anatolia, Mesopotamia, the South Caucasus, Ancient Carthage, Egypt, and Ethiopia, despite significant initial persecution. It soon attracted gentile God-fearers, which led to a departure from Jewish customs, and, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Britain
Britain most often refers to: * The United Kingdom, a sovereign state in Europe comprising the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland and many smaller islands * Great Britain, the largest island in the United Kingdom and Europe. Britain may also refer to: Places * British Isles, an archipelago comprising Great Britain, Ireland and many other smaller islands * Roman Britain, a Roman province corresponding roughly to modern-day England and Wales * Historical predecessors to the present-day United Kingdom: ** Kingdom of Great Britain (1707 to 1801) ** United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland (1801 to 1922) * Britain (place name) * Britain, Virginia, an unincorporated community in the United States People * Calvin Britain (1800–1862), an American politician * Kristen Britain, an American novelist Other uses * Captain Britain, a Marvel Comics superhero See also * * * Terminology of the British Isles * England * Britains * Britannia * Britis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ogham
Ogham (Modern Irish: ; mga, ogum, ogom, later mga, ogam, label=none ) is an Early Medieval alphabet used primarily to write the early Irish language (in the "orthodox" inscriptions, 4th to 6th centuries AD), and later the Old Irish language (scholastic ogham, 6th to 9th centuries). There are roughly 400 surviving orthodox inscriptions on stone monuments throughout Ireland and western Britain, the bulk of which are in southern Munster. The largest number outside Ireland are in Pembrokeshire, Wales. The vast majority of the inscriptions consist of personal names. According to the High Medieval ''Bríatharogam'', the names of various trees can be ascribed to individual letters. For this reason, ogam is sometimes known as the Celtic tree alphabet. The etymology of the word ''ogam'' or ''ogham'' remains unclear. One possible origin is from the Irish ''og-úaim'' 'point-seam', referring to the seam made by the point of a sharp weapon. Origins It is generally thought that th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





_(14760479206).jpg)