|
Gunpowder Engine
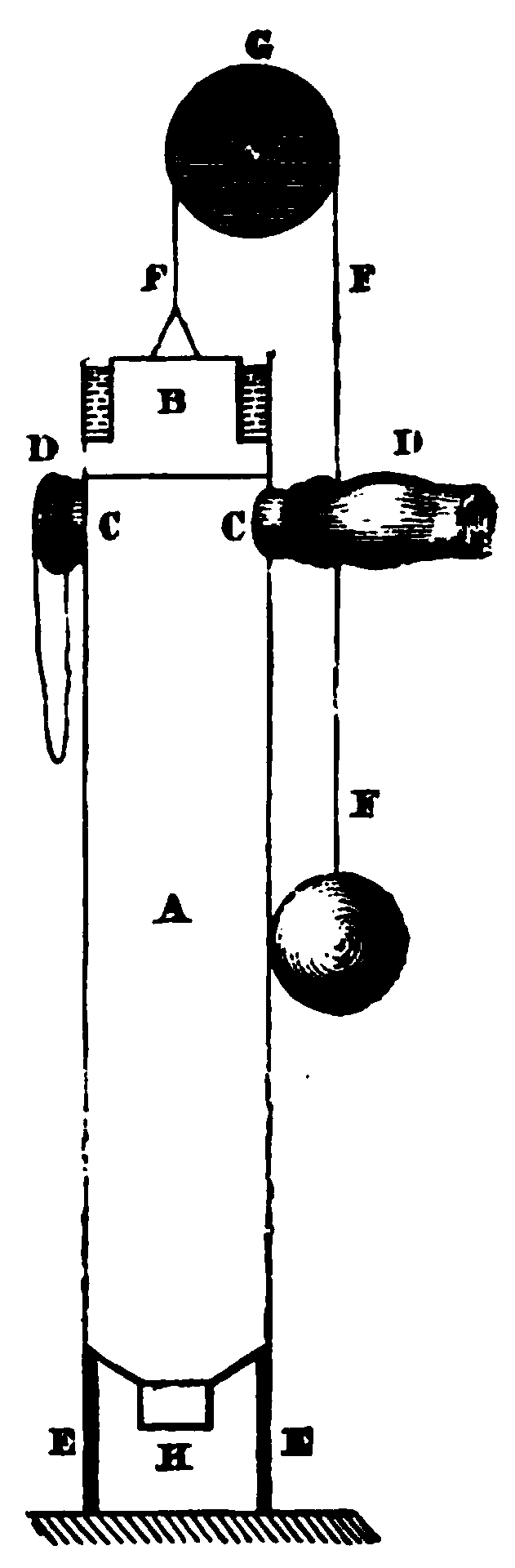
A gunpowder engine, also known as an explosion engine or Huygens' engine, is a type of internal combustion engine using gunpowder as its fuel. The concept was first explored during the 1600s, most notably by famous Dutch polymath Christiaan Huygens. George Cayley also experimented with the design in the early 1800s as an aircraft engine, and claims to have made models that worked for a short time. There is also a persistent claim that conventional carboretted gasoline engine can be run on gunpowder, but no examples of a successful conversion can be documented. Earliest mentions The gunpowder engine is based on many previous ideas and scientific discoveries, developed by multiple people independently. Early devices just aimed at lifting and/or holding weight (usually to study and demonstrate the physics), while engines aim at doing work contentiously (usually with the intention of doing something useful). Vacuum devices to lift/hold weight Leonardo da Vinci described in 1508 a d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internal Combustion Engine
An internal combustion engine (ICE or IC engine) is a heat engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer (usually air) in a combustion chamber that is an integral part of the working fluid flow circuit. In an internal combustion engine, the expansion of the high-temperature and high-pressure gases produced by combustion applies direct force to some component of the engine. The force is typically applied to pistons ( piston engine), turbine blades (gas turbine), a rotor (Wankel engine), or a nozzle ( jet engine). This force moves the component over a distance, transforming chemical energy into kinetic energy which is used to propel, move or power whatever the engine is attached to. This replaced the external combustion engine for applications where the weight or size of an engine was more important. The first commercially successful internal combustion engine was created by Étienne Lenoir around 1860, and the first modern internal combustion engine, known ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean De Hautefeuille
Jean de Hautefeuille (, 20 March 1647 – 18 October 1724) was a French abbé, physicist and inventor. Biography Hautefeuille was born in Orléans, France. While still young, his experimental activities came to the attention of Marie Anne Mancini, Duchesse de Bouillon, who became his patroness and brought him into her entourage. In this way, he was able to travel through Italy and England. Through the Duchess' patronage, he came to be ordained as a priest of the Roman Catholic Church. His passion, however, was for the sciences rather than religious matters, and he focused on the field of engineering design. One of Hautefeuille's most important achievements was his proposal to use a spiral spring with a balance wheel in place of a pendulum to control a clock. In the 1670s, he was involved in a dispute with Christiaan Huygens, who along with Robert Hooke claimed priority. Huygens is today generally credited with the invention as he managed to perfect it and the first watch usi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breech-loading Weapon
A breechloader is a firearm in which the user loads the ammunition (cartridge or shell) via the rear (breech) end of its barrel, as opposed to a muzzleloader, which loads ammunition via the front ( muzzle). Modern firearms are generally breech-loading – except for replicas of vintage weapons. Early firearms before the mid-19th century were almost entirely muzzle-loading. Mortars and the Russian GP-25 grenade launcher are the only muzzleloaders remaining in frequent modern usage. However, referring to a weapon specifically as breech loading is mostly limited to single-shot or otherwise non-repeating firearms, such as double-barreled shotguns. Breech-loading provides the advantage of reduced reloading time, because it is far quicker to load the projectile and propellant into the chamber of a gun/cannon than to reach all the way over to the front end to load ammunition and then push them back down a long tube – especially when the projectile fits tightly and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piston
A piston is a component of reciprocating engines, reciprocating pumps, gas compressors, hydraulic cylinders and pneumatic cylinders, among other similar mechanisms. It is the moving component that is contained by a cylinder and is made gas-tight by piston rings. In an engine, its purpose is to transfer force from expanding gas in the cylinder to the crankshaft via a piston rod and/or connecting rod. In a pump, the function is reversed and force is transferred from the crankshaft to the piston for the purpose of compressing or ejecting the fluid in the cylinder. In some engines, the piston also acts as a valve by covering and uncovering ports in the cylinder. __TOC__ Piston engines Internal combustion engines An internal combustion engine is acted upon by the pressure of the expanding combustion gases in the combustion chamber space at the top of the cylinder. This force then acts downwards through the connecting rod and onto the crankshaft. The connecting rod is att ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huyghens Engine
Christiaan Huygens, Lord of Zeelhem, ( , , ; also spelled Huyghens; la, Hugenius; 14 April 1629 – 8 July 1695) was a Dutch mathematician, physicist, engineer, astronomer, and inventor, who is regarded as one of the greatest scientists of all time and a major figure in the Scientific Revolution. In physics, Huygens made groundbreaking contributions in optics and mechanics, while as an astronomer he is chiefly known for his studies of the rings of Saturn and the discovery of its moon Titan. As an engineer and inventor, he improved the design of telescopes and invented the pendulum clock, a breakthrough in timekeeping and the most accurate timekeeper for almost 300 years. An exceptionally talented mathematician and physicist, Huygens was the first to idealize a physical problem by a set of mathematical parameters, and the first to fully mathematize a mechanistic explanation of an unobservable physical phenomenon.Dijksterhuis, F.J. (2008) Stevin, Huygens and the Dutch republ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |