|
Gulf Menhaden
The Gulf menhaden (''Brevoortia patronus'') is a small marine filter-feeding fish belonging to the family Clupeidae. The range of Gulf menhaden encompasses the entirety of the Gulf of Mexico nearshore waters, with the exception of the extreme eastern Yucatan and western Cuba.FAO 2002. The living marine resources of the western central Atlantic. ASIH special publication No. 5, Kent E. Carpenter, ed. ISSN 1020-6868. Evidence from morphology Dahlberg, M.D. 1970. Atlantic and Gulf of Mexico menhadens, genus Brevoortia (Pisces:Clupeidae). Bulletin of the Florida State Museum, Biological Sciences 15:91-162. and DNA analyses suggest that the Gulf menhaden is the Gulf of Mexico complement to the Atlantic menhaden (''Brevoortia tyrannus''). Both species support large commercial reduction fisheries, with Gulf menhaden supporting the second largest fishery, by weight, in the United States.Pritchard, E.S. 2005. Fisheries of the United States 2004. Silver Spring, MD: National Marine F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Kingdom (biology), biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals Heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, are Motility, able to move, can Sexual reproduction, reproduce sexually, and go through an ontogenetic stage in which their body consists of a hollow sphere of Cell (biology), cells, the blastula, during Embryogenesis, embryonic development. Over 1.5 million Extant taxon, living animal species have been Species description, described—of which around 1 million are Insecta, insects—but it has been estimated there are over 7 million animal species in total. Animals range in length from to . They have Ecology, complex interactions with each other and their environments, forming intricate food webs. The scientific study of animals is known as zoology. Most living animal species are in Bilateria, a clade whose members have a Symmetry in biology#Bilate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
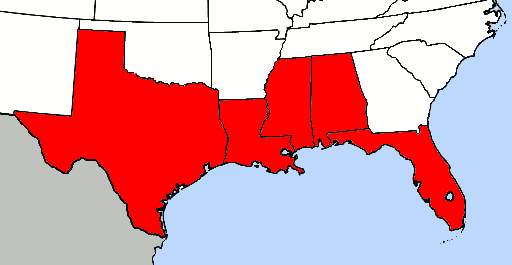
Texas
Texas (, ; Spanish: ''Texas'', ''Tejas'') is a state in the South Central region of the United States. At 268,596 square miles (695,662 km2), and with more than 29.1 million residents in 2020, it is the second-largest U.S. state by both area (after Alaska) and population (after California). Texas shares borders with the states of Louisiana to the east, Arkansas to the northeast, Oklahoma to the north, New Mexico to the west, and the Mexican states of Chihuahua, Coahuila, Nuevo León, and Tamaulipas to the south and southwest; and has a coastline with the Gulf of Mexico to the southeast. Houston is the most populous city in Texas and the fourth-largest in the U.S., while San Antonio is the second most populous in the state and seventh-largest in the U.S. Dallas–Fort Worth and Greater Houston are, respectively, the fourth- and fifth-largest metropolitan statistical areas in the country. Other major cities include Austin, the second most populous s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gulf States Marine Fisheries Commission
The Gulf States Marine Fisheries Commission (GSMFC) is an interstate compact among the five U.S. states that border the Gulf of Mexico: Alabama, Florida, Louisiana, Mississippi and Texas. Its purpose is to promote the conservation, development and utilization of the fishery Fishery can mean either the enterprise of raising or harvesting fish and other aquatic life; or more commonly, the site where such enterprise takes place ( a.k.a. fishing ground). Commercial fisheries include wild fisheries and fish farms, ... resources of the gulf. The GSMFC was created on July 16, 1949, and is headquartered in Ocean Springs, Mississippi. References External linksOfficial website Fisheries agencies 1949 establishments in the United States Government agencies established in 1949 Alabama law Florida law Louisiana law Mississippi law Texas law United States interstate compacts {{US-org-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friend Of The Sea
Friend of the Sea is a project of the World Sustainability Organization for the certification and promotion of seafood from sustainable fisheries and sustainable aquaculture. It is the only certification scheme which, with the same logo, certifies both wild and farmed seafood. Overview Friend of the Sea was started in 2008, by environmentalist and economist Paolo Bray, Director of International Programs of the Dolphin-Safe Tuna program and as a project of the Earth Island Institute, the NGO which operates the successful International Dolphin-Safe project. Some of the main world retailers participate, such as Carrefour, Coop Italia, Manor, Finiper, Aligro, Citysuper, Coldstorage, Conad, Despar, Esselunga, Fairprice, Lidl, Metro, Rewe, Spar, Walgreens, Walmart. Some important producers also have their products certified. Friend of the Sea's mission, in line with the United Nations 2020 Sustainable Development Goal 14, is to use its ecolabel and conservation projects and campaig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pelagic
The pelagic zone consists of the water column of the open ocean, and can be further divided into regions by depth (as illustrated on the right). The word ''pelagic'' is derived . The pelagic zone can be thought of as an imaginary cylinder or water column between the surface of the sea and the bottom. Conditions in the water column change with depth: pressure increases; temperature and light decrease; salinity, oxygen, micronutrients (such as iron, magnesium and calcium) all change. Marine life is affected by bathymetry (underwater topography) such as the seafloor, shoreline, or a submarine seamount, as well as by proximity to the boundary between the ocean and the atmosphere at the ocean surface, which brings light for photosynthesis, predation from above, and wind stirring up waves and setting currents in motion. The pelagic zone refers to the open, free waters away from the shore, where marine life can swim freely in any direction unhindered by topographical constraints. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
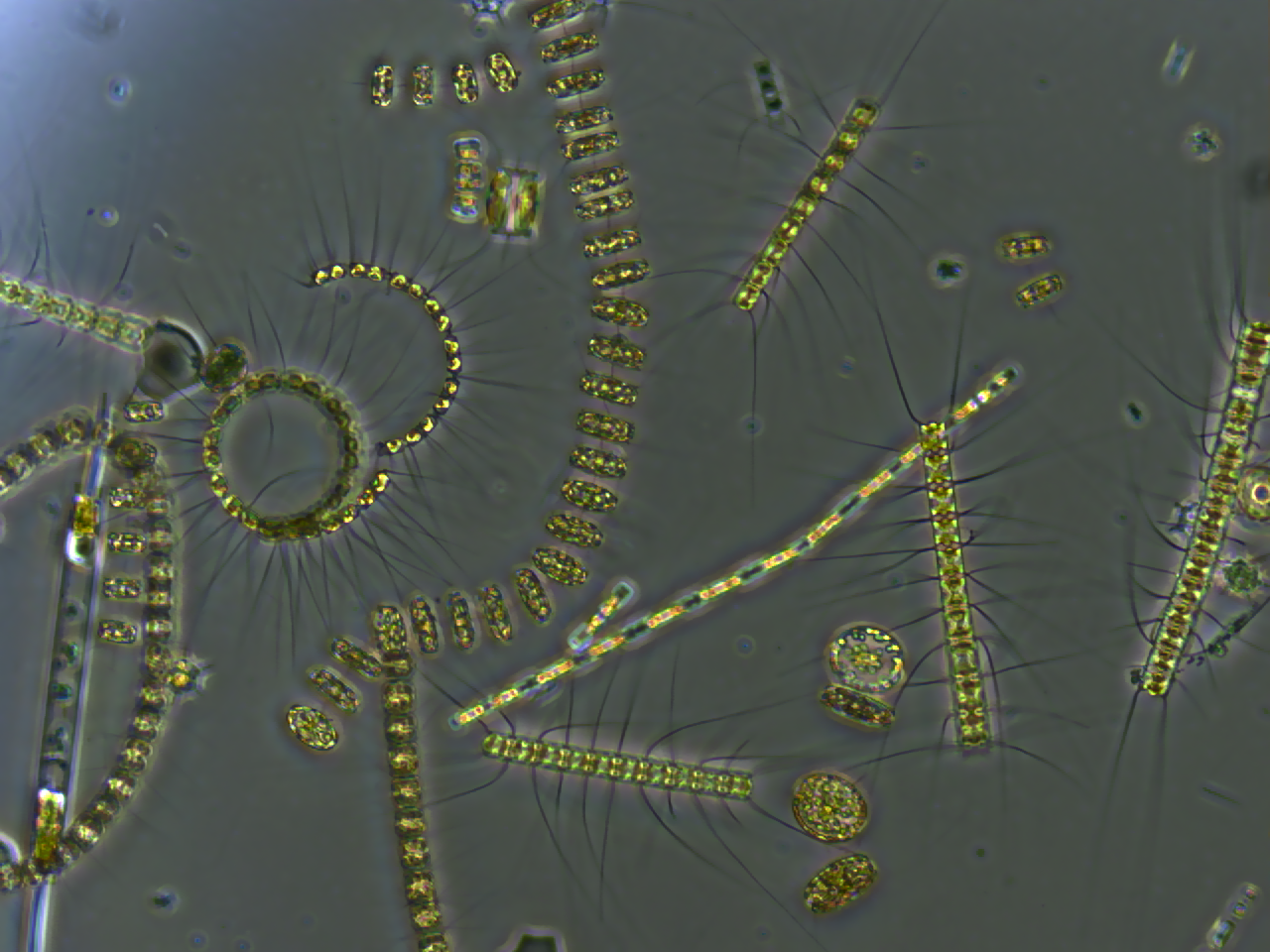
Zooplankton
Zooplankton are the animal component of the planktonic community ("zoo" comes from the Greek word for ''animal''). Plankton are aquatic organisms that are unable to swim effectively against currents, and consequently drift or are carried along by currents in the ocean, or by currents in seas, lakes or rivers. Zooplankton can be contrasted with phytoplankton, which are the plant component of the plankton community ("phyto" comes from the Greek word for ''plant''). Zooplankton are heterotrophic (other-feeding), whereas phytoplankton are autotrophic (self-feeding). This means zooplankton cannot manufacture their own food but must eat other plants or animals instead — in particular they eat phytoplankton. Zooplankton are generally larger than phytoplankton, most are microscopic, but some (such as jellyfish) are macroscopic and can be seen with the naked eye. Many protozoans (single-celled protists that prey on other microscopic life) are zooplankton, including zooflagellates, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phytoplankton
Phytoplankton () are the autotrophic (self-feeding) components of the plankton community and a key part of ocean and freshwater ecosystems. The name comes from the Greek words (), meaning 'plant', and (), meaning 'wanderer' or 'drifter'. Phytoplankton obtain their energy through photosynthesis, as do trees and other plants on land. This means phytoplankton must have light from the sun, so they live in the well-lit surface layers ( euphotic zone) of oceans and lakes. In comparison with terrestrial plants, phytoplankton are distributed over a larger surface area, are exposed to less seasonal variation and have markedly faster turnover rates than trees (days versus decades). As a result, phytoplankton respond rapidly on a global scale to climate variations. Phytoplankton form the base of marine and freshwater food webs and are key players in the global carbon cycle. They account for about half of global photosynthetic activity and at least half of the oxygen production, desp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlantic Menhaden
The Atlantic menhaden (''Brevoortia tyrannus'') is a North American species of fish in the herring family, Clupeidae. Atlantic menhaden are found in North Atlantic coastal and estuarine waters from Nova Scotia south to northern Florida. They are commonly found in all salinities of the Chesapeake Bay and Mid-Atlantic water. They swim in large schools that stratify by size and age along the coast. Younger and smaller fish are found in the Chesapeake Bay and southern coastline while older, larger fish are found along the northern coastline. Characteristics Atlantic menhaden are silvery coloured fishes characterized by a moderately compressed body and a black spot on their shoulder behind their gill openings. They can reach a size of approximately 15 inches. Biology Diet The Atlantic menhaden is a filter feeder, which that it collects food by filtering water through modifications of the branchial apparatus (gill arches and gill rakers). Its diet depends on the size of their gill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gill Raker
Gill rakers in fish are bony or cartilaginous processes that project from the branchial arch (gill arch) and are involved with suspension feeding tiny prey. They are not to be confused with the gill filaments that compose the fleshy part of the gill used for gas exchange. Rakers are usually present in two rows, projecting from both the anterior and posterior side of each gill arch. Rakers are widely varied in number, spacing, and form. By preventing food particles from exiting the spaces between the gill arches, they enable the retention of food particles in filter feeders. The structure and spacing of gill rakers in fish determines the size of food particles trapped, and correlates with feeding behavior. Fish with densely spaced, elongated, comb-like gill rakers are efficient at filtering tiny prey, whereas carnivores and omnivores often have more widely spaced gill rakers with secondary projections. Because gill raker characters often vary between closely related taxa, they are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Branchial Arch
Branchial arches, or gill arches, are a series of bony "loops" present in fish, which support the gills. As gills are the primitive condition of vertebrates, all vertebrate embryos develop pharyngeal arches, though the eventual fate of these arches varies between taxa. In jawed fish, the first arch develops into the jaws, the second into the hyomandibular complex, with the posterior arches supporting gills. In amphibians and reptiles, many elements are lost including the gill arches, resulting in only the oral jaws and a hyoid apparatus remaining. In mammals and birds, the hyoid is still more simplified. All basal vertebrates breathe with gills. The gills are carried right behind the head, bordering the posterior margins of a series of openings from the esophagus to the exterior. Each gill is supported by a cartilaginous or bony gill arch. Bony fish have four pairs of arches, cartilaginous fish have five to seven pairs, and primitive jawless fish have seven. The vertebrate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yellowfin Menhaden
Yellow-fin may refer to one of the following species of fish: * Yellowfin bream, several fishes in the family Sparidae * Yellowfin croaker, a fish in the family Sciaenidae * Yellowfin cutthroat trout, a fish in the family Salmonidae * Yellowfin fairy-wrasse, a fish in the family Labridae * Yellowfin grouper, a fish in the family Serranidae * Yellowfin madtom, a fish in the family Ictaluridae * Yellow-fin perchlet, a fish in the family Ambassidae * Yellowfin pike, a fish in the family Dinolestidae * Yellowfin seabream, several fishes in the family Sparidae * Yellowfin surgeon, a fish in the family Acanthuridae * Yellowfin tuna The yellowfin tuna (''Thunnus albacares'') is a species of tuna found in pelagic waters of tropical and subtropical oceans worldwide. Yellowfin is often marketed as ahi, from the Hawaiian , a name also used there for the closely related bigeye ..., a fish in the family Scombridae * Yellowfin whiting, a fish in the family Sillaginidae It may also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louisiana
Louisiana , group=pronunciation (French: ''La Louisiane'') is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It is the 20th-smallest by area and the 25th most populous of the 50 U.S. states. Louisiana is bordered by the state of Texas to the west, Arkansas to the north, Mississippi to the east, and the Gulf of Mexico to the south. A large part of its eastern boundary is demarcated by the Mississippi River. Louisiana is the only U.S. state with political subdivisions termed parishes, which are equivalent to counties, making it one of only two U.S. states not subdivided into counties (the other being Alaska and its boroughs). The state's capital is Baton Rouge, and its largest city is New Orleans, with a population of roughly 383,000 people. Some Louisiana urban environments have a multicultural, multilingual heritage, being so strongly influenced by a mixture of 18th century Louisiana French, Dominican Creole, Spanish, French Canadian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)