|
Guinea-Bissau Television
Guinea-Bissau Television ('' pt, Televisão da Guiné-Bissau'', or TGB) is the state television of the African country of Guinea-Bissau. The headquarters are in the capital city of Bissau. The station's main transmitter is located in Nhacra and covers the Bissau metropolitan area. The system also includes two relay towers, one in the east of the country, in Gabu, and another in the south, in Catió. History The installation of the very first television network in Guinea-Bissau began in the 1980s following a public tender won by a Portuguese company. The first broadcasting service went on air in several experimental stages in October 1987, when the initial contract to create a state television was signed. The television was officially launched in November 1989, under the name ''Televisão Experimental da Guiné-Bissau'' (TEGB), through the partnership agreement with Portuguese Radiotelevision (since renamed Rádio e Televisão de Portugal, or RTP). At the time, the country was rul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terrestrial Television
Terrestrial television or over-the-air television (OTA) is a type of television broadcasting in which the signal transmission occurs via radio waves from the terrestrial (Earth-based) transmitter of a TV station to a TV receiver having an antenna. The term ''terrestrial'' is more common in Europe and Latin America, while in Canada and the United States it is called ''over-the-air'' or simply ''broadcast''. This type of TV broadcast is distinguished from newer technologies, such as satellite television (direct broadcast satellite or DBS television), in which the signal is transmitted to the receiver from an overhead satellite; cable television, in which the signal is carried to the receiver through a cable; and Internet Protocol television, in which the signal is received over an Internet stream or on a network utilizing the Internet Protocol. Terrestrial television stations broadcast on television channels with frequencies between about 52 and 600 MHz in the VHF and U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1980 Guinea-Bissau Coup D'état
The 1980 Guinea-Bissau coup d'état was the bloodless military coup that took place in Guinea-Bissau on 14 November 1980, led by Prime Minister General João Bernardo Vieira. It led to the deposition of President Luís Cabral (half-brother of anti-colonial leader Amílcar Cabral), who held the office since 1973, while the country's War of Independence was still ongoing. Aftermath General Vieira announced the creation of the Revolutionary Council, which would exercise all executive and legislative powers in the country. Eventually, a power struggle developed between Vieira and Victor Saúde Maria, Prime Minister and Vice President of the Revolutionary Council, the only civilian member of the body, with the latter being forced into exile in Portugal in March 1984. Two months later a new Constitution was promulgated, proclaiming Vieira as President and returning the country to civilian rule. Vieira himself was deposed in the 1998–99 Civil War and exiled to Portugal in June 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portuguese-language Television Networks
Portuguese ( or, in full, ) is a western Romance languages, Romance language of the Indo-European language family, originating in the Iberian Peninsula of Europe. It is an official language of Portugal, Brazil, Cape Verde, Angola, Mozambique, Guinea-Bissau and São Tomé and Príncipe, while having co-official language status in East Timor, Equatorial Guinea, and Macau. A Portuguese-speaking person or nation is referred to as "Lusophone" (). As the result of expansion during colonial times, a cultural presence of Portuguese speakers is also found around the world. Portuguese is part of the Iberian Romance languages, Ibero-Romance group that evolved from several dialects of Vulgar Latin in the medieval Kingdom of Galicia and the County of Portugal, and has kept some Gallaecian language, Celtic phonology in its lexicon. With approximately 250 million native speakers and 24 million L2 (second language) speakers, Portuguese has approximately 274 million total speakers. It is usual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Television Stations In Guinea-Bissau
Television, sometimes shortened to TV, is a telecommunication medium for transmitting moving images and sound. The term can refer to a television set, or the medium of television transmission. Television is a mass medium for advertising, entertainment, news, and sports. Television became available in crude experimental forms in the late 1920s, but only after several years of further development was the new technology marketed to consumers. After World War II, an improved form of black-and-white television broadcasting became popular in the United Kingdom and the United States, and television sets became commonplace in homes, businesses, and institutions. During the 1950s, television was the primary medium for influencing public opinion.Diggs-Brown, Barbara (2011''Strategic Public Relations: Audience Focused Practice''p. 48 In the mid-1960s, color broadcasting was introduced in the U.S. and most other developed countries. The availability of various types of archival storag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Broadcasting Of Guinea-Bissau
The National Broadcasting of Guinea-Bissau (RDN; in Portuguese: ''Radiodifusão Nacional da Guiné-Bissau''), also known only as National Radio (in Portuguese: ''Rádio Nacional''), is a public broadcasting company in Guinea-Bissau, whose head office is located in Bissau. The RDN operates three radio stations in the country - Bissau (in city suburb of Nhacra), Catió and Gabu -, in addition to several regional stations and an international broadcast service. A network of transmitters allows the radio to cover about 80% of the country, in frequency modulation (91.5 / 104.0 FM). The broadcasts are made mostly in Portuguese, and also have programs in the national languages of the country, namely: Creole, Fula, Balanta, Susso, Mankanya, Papel, Bijago, Felupe, Mandinka, Manjak, Beafada, Balanta Mané, Pajadinka and Nalu. Historic The current RDN arose from the merger of two important broadcasting services that were installed in Guinea-Bissau still in the colonial period ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Media Of Guinea-Bissau
Mass media in Guinea-Bissau includes print, radio, television, and the Internet. "The Conselho Nacional de Comunicação Social regulates the press." The government-run Guinea-Bissau National Radio began in 1973 and Guinea-Bissau Television began in 1987. Radio * Guinea-Bissau National Radio * Radio Bafata * Rádio Bombolom * Rádio Jovem * Radio Mavegro * Radio Nacional * Radio Pindjiguiti * Radio Sintcha Oco * Rádio Sol Mansi Television * Guinea-Bissau Television (TGB) * RTP África RTP África is a Portuguese television channel owned and operated by state-owned public broadcaster Rádio e Televisão de Portugal (RTP). It is available in the Portuguese-speaking African countries, where it is available as a basic cable and sa ... * TV Klélé (est. 2013) Publications Print and online publications include: * ''Banobero'' * ''Bissau Digital'' * ' * ''Comdev Negocios'' * ''Correio-Bissau'' * ''Diario de Bissau'' * ''Expresso de Bissau'' * ''Fraskera'' * ''Gazeta de Noticias' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2006 FIFA World Cup
The 2006 FIFA World Cup, also branded as Germany 2006, was the 18th FIFA World Cup, the quadrennial international football world championship tournament. It was held from 9 June to 9 July 2006 in Germany, which had won the right to host the event in July 2000. Teams representing 198 national football associations from all six populated continents participated in the qualification process which began in September 2003. Thirty-one teams qualified from this process along with hosts Germany for the finals tournament. It was the second time that Germany staged the competition and the first as a unified country along with the former East Germany with Leipzig as a host city (the other was in 1974 in West Germany), and the 10th time that the tournament was held in Europe. Italy won the tournament, claiming their fourth World Cup title, defeating France 5–3 in a penalty shoot-out in the final after extra time had finished in a 1–1 draw. Germany defeated Portugal 3–1 to finis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guinea-Bissau Civil War
The Guinea-Bissau Civil War was fought from 7 June 1998 to 10 May 1999 and was triggered by an attempted coup d'état against the government of President João Bernardo Vieira led by Brigadier-General Ansumane Mané.Uppsala Conflict Data Program Conflict Encyclopedia, Guinea Bissau: government, in depth, Negotiations, Veira's surrender and the end of the conflict, viewed 12 July 2013, http://www.ucdp.uu.se/gpdatabase/gpcountry.php?id=68®ionSelect=2-Southern_Africa# Government forces, backed by neighbouring states, clashed with the coup leaders who had quickly gained almost total control over the country's armed forces. The conflict resulted in the deaths of hundreds if not thousands of people and the displacement of hundreds of thousands. An eventual peace agreement in November 1998 provided for a national unity government and new elections in the next year. However, a subsequent and brief outbreak of fighting in May 1999 ended with the deposing of Vieira on 10 May 1999 whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
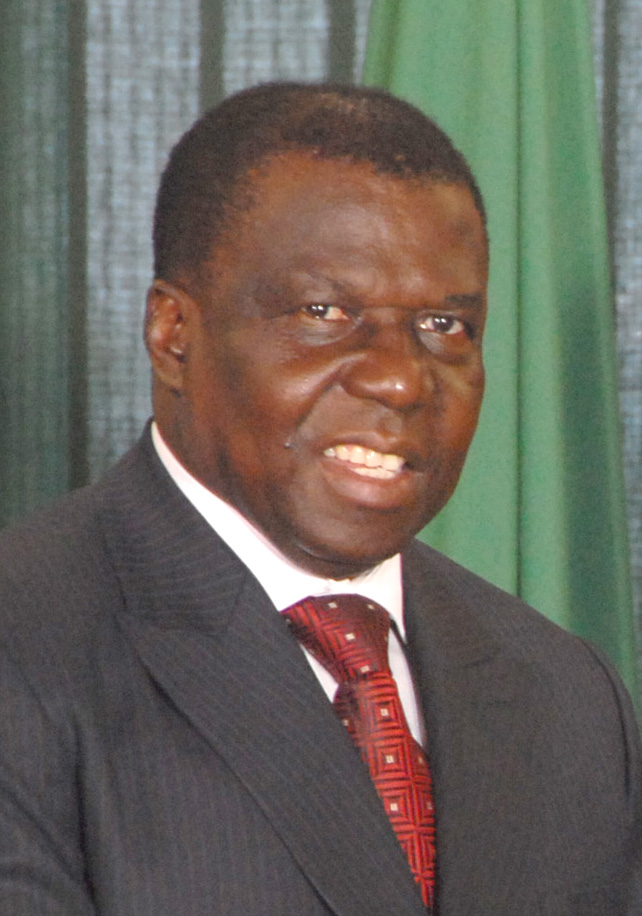
João Bernardo Vieira
João Bernardo "Nino" Vieira (; 27 April 1939 – 2 March 2009) was a Bissau-Guinean politician who was the President of Guinea-Bissau from 1980 to 1999, except for a three-day period in May 1984, and from 2005 to 2009. After seizing power from President Luís Cabral in a military coup in 1980, Vieira ruled as part of the Military Council of the Revolution until 1984, when civilian rule was returned. Opposition parties were allowed in 1991, and Vieira won a multiparty presidential election in 1994. He was ousted at the end of the 1998–1999 civil war and went into exile. He made a political comeback in 2005, winning that year's presidential election. Vieira was killed by soldiers on 2 March 2009, apparently in retaliation for a bomb blast that killed Guinea-Bissau's military chief General Batista Tagme Na Waie hours before. The military officially denied these allegations after unidentified Army officials claimed responsibility of Vieira for Na-Waie's death. Viei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guinea-Bissau
Guinea-Bissau ( ; pt, Guiné-Bissau; ff, italic=no, 𞤘𞤭𞤲𞤫 𞤄𞤭𞤧𞤢𞥄𞤱𞤮, Gine-Bisaawo, script=Adlm; Mandinka: ''Gine-Bisawo''), officially the Republic of Guinea-Bissau ( pt, República da Guiné-Bissau, links=no ), is a country in West Africa that covers with an estimated population of 1,726,000. It borders Senegal to the north and Guinea to the south-east. Guinea-Bissau was once part of the kingdom of Kaabu, as well as part of the Mali Empire. Parts of this kingdom persisted until the 18th century, while a few others were under some rule by the Portuguese Empire since the 16th century. In the 19th century, it was colonised as Portuguese Guinea. Portuguese control was restricted and weak until the early 20th century with the pacification campaigns, these campaigns solidified Portuguese sovereignty in the area. The final Portuguese victory over the remaining bastion of mainland resistance, the Papel ruled Kingdom of Bissau in 1915 by the Portu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rádio E Televisão De Portugal
Rádio e Televisão de Portugal (RTP) is the public service broadcasting organisation of Portugal. It operates four national television channels and three national radio stations, as well as several satellite and cable offerings. The current company dates from 2007, with the merger of two previously separate companies Radiodifusão Portuguesa (RDP; the radio broadcaster) and Radiotelevisão Portuguesa (television broadcaster), although they had been grouped under a single holding company and common branding since 2004. RTP is funded by the ''taxa de contribuição audiovisual'' (broadcasting contribution tax), which is incorporated in electricity bills, and television advertising revenues. History Radio The Emissora Nacional de Radiodifusão - usually referred to by its abbreviated designation Emissora Nacional (EN) - was established on 4 August 1935 as the public national radio broadcaster, inheriting the previous broadcasting operations of the Portuguese postal service (CT ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catió
Catió is a city in south eastern Guinea-Bissau. It is the capital of Tombali Region. Population 9,217 (2008 est). Catio, along with Canjadude and other camps were besieged by the Portuguese in 1973. Notable people *Abdulai Silá (1958-) -engineer and writer Climate Catió has a tropical monsoon climate (Köppen climate classification, Köppen ''Am'') featuring hot temperatures year-round, little to no rainfall from November to May and heavy to extremely heavy rainfall from June to October. References [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |