|
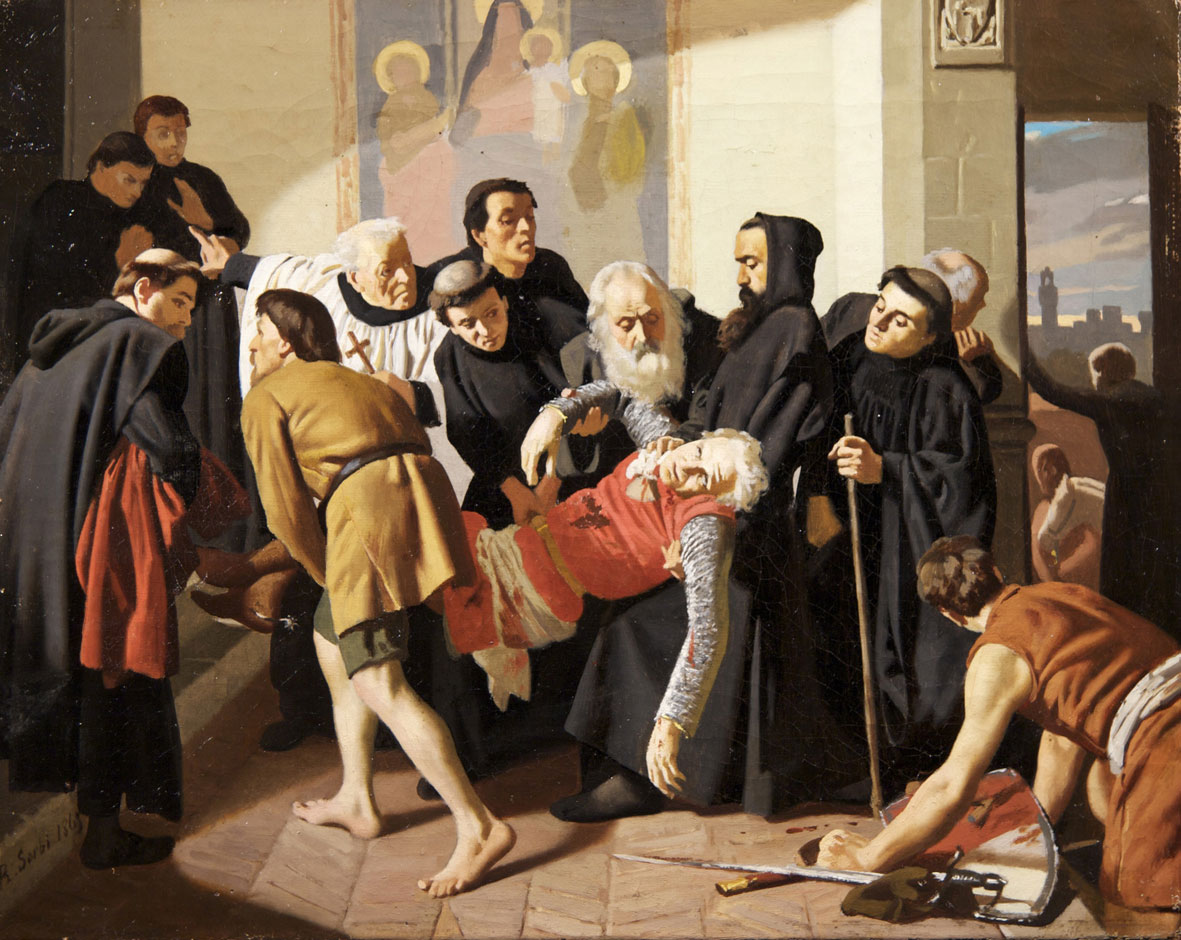
Guido Cavalcanti
Guido Cavalcanti (between 1250 and 1259 – August 1300) was an Italian poet. He was also a friend and intellectual influence on Dante Alighieri. Historical background Cavalcanti was born in Florence at a time when the comune was beginning its economic, political, intellectual and artistic ascendancy as one of the leading cities of the Renaissance. The disunited Italian peninsula was dominated by a political particularism that pitted city-states against one another, often with this factionalism contributing to the fractious and sometimes violent political environments of each ''comune''. The domination of medieval religious interpretations of reality, morality and society were challenged by a rise of a new urban culture across Europe that gradually supplanted rural, local, ecclesiastical and feudal ways of thinking. There was an accompanying return to study, and to interpretation and emulation of the classics, known as a revival of antiquity. New secular and humanistic views la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Italians
, flag = , flag_caption = Flag of Italy, The national flag of Italy , population = , regions = Italy 55,551,000 , region1 = Brazil , pop1 = 25–33 million , ref1 = , region2 = Argentina , pop2 = 20–25 million , ref2 = , region3 = United States , pop3 = 17-20 million , ref3 = , region4 = France , pop4 = 1-5 million , ref4 = , region5 = Venezuela , pop5 = 1-5 million , ref5 = , region6 = Paraguay , pop6 = 2.5 million , region7 = Colombia , pop7 = 2 million , ref7 = , region8 = Canada , pop8 = 1.5 million , ref8 = , region9 = Australia , pop9 = 1.0 million , ref9 = , region10 = Uruguay , pop10 = 1.0 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Benevento
The Battle of Benevento was a major medieval battle fought on 26 February 1266, near Benevento in present-day Southern Italy, between the forces of Charles I of Anjou and those of King Manfred of Sicily. Manfred's defeat and death resulted in Charles' conquest of the Kingdom of Sicily, effectively ending the rule of the Hohenstaufen dynasty in the Italian Peninsula and marking the rise of the royal Capetian House of Anjou. The engagement was part of the conflict which pitted Guelphs against Ghibellines. Background The Papacy had long been in conflict with the Imperial house of Hohenstaufen over their rule in Italy. At the time of the battle, the Hohenstaufen ruler of the Kingdom of Sicily (which included Sicily and southern Italy) was Manfred, illegitimate son of Frederick II, Holy Roman Emperor. However, the rightful heir to the kingdom was Frederick's legitimate 14-year-old grandson Conradin, living with his uncle and guardian Louis II, Duke of Bavaria. Manfred, ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Champagne, France
Champagne () was a province in the northeast of the Kingdom of France, now best known as the Champagne wine region for the sparkling white wine that bears its name in modern-day France. The County of Champagne, descended from the early medieval kingdom of Austrasia, passed to the French crown in 1314. Formerly ruled by the counts of Champagne, its western edge is about 160 km (100 miles) east of Paris. The cities of Troyes, Reims, and Épernay are the commercial centers of the area. In 1956, most of Champagne became part of the French administrative region of Champagne-Ardenne, which comprised four departments: Ardennes, Aube, Haute-Marne, and Marne. From 1 January 2016, Champagne-Ardenne merged with the adjoining regions of Alsace and Lorraine to form the new region of Grand Est. Etymology The name ''Champagne'', formerly written ''Champaigne'', comes from French meaning "open country" (suited to military maneuvers) and from Latin ''campanius'' meaning "level country ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aquitaine
Aquitaine ( , , ; oc, Aquitània ; eu, Akitania; Poitevin-Saintongeais: ''Aguiéne''), archaic Guyenne or Guienne ( oc, Guiana), is a historical region of southwestern France and a former administrative region of the country. Since 1 January 2016 it has been part of the region of Nouvelle-Aquitaine. It is situated in the southwest corner of Metropolitan France, along the Atlantic Ocean and the Pyrenees mountain range on the border with Spain, and for most of its written history Bordeaux has been a vital port and administrative center. It is composed of the five departments of Dordogne, Lot-et-Garonne, Pyrénées-Atlantiques, Landes and Gironde. Gallia Aquitania was established by the Romans in ancient times and in the Middle Ages, Aquitaine was a kingdom and a duchy, whose boundaries fluctuated considerably. History Ancient history There are traces of human settlement by prehistoric peoples, especially in the Périgord, but the earliest attested inhabitants in the sou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Courtly Love
Courtly love ( oc, fin'amor ; french: amour courtois ) was a medieval European literary conception of love that emphasized nobility and chivalry. Medieval literature is filled with examples of knights setting out on adventures and performing various deeds or services for ladies because of their "courtly love". This kind of love is originally a literary fiction created for the entertainment of the nobility, but as time passed, these ideas about love changed and attracted a larger audience. In the high Middle Ages, a "game of love" developed around these ideas as a set of social practices. "Loving nobly" was considered to be an enriching and improving practice. Courtly love began in the ducal and princely courts of Aquitaine, Provence, Champagne, ducal Burgundy and the Norman Kingdom of Sicily at the end of the eleventh century. In essence, courtly love was an experience between erotic desire and spiritual attainment, "a love at once illicit and morally elevating, passionate and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trobairitz
The ''trobairitz'' () were Occitan female troubadours of the 12th and 13th centuries, active from around 1170 to approximately 1260. ''Trobairitz'' is both singular and plural. The word ''trobairitz'' is first attested in the 13th-century romance '' Flamenca''. It comes from the Provençal word ''trobar'', the literal meaning of which is "to find", and the technical meaning of which is "to compose". The word ''trobairitz'' is used very rarely in medieval Occitan, as it does not occur in lyrical poetry, grammatical treatises or in the biographies (''vidas'') of the ''trobairitz'' or troubadours.Paden It does occur in the treatise ''Doctrina d'acort'' by Terramagnino da Pisa, written between 1282 and 1296. He uses it as an example of a word the plural and singular of which are the same.Elizabeth W. Poe, "Cantairitz e Trobairitz: A Forgotten Attestation of Old Provençal »Trobairitz«," ''Romanische Forschungen'', 114, 2 (2002), pp. 206–215, at 207: "which are correctly us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Troubadour
A troubadour (, ; oc, trobador ) was a composer and performer of Old Occitan lyric poetry during the High Middle Ages (1100–1350). Since the word ''troubadour'' is etymologically masculine, a female troubadour is usually called a '' trobairitz''. The troubadour school or tradition began in the late 11th century in Occitania, but it subsequently spread to the Italian and Iberian Peninsulas. Under the influence of the troubadours, related movements sprang up throughout Europe: the Minnesang in Germany, '' trovadorismo'' in Galicia and Portugal, and that of the trouvères in northern France. Dante Alighieri in his '' De vulgari eloquentia'' defined the troubadour lyric as ''fictio rethorica musicaque poita'': rhetorical, musical, and poetical fiction. After the "classical" period around the turn of the 13th century and a mid-century resurgence, the art of the troubadours declined in the 14th century and around the time of the Black Death (1348) it died out. The texts of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dolce Stil Novo
''Dolce Stil Novo'' (), Italian for "sweet new style," is the name given to a literary movement in 13th and 14th century Italy. Influenced by the Sicilian School and Tuscan poetry, its main theme is Divine Love. The name ''Dolce Stil Novo'' was used for the first time by Dante Alighieri in ''Purgatorio'', the second canticle of the ''Divina Commedia''. In the ''Divina Commedia'' Purgatory he meets Bonagiunta Orbicciani, a 13th-century Italian poet, who tells Dante that Dante himself, Guido Guinizelli, and Guido Cavalcanti had been able to create a new genre: a ''stil novo''. Poetry from this school is marked by adoration of the human form, incorporating vivid descriptions of female beauty and frequently comparing the desired woman to a creature from paradise. The woman is described as an "angel" or as "a bridge to God." Rather than being material in nature, the Love of the ''Dolce Stil Novo'' is a sort of Divine Love. Poetry of this movement also often includes profound intr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rime Di Guido Cavalcanti
Rime may refer to: *Rime ice, ice that forms when water droplets in fog freeze to the outer surfaces of objects, such as trees Rime is also an alternative spelling of "rhyme" as a noun: *Syllable rime, term used in the study of phonology in linguistics *Rime dictionary, type of ancient Chinese dictionary used for writing poetry *Rime table, a syllable chart of the Chinese language *Rime riche, a form of rhyme using identical sounds Literature *''The Rime of the Ancient Mariner'', a 1798 poem by Samuel Taylor Coleridge *''Le Rime'', a collection of lyrical poems by Dante Alighieri *''The Rime of King William'', a poetic eulogy of William the Conqueror written in Old English Other uses *Noémi Rime, French opera singer *Rimé movement, an ecumenical movement within Tibetan Buddhism * RelayNet International Mail Exchange (RIME), an e-mail exchange networking protocol * ''Rime'' (video game), an action-adventure video game See also *Rhyme A rhyme is a repetition of similar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marriage Of Convenience
A marriage of convenience is a marriage contracted for reasons other than that of love and commitment. Instead, such a marriage is entered into for personal gain, or some other sort of strategic purpose, such as a political marriage. There are some cases in which those married do not intend to live together as a couple, and typically got married only for one of them to gain the right to reside in a country, meaning a marriage of benefit. In many cultures, it is usual for parents to decide their adult children's marriages; this is called an arranged marriage. A marriage of convenience that is neither a sham marriage entered into for fraudulent purposes nor a forced marriage, is not against the law. Legal loophole Marriages of convenience are often contracted to exploit legal loopholes of various sorts. A couple may wed for one of them to gain citizenship or right of abode, for example, as many countries around the world will grant such rights to anyone married to a resident ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malaria
Malaria is a mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects humans and other animals. Malaria causes symptoms that typically include fever, tiredness, vomiting, and headaches. In severe cases, it can cause jaundice, seizures, coma, or death. Symptoms usually begin ten to fifteen days after being bitten by an infected mosquito. If not properly treated, people may have recurrences of the disease months later. In those who have recently survived an infection, reinfection usually causes milder symptoms. This partial resistance disappears over months to years if the person has no continuing exposure to malaria. Malaria is caused by single-celled microorganisms of the '' Plasmodium'' group. It is spread exclusively through bites of infected '' Anopheles'' mosquitoes. The mosquito bite introduces the parasites from the mosquito's saliva into a person's blood. The parasites travel to the liver where they mature and reproduce. Five species of ''Plasmodium'' can infect and be spr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corso Donati
Corso Donati was a leader of the Black Guelph faction in 13th- and early 14th- century Florence. Bologna and Pistoia In the late thirteenth century, power in Florence and the other Tuscan cities was divided between the Podestà, an outsider who served as chief magistrate, and the guildmasters. Corso served as Podestà of Bologna in 1283 and 1288, and of Pistoia in 1289. In 1289, as captain of the people in Pistoia, he led a group of soldiers in a cavalry charge at the Battle of Campaldino, in which the Guelphs defeated the Ghibellines and cemented their control over Florence. Leader of the Black Guelphs In 1293, the merchants of Florence, led by Giano della Bella, prevented the nobility from taking the office of guildmaster. Corso led the noble faction which aligned with the working class against the merchants. In 1294 Corso was acquitted of killing a man in a fight; an angry mob came to della Bella seeking justice after the acquittal, but he sent them away whereupon they rioted a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)