|
Grunewald (locality)
Grunewald () is a locality (''Ortsteil'') within the Berlin borough (''Bezirk'') of Charlottenburg-Wilmersdorf. Famous for the homonymous forest, until 2001 administrative reform it was part of the former district of Wilmersdorf. Next to Lichterfelde West, Dahlem and Westend, it is part of the affluent Berlin "Villenbogen", a row of 19th century suburbs completely made up of mansions. Geography The locality is situated in the western side of the city and is separated from Spandau by the river Havel. It borders with the localities of Westend, Halensee, Schmargendorf, Wilhelmstadt, Gatow (both in Spandau district), Nikolassee, Zehlendorf and Dahlem (all three in Steglitz-Zehlendorf district). The Grunewald forest is 10 km away from Berlin-Mitte (Germany's capital). History Etymology The name derives from the Grunewald hunting lodge of 1543, the oldest preserved castle in Berlin, which is, however, officially located within the adjacent Dahlem locality. It was erected ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berlin
Berlin ( , ) is the capital and List of cities in Germany by population, largest city of Germany by both area and population. Its 3.7 million inhabitants make it the European Union's List of cities in the European Union by population within city limits, most populous city, according to population within city limits. One of Germany's States of Germany, sixteen constituent states, Berlin is surrounded by the Brandenburg, State of Brandenburg and contiguous with Potsdam, Brandenburg's capital. Berlin's urban area, which has a population of around 4.5 million, is the second most populous urban area in Germany after the Ruhr. The Berlin/Brandenburg Metropolitan Region, Berlin-Brandenburg capital region has around 6.2 million inhabitants and is Metropolitan regions in Germany, Germany's third-largest metropolitan region after the Rhine-Ruhr and Frankfurt Rhine-Main, Rhine-Main regions. Berlin straddles the banks of the Spree (river), Spree, which flows into the Havel (a tributary of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steglitz-Zehlendorf
Steglitz-Zehlendorf () is the sixth borough of Berlin, formed in Berlin's 2001 administrative reform by merging the former boroughs of Steglitz and Zehlendorf. Home to Free University of Berlin, the Berlin Botanical Garden, and a variety of museums and art collections, Steglitz-Zehlendorf is an important hub for research, science and culture in Berlin. It is known to be the wealthiest borough of Berlin, having the city's highest median household income. History The first mention of a present-day locality in the district by name was Lankwitz (Lancewitz) in 1239. It is assumed that Slavic and German settlements were established at the Schlachtensee and Krume Lanke lakes after 1200 at the latest. The first documented mention of Zehlendorf (then Cedelendorp) dates back to 1242. Here the Lehnin Abbey bought the settlement and kept it until 1542. Frederick the Great donated a church to the village in 1768 during a stopover on the journey from the Berlin Palace to the Sanssouci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WTA Tour
The WTA Tour is a worldwide top-tier tennis tour for women organized by the Women's Tennis Association. The second-tier tour is the WTA 125K series, and third-tier is the ITF Women's Circuit. The men's equivalent is the ATP Tour. WTA Tour tournaments Structure (2021–present) The WTA Tour underwent slight change in the classification of tournaments in 2021, which were organized on par with the nomenclature used on ATP Tour: * Grand Slam tournaments (4) *Year-ending WTA Finals (1) * WTA 1000 tournaments (9): ** Mandatory: Four combined tournaments with male professional players with prize money ranging from US$6.5 million to US$8.3 million. These tournaments are held in Indian Wells, Miami, Madrid, and Beijing. However, Beijing tournament could not be held in 2021–22 due to the impact of Covid-19 Pandemic. ** Non-mandatory: Five events in Doha/Dubai, Rome, Montreal/Toronto, Cincinnati, and Wuhan with prize money ranging from US$2.3 million to US$2.7 million. In 2021–22, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rot-Weiss Tennis Club
The Lawn-Tennis-Turnier-Club "Rot-Weiß" (abbr.: LTTC, ''red-white'') is a tennis club located in Grunewald, part of a district in Berlin, Germany. The club was founded in 1897 as ''Lawn Tennis Turnier Club'', and was the origin for careers of many German tennis players in the 20th century like Cilly Aussem, Otto Froitzheim, Henner Henkel, Hans Moldenhauer, Hans-Jürgen Pohmann, Roman Najuch and Daniel Prenn. The central court has been the venue of the German Pro Championships since 1911 and later the German Open WTA Tour tournament from 1979 until 2008, and again since 2021. The club has 16 clay courts. During winter season there are eight indoor courts available. A larger 7,000-seat stadium court was built in 1996 to replace the old one with 3,500. This stadium was named '' Steffi-Graf-Stadion'' in September 2004. For the 2020 season its clay surface was replaced with grass. Steffi Graf was member of the club since 1984. Also Boris Becker represented the club 1985-1987. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greater Berlin Act
The Greater Berlin Act (german: Groß-Berlin-Gesetz), officially Law Regarding the Creation of the New Municipality of Berlin (german: Gesetz über die Bildung einer neuen Stadtgemeinde Berlin), was a law passed by the Prussian state government in 1920, which greatly expanded the size of the Prussian and German capital of Berlin. History Berlin had been part of the Province of Brandenburg since 1815. On 1 April 1881, the city became Stadtkreis Berlin, a city district separate from Brandenburg. The Greater Berlin Act was passed by the Prussian Parliament on 27 April 1920 and came into effect on 1 October of the same year. The new Prussian province then termed ''Greater Berlin'' acquired territories from the Province of Brandenburg and consisted of the following: * The city of Berlin (''Alt-Berlin''); * 7 towns that surrounded Berlin: Charlottenburg, Köpenick, Lichtenberg, Neukölln/Rixdorf, Schöneberg, Spandau and Wilmersdorf; * 59 rural communities and 27 estate district ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otto Von Bismarck
Otto, Prince of Bismarck, Count of Bismarck-Schönhausen, Duke of Lauenburg (, ; 1 April 1815 – 30 July 1898), born Otto Eduard Leopold von Bismarck, was a conservative German statesman and diplomat. From his origins in the upper class of Junker landowners, Bismarck rose rapidly in Prussian politics, and from 1862 to 1890 he was the minister president and foreign minister of Prussia. Before his rise to the executive, he was the Prussian ambassador to Russia and France and served in both houses of the Prussian Parliament. He masterminded the unification of Germany in 1871 and served as the first Chancellor of the German Empire until 1890, in which capacity he dominated European affairs. He had served as the chancellor of the North German Confederation from 1867 to 1871, alongside his responsibilities in the Kingdom of Prussia. He cooperated with King Wilhelm I of Prussia to unify the various German states, a partnership that would last for the rest of Wilhelm's life. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kurfürstendamm
The Kurfürstendamm (; colloquially ''Ku'damm'', ; en, Prince Elector Embankment) is one of the most famous avenues in Berlin. The street takes its name from the former ''Kurfürsten'' (prince-electors) of Brandenburg. The broad, long boulevard can be considered the Champs-Élysées of Berlin and is lined with shops, houses, hotels and restaurants. In particular, many fashion designers have their shops there, as well as several car manufacturers' show rooms. Description The avenue includes four lines of plane trees and runs for through the city. It branches off from the Breitscheidplatz, where the ruins of the Kaiser Wilhelm Memorial Church stand, and leads southwestward up to the district of Grunewald. At the junction with Joachimstaler Straße it passes the Café Kranzler, successor of the Café des Westens, a famous venue for artists and bohémiens of the pre–World War I era. The Kurfürstendamm U-Bahn station and the Swissôtel Berlin can be found at the same ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
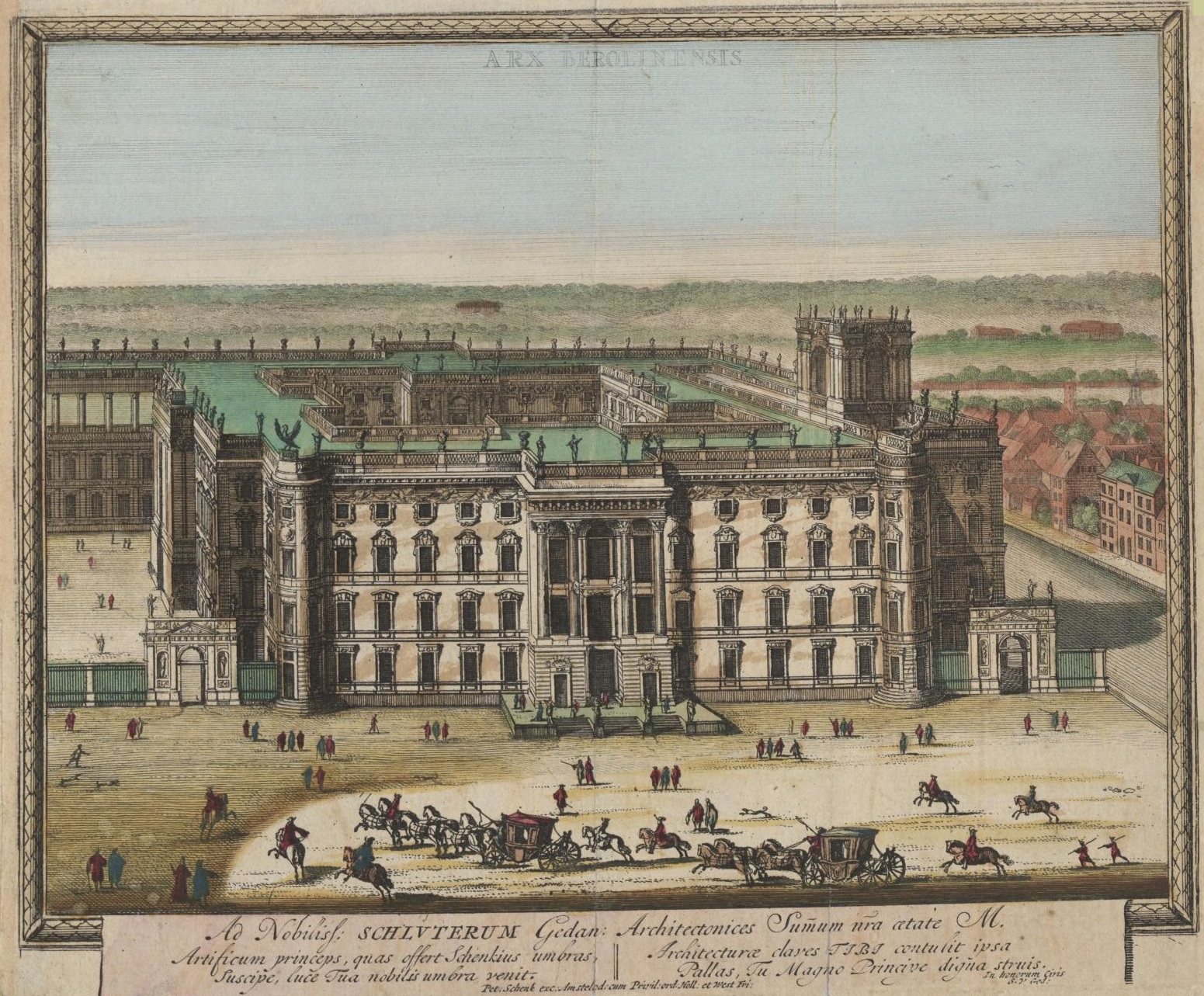
Stadtschloss, Berlin
The Berlin Palace (german: Berliner Schloss), formally the Royal Palace (german: Königliches Schloss), on the Museum Island in the Mitte area of Berlin, was the main residence of the House of Hohenzollern from 1443 to 1918. Expanded by order of King Frederick I of Prussia according to plans by Andreas Schlüter from 1689 to 1713, it was thereafter considered a major work of Prussian Baroque architecture. The former royal palace was one of Berlin’s largest buildings and shaped the cityscape with its dome. Used for various government functions after the fall of the monarchy in 1918, it was damaged during the Allied bombing in World War II, and was demolished by the East German authorities in 1950. In the 1970s, it became the location of the modernist East German Palace of the Republic (the central government building of East Germany). After German reunification and several years of debate and discussion, particularly regarding the fraught historical legacy of both buildi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
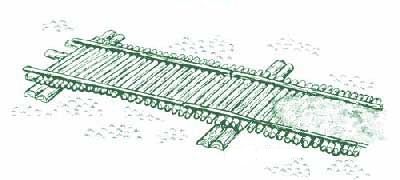
Corduroy Road
A corduroy road or log road is a type of road or timber trackway made by placing logs, perpendicular to the direction of the road over a low or swampy area. The result is an improvement over impassable mud or dirt roads, yet rough in the best of conditions and a hazard to horses due to shifting loose logs. Corduroy roads can also be built as a foundation for other surfacing. If the logs are buried in wet, acidic, anaerobic soils such as peat or muskeg, they decay very slowly. A few corduroy road foundations that date back to the early 20th century still exist in North America. One example is the Alaska Highway between Burwash Landing and Koidern, Yukon, Canada, which was rebuilt in 1943, less than a year after the original route was graded on thin soil and vegetation over permafrost, by using corduroy, then building a gravel road on top. During the 1980s, the gravel was covered with a chip-seal. The late 1990s saw replacement of this road with modern road construction, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Umlaut (diacritic)
The umlaut () is the diacritical mark used to indicate in writing (as part of the letters , , and ) the result of the historical sound shift due to which former back vowels are now pronounced as front vowels (for example , , and as , , and ). (The term ermanicumlaut is also used for the underlying historical sound shift process.) In its contemporary printed form, the mark consists of two dots placed over the letter to represent the changed vowel sound. It looks identical to the diaeresis mark used in other European languages and is represented by the same Unicode code point. The word ''trema'' (french: tréma), used in linguistics and also classical scholarship, describes the form of both the umlaut diacritic and the diaeresis rather than their function and can therefore be used to refer to both. German origin and current usage (literally "changed sound") is the German name of the sound shift phenomenon also known as '' i-mutation''. In German, this term is also use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
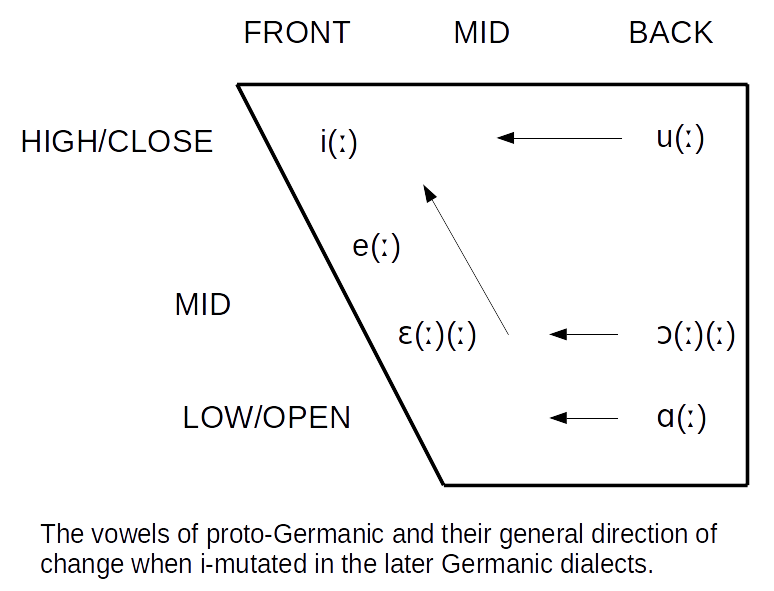
Germanic Umlaut
The Germanic umlaut (sometimes called i-umlaut or i-mutation) is a type of linguistic umlaut in which a back vowel changes to the associated front vowel ( fronting) or a front vowel becomes closer to ( raising) when the following syllable contains , , or . It took place separately in various Germanic languages starting around AD 450 or 500 and affected all of the early languages except Gothic. An example of the resulting vowel alternation is the English plural ''foot ~ feet'' (from Proto-Germanic , pl. ). Germanic umlaut, as covered in this article, does not include other historical vowel phenomena that operated in the history of the Germanic languages such as Germanic a-mutation and the various language-specific processes of u-mutation, nor the earlier Indo-European ablaut (''vowel gradation''), which is observable in the conjugation of Germanic strong verbs such as ''sing/sang/sung''. While Germanic umlaut has had important consequences for all modern Germanic langua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |