|
Grosvenor Atterbury
Grosvenor Atterbury (July 7, 1869 in Detroit, MI – October 18, 1956 in Southampton, New York, Southampton, NY) was an American architect, urban planner and writer. He studied at Yale University, where he was an editor of campus humor magazine ''The Yale Record'' After travelling in Europe, he studied architecture at Columbia University and worked in the offices of McKim, Mead & White. Much of Atterbury's early work consisted of weekend houses for wealthy industrialists. Atterbury was given the commission for the model housing community of Forest Hills Gardens which began in 1909 under the sponsorship of the Russell Sage Foundation. For Forest Hills, Atterbury developed an innovative construction method: each house was built from approximately 170 standardized precast concrete panels, fabricated off-site and assembled by crane. The system was sophisticated even by modern standards: panels were cast with integral hollow insulation chambers; casting formwork incorporated an interna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forest Hills Gardens
Forest Hills is a mostly residential neighborhood in the central portion of the borough of Queens in New York City. It is adjacent to Corona to the north, Rego Park and Glendale to the west, Forest Park to the south, Kew Gardens to the southeast, and Flushing Meadows–Corona Park to the east. The area was originally referred to as "Whitepot".About Forest Hills at QueensNewYork.com The current name comes from the Cord Meyer Development Company, which bought in central Queens in 1906 and renamed it after Forest Park. Further development came in the 1920s and 1930s with the widening of throug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Connecticut Hall
Connecticut Hall (formerly South Middle College) is a Georgian building on the Old Campus of Yale University. Completed in 1752, it was originally a student dormitory, a function it retained for 200 years. Part of the first floor became home to the Yale College Dean's Office after 1905, and the full building was converted to departmental offices in the mid-twentieth century. It is currently used by the Department of Philosophy, and its third story contains a room for meetings of the Yale Faculty of Arts & Sciences, the academic faculty of Yale College and the Graduate School. Connecticut Hall is the third-oldest of only seven surviving American colonial-era college buildings, and the second-oldest structure built for Yale College in New Haven. It was built, in part, by enslaved laborers. The first building in a campus plan known as Old Brick Row that stood from 1750 to 1870, it is the only survivor of a demolition campaign that created the modern Old Campus quadrangle. It was des ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hartford, Connecticut
Hartford is the capital city of the U.S. state of Connecticut. It was the seat of Hartford County until Connecticut disbanded county government in 1960. It is the core city in the Greater Hartford metropolitan area. Census estimates since the 2010 United States census have indicated that Hartford is the fourth-largest city in Connecticut with a 2020 population of 121,054, behind the coastal cities of Bridgeport, New Haven, and Stamford. Hartford was founded in 1635 and is among the oldest cities in the United States. It is home to the country's oldest public art museum (Wadsworth Atheneum), the oldest publicly funded park (Bushnell Park), the oldest continuously published newspaper (the ''Hartford Courant''), and the second-oldest secondary school (Hartford Public High School). It is also home to the Mark Twain House, where the author wrote his most famous works and raised his family, among other historically significant sites. Mark Twain wrote in 1868, "Of all the beautifu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Children's Village Of The Hartford Orphan Asylum
The Village is a social service agency providing community services and resources for at-risk families and children in Hartford, Connecticut. With an organizational history dating to the early 19th century, it is one of the oldest such institutions in the state. Its architecturally distinguished campus, located 1680 Albany Avenue, is listed on the National Register of Historic Places. Services The Village provides a broad array of services intended to support the needs of children and families. Services offered include financial and social services for at-risk families, more intensive services including outpatient and inpatient residential treatments for children with emotional and mental health issues, and adoption placement services. Campus The Village's primary facilities are located in northwestern Hartford, at the junction of Albany Avenue (United States Route 44) and Bloomfield Avenue (Connecticut Route 189 Connecticut () is the southernmost state in the New England ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Winter Harbor, Maine
Winter Harbor is a town on the Schoodic Peninsula in Hancock County, Maine, United States. The population was 461 at the 2020 census. The town is located just outside the Schoodic Peninsula portion of Acadia National Park, and is due east of the town of Bar Harbor and Ellsworth. Winter Harbor was once the location of a US Naval Station, NSGA-WH, which closed in the mid-2000s, and is now home to the Schoodic Institute’s Education and Research Center. The Schoodic Point District of Acadia National Park is adjacent to the town, and has played an important role in the community’s economic and social development. The Municipality includes the village proper of Winter Harbor, the summer colony of Grindstone Neck, and the hamlets of Gerrishville and Summer Harbor. An iconic, Downeast fishing village, Winter Harbor is home to an active, multigenerational fishing fleet, and is the namesake of the Winter Harbor model boat. In addition, the community is or was a summer residence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russell Sage Foundation Building
The Russell Sage Foundation is an American non-profit organisation established by Margaret Olivia Sage in 1907 for “the improvement of social and living conditions in the United States.” It was named after her recently deceased husband, railroad executive Russell Sage. The foundation dedicates itself to strengthening the methods, data, and theoretical core of the social sciences in order to better understand societal problems and develop informed responses. It supports visiting scholars in residence and publishes books and a journal under its own imprint. It also funds researchers at other institutions and supports programs intended to develop new generations of social scientists. The foundation focuses on labor markets, immigration and ethnicity, and social inequality in the United States, as well as behavioral economics. History The Russell Sage Foundation was established in 1907 for "the improvement of social and living conditions in the United States" by a gift of $10& ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
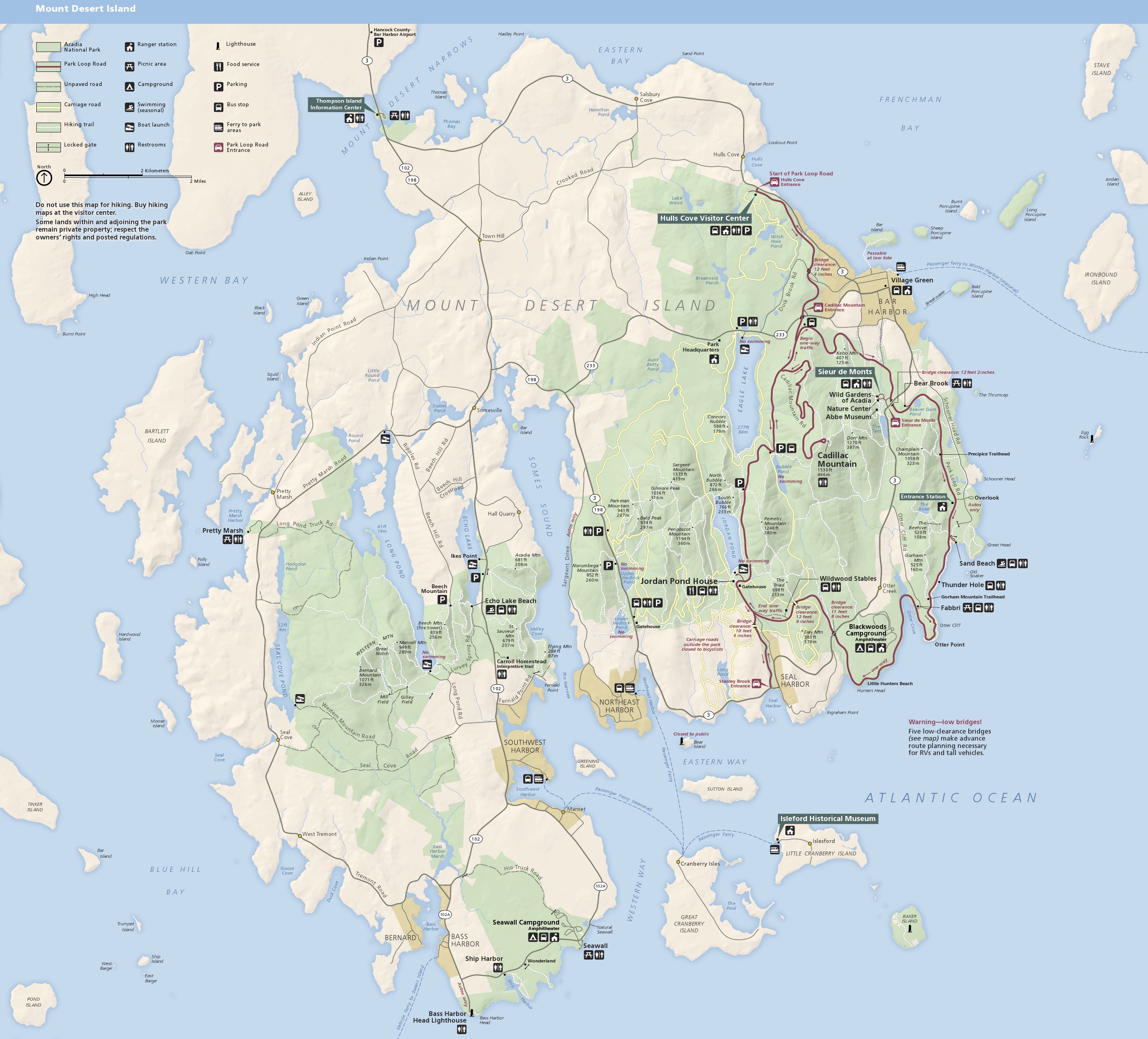
Acadia National Park, Maine
Acadia National Park is an American national park located along the mid-section of the Maine coast, southwest of Bar Harbor, Maine, Bar Harbor. The park preserves about half of Mount Desert Island, part of the Isle au Haut, the tip of the Schoodic Peninsula, and portions of 16 smaller outlying islands. It protects the natural beauty of the rocky headlands, including the highest mountains along the Atlantic coast. Acadia boasts a glaciated coastal and island landscape, an abundance of habitats, a high level of biodiversity, clean air and water, and a rich cultural heritage. The park contains the tallest mountain on the Atlantic Coast of the United States (Cadillac Mountain), exposed granite domes, glacial erratics, U-shaped valleys, and Cobble (geology), cobble beaches. Its mountains, lakes, streams, wetlands, forests, meadows, and coastlines contribute to a diversity of plants and animals. Weaved into this landscape is a Acadia National Park carriage paths, bridges and gatehouse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acadia National Park
Acadia National Park is an American national park located along the mid-section of the Maine coast, southwest of Bar Harbor. The park preserves about half of Mount Desert Island, part of the Isle au Haut, the tip of the Schoodic Peninsula, and portions of 16 smaller outlying islands. It protects the natural beauty of the rocky headlands, including the highest mountains along the Atlantic coast. Acadia boasts a glaciated coastal and island landscape, an abundance of habitats, a high level of biodiversity, clean air and water, and a rich cultural heritage. The park contains the tallest mountain on the Atlantic Coast of the United States (Cadillac Mountain), exposed granite domes, glacial erratics, U-shaped valleys, and cobble beaches. Its mountains, lakes, streams, wetlands, forests, meadows, and coastlines contribute to a diversity of plants and animals. Weaved into this landscape is a historic carriage road system financed by John D. Rockefeller Jr. In total, it encompasses . ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acadia National Park Carriage Paths, Bridges And Gatehouses
Acadia National Park, largely on Mount Desert Island, off the coast of the U.S. state of Maine, was created in part by land and other donations by John D. Rockefeller Jr. Between 1919 and 1931, Rockefeller, who was opposed to the introduction of automobiles on the island, personally oversaw the construction of a network of carriage roads, closed to motorized vehicles, on the eastern half of the island, including sixteen granite bridges and two gatehouses. The major portion of this network now falls within the bounds of the national park, and was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1979. The network of carriage roads is open to the public for non-motorized uses in the summer, including walking and bicycling. In the winter, most of the network is open to cross-country skiing, and a portion of it is open to snowmobiling. History Beginning in about 1890, Mount Desert Island became a summer resort haven for a number of wealthy families, including the Rockefellers, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Islip (CDP), New York
Islip ( ) is a hamlet and census-designated place (CDP) that lies within the town of the same name in Suffolk County, New York. Located on the south shore of Long Island, the CDP had a population of 18,869 at the time of the 2010 census, a decline of 8% from the 2000 census. Geography According to the United States Census Bureau, the CDP of Islip has a total area of . is land and , or 2.43%, is water. Islip is situated on Long Island's South Shore, on the north side of Great South Bay, across from Fire Island. The Seatuck National Wildlife Refuge is located at its southeastern corner. Demographics Demographics of the CDP As of the census of 2000, there were 20,575 people, 6,868 households and 5,302 families residing in Islip CDP. The population density was 3,808.8 per square mile (1,471.1/km2). There were 7,026 housing units, at an average density of 1,300.6/sq mi (502.4/km2). The racial makeup of Islip was 87.67% White, 10.67% Hispanic, 4.90% Black or African-Ame ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Church-in-the-Gardens
The Church-in-the-Gardens, also known as Community Congregational Christian Church, is a historic Congregational church complex located in Forest Hills, Queens, New York. The complex includes the church (1915), Community House (1926), and Parish Hall (1953) connected by breezeways and a separate parsonage (1929). The buildings are all in an eclectic Tudor Revival style. The church was designed by architect Grosvenor Atterbury and is a rectangular building with a prominent tower and attached bell tower. ''Note:'' This includes ''See also:'' The congregation joined the United Church of Christ in May 2012. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places The National Register of Historic Places (NRHP) is the United States federal government's official list of districts, sites, buildings, structures and objects deemed worthy of preservation for their historical significance or "great artistic v ... in 2009. References External links * * United Church of Chri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greenwood Lake, New York
Greenwood Lake is a village in Orange County, New York, United States, in the southern part of the town of Warwick. As of the United States 2010 Census, the village population was 3,154. It is part of the Poughkeepsie– Newburgh– Middletown, NY Metropolitan Statistical Area as well as the larger New York–Newark–Bridgeport Combined Statistical Area. History Greenwood Lake was settled by Europeans as a farming community in the 1700s in the area of an earlier village occupied by the Munsee Indians. The Munsees, considered a branch of the Lenape people (also known as the Delaware), were Algonquian speakers who called the lake ''Quampium.'' Some of the farms at the head of the lake were purchased by the Morris Canal and Banking Company in 1837, and portions of these properties were inundated after a dam was built that same year. It greatly increased the size of the lake to its current condition. The enlarged lake attracted tourists, and a grand hotel operate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)