|
Gross–Pitaevskii Equation
The Gross–Pitaevskii equation (GPE, named after Eugene P. Gross and Lev Petrovich Pitaevskii) describes the ground state of a quantum system of identical bosons using the Hartree–Fock approximation and the pseudopotential interaction model. A Bose–Einstein condensate (BEC) is a gas of bosons that are in the same quantum state, and thus can be described by the same wavefunction. A free quantum particle is described by a single-particle Schrödinger equation. Interaction between particles in a real gas is taken into account by a pertinent many-body Schrödinger equation. In the Hartree–Fock approximation, the total wave-function \Psi of the system of N bosons is taken as a product of single-particle functions \psi: \Psi(\mathbf_1, \mathbf_2, \dots, \mathbf_N) = \psi(\mathbf_1) \psi(\mathbf_2) \dots \psi(\mathbf_N), where \mathbf_i is the coordinate of the i-th boson. If the average spacing between the particles in a gas is greater than the scattering length (that is, in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eugene P
Eugene may refer to: People and fictional characters * Eugene (given name), including a list of people and fictional characters with the given name * Eugene (actress) (born 1981), Kim Yoo-jin, South Korean actress and former member of the singing group S.E.S. * Eugene (wrestler), professional wrestler Nick Dinsmore * Franklin Eugene (producer), American film producer * Gene Eugene, stage name of Canadian born actor, record producer, engineer, composer and musician Gene Andrusco (1961–2000) * Wendell Eugene (1923–2017), American jazz musician Places Canada * Mount Eugene, in Nunavut; the highest mountain of the United States Range on Ellesmere Island United States * Eugene, Oregon, a city ** Eugene, OR Metropolitan Statistical Area ** Eugene (Amtrak station) * Eugene Apartments, NRHP-listed apartment complex in Portland, Oregon * Eugene, Indiana, an unincorporated town * Eugene, Missouri, an unincorporated town Business * Eugene Green Energy Standard, an int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nonlinear
In mathematics and science, a nonlinear system is a system in which the change of the output is not proportional to the change of the input. Nonlinear problems are of interest to engineers, biologists, physicists, mathematicians, and many other scientists because most systems are inherently nonlinear in nature. Nonlinear dynamical systems, describing changes in variables over time, may appear chaotic, unpredictable, or counterintuitive, contrasting with much simpler linear systems. Typically, the behavior of a nonlinear system is described in mathematics by a nonlinear system of equations, which is a set of simultaneous equations in which the unknowns (or the unknown functions in the case of differential equations) appear as variables of a polynomial of degree higher than one or in the argument of a function which is not a polynomial of degree one. In other words, in a nonlinear system of equations, the equation(s) to be solved cannot be written as a linear combination of the un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dipolar Interaction
In physics, a dipole () is an electromagnetic phenomenon which occurs in two ways: *An electric dipole deals with the separation of the positive and negative electric charges found in any electromagnetic system. A simple example of this system is a pair of charges of equal magnitude but opposite sign separated by some typically small distance. (A permanent electric dipole is called an electret.) *A magnetic dipole is the closed circulation of an electric current system. A simple example is a single loop of wire with constant current through it. A bar magnet is an example of a magnet with a permanent magnetic dipole moment. Dipoles, whether electric or magnetic, can be characterized by their dipole moment, a vector quantity. For the simple electric dipole, the electric dipole moment points from the negative charge towards the positive charge, and has a magnitude equal to the strength of each charge times the separation between the charges. (To be precise: for the definition of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contact Interaction
The Fermi contact interaction is the magnetic interaction between an electron and an atomic nucleus. Its major manifestation is in electron paramagnetic resonance and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopies, where it is responsible for the appearance of isotropic hyperfine coupling. This requires that the electron occupy an s-orbital. The interaction is described with the parameter ''A'', which takes the units megahertz. The magnitude of ''A'' is given by this relationships : A = -\frac \pi \left \langle \boldsymbol_n \cdot \boldsymbol_e \right \rangle , \Psi (0), ^2\qquad \mbox and : A = -\frac \mu_0 \left \langle \boldsymbol_n \cdot \boldsymbol_e \right \rangle , \Psi(0), ^2, \qquad \mbox where ''A'' is the energy of the interaction, ''μ''''n'' is the nuclear magnetic moment, ''μ''''e'' is the electron magnetic dipole moment, Ψ(0) is the value of the electron wavefunction at the nucleus, and \left\langle \cdots \right\rangle denotes the quantum mechanical spin coupling. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spectral Method
Spectral methods are a class of techniques used in applied mathematics and scientific computing to numerically solve certain differential equations. The idea is to write the solution of the differential equation as a sum of certain " basis functions" (for example, as a Fourier series which is a sum of sinusoids) and then to choose the coefficients in the sum in order to satisfy the differential equation as well as possible. Spectral methods and finite element methods are closely related and built on the same ideas; the main difference between them is that spectral methods use basis functions that are generally nonzero over the whole domain, while finite element methods use basis functions that are nonzero only on small subdomains (compact support). Consequently, spectral methods connect variables ''globally'' while finite elements do so ''locally''. Partially for this reason, spectral methods have excellent error properties, with the so-called "exponential convergence" being the fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crank–Nicolson Method
In numerical analysis, the Crank–Nicolson method is a finite difference method used for numerically solving the heat equation and similar partial differential equations. It is a second-order method in time. It is implicit in time, can be written as an implicit Runge–Kutta method, and it is numerically stable. The method was developed by John Crank and Phyllis Nicolson in the mid 20th century. For diffusion equations (and many other equations), it can be shown the Crank–Nicolson method is unconditionally stable. However, the approximate solutions can still contain (decaying) spurious oscillations if the ratio of time step \Delta t times the thermal diffusivity to the square of space step, \Delta x^2, is large (typically, larger than 1/2 per Von Neumann stability analysis). For this reason, whenever large time steps or high spatial resolution is necessary, the less accurate backward Euler method is often used, which is both stable and immune to oscillations. The method ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ansatz
In physics and mathematics, an ansatz (; , meaning: "initial placement of a tool at a work piece", plural Ansätze ; ) is an educated guess or an additional assumption made to help solve a problem, and which may later be verified to be part of the solution by its results. Use An ansatz is the establishment of the starting equation(s), the theorem(s), or the value(s) describing a mathematical or physical problem or solution. It typically provides an initial estimate or framework to the solution of a mathematical problem, and can also take into consideration the boundary conditions (in fact, an ansatz is sometimes thought of as a "trial answer" and an important technique in solving differential equations). After an ansatz, which constitutes nothing more than an assumption, has been established, the equations are solved more precisely for the general function of interest, which then constitutes a confirmation of the assumption. In essence, an ansatz makes assumptions about the form o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Topological Defect
A topological soliton occurs when two adjoining structures or spaces are in some way "out of phase" with each other in ways that make a seamless transition between them impossible. One of the simplest and most commonplace examples of a topological soliton occurs in old-fashioned coiled telephone handset cords, which are usually coiled clockwise. Years of picking up the handset can end up coiling parts of the cord in the opposite counterclockwise direction, and when this happens there will be a distinctive larger loop that separates the two directions of coiling. This odd looking transition loop, which is neither clockwise nor counterclockwise, is an excellent example of a topological soliton. No matter how complex the context, anything that qualifies as a topological soliton must at some level exhibit this same simple issue of reconciliation seen in the twisted phone cord example. Topological solitons arise with ease when creating the crystalline semiconductors used in modern elect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soliton
In mathematics and physics, a soliton or solitary wave is a self-reinforcing wave packet that maintains its shape while it propagates at a constant velocity. Solitons are caused by a cancellation of nonlinear and dispersive effects in the medium. (Dispersive effects are a property of certain systems where the speed of a wave depends on its frequency.) Solitons are the solutions of a widespread class of weakly nonlinear dispersive partial differential equations describing physical systems. The soliton phenomenon was first described in 1834 by John Scott Russell (1808–1882) who observed a solitary wave in the Union Canal in Scotland. He reproduced the phenomenon in a wave tank and named it the "Wave of Translation". Definition A single, consensus definition of a soliton is difficult to find. ascribe three properties to solitons: # They are of permanent form; # They are localized within a region; # They can interact with other solitons, and emerge from the collision unchanged, e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Partial Differential Equation
In mathematics, a partial differential equation (PDE) is an equation which imposes relations between the various partial derivatives of a Multivariable calculus, multivariable function. The function is often thought of as an "unknown" to be solved for, similarly to how is thought of as an unknown number to be solved for in an algebraic equation like . However, it is usually impossible to write down explicit formulas for solutions of partial differential equations. There is, correspondingly, a vast amount of modern mathematical and scientific research on methods to Numerical methods for partial differential equations, numerically approximate solutions of certain partial differential equations using computers. Partial differential equations also occupy a large sector of pure mathematics, pure mathematical research, in which the usual questions are, broadly speaking, on the identification of general qualitative features of solutions of various partial differential equations, such a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
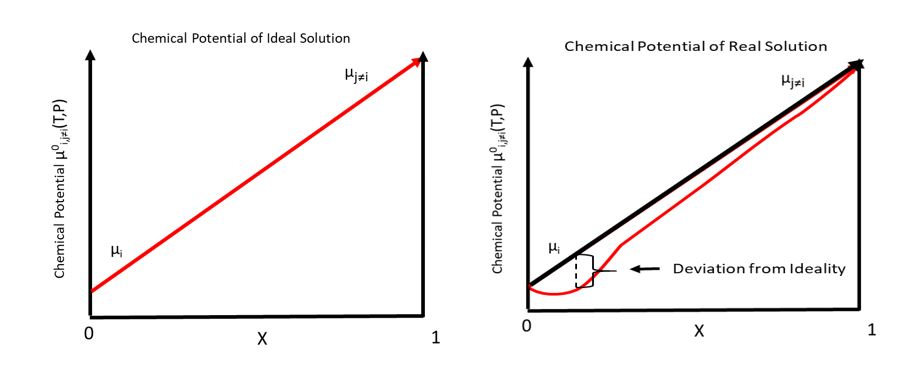
Chemical Potential
In thermodynamics, the chemical potential of a species is the energy that can be absorbed or released due to a change of the particle number of the given species, e.g. in a chemical reaction or phase transition. The chemical potential of a species in a mixture is defined as the rate of change of free energy of a thermodynamic system with respect to the change in the number of atoms or molecules of the species that are added to the system. Thus, it is the partial derivative of the free energy with respect to the amount of the species, all other species' concentrations in the mixture remaining constant. When both temperature and pressure are held constant, and the number of particles is expressed in moles, the chemical potential is the partial molar Gibbs free energy. At chemical equilibrium or in phase equilibrium, the total sum of the product of chemical potentials and stoichiometric coefficients is zero, as the free energy is at a minimum. In a system in diffusion equilibrium, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |