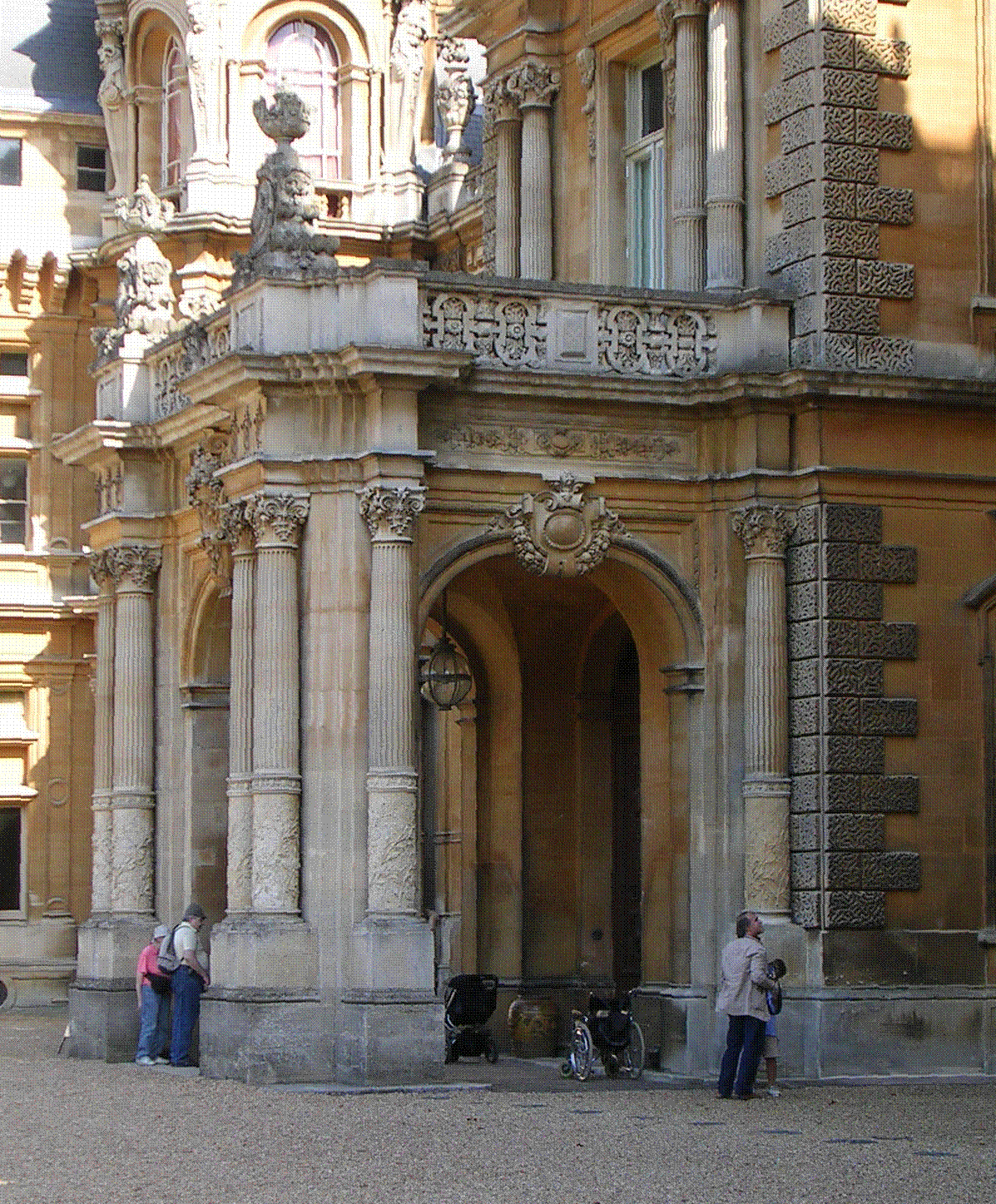|
Greathed Manor
Greathed Manor, Dormansland, Surrey, is a Victorian country house. Designed by the architect Robert Kerr in 1862–8, it is a Grade II listed building. History Greathed Manor, originally called Ford Manor, was designed by Robert Kerr for the Spender-Clay family, and was completed in 1868. The actress Joyce Grenfell was related to the family by marriage and often visited the house. Accounts of her time there are described in her autobiography “Joyce Grenfell Requests the Pleasure”. In 1904 Herbert Spender-Clay, MP and founder of the 1922 Committee, married Pauline Astor, daughter of the American billionaire William Waldorf Astor. The couple lived at the house until 1937. Greathed Manor was requisitioned by the British Government during both World Wars. In the Great War it became a Hospital for wounded American Army officers. In the Second World War it was used as the Headquarters of a Canadian Armoured Division in the run-up to D-Day. It acted as temporary premises for the L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Kerr (architect)
Robert Kerr (Aberdeen 17 January 1823 – 21 October 1904) was a British architect, architectural writer and co-founder of the Architectural Association. Biography Kerr was born in Aberdeen, where he trained as an architect. In 1844, he moved to London and in 1845 spent a year in New York City, from where he returned to London with a rebellious spirit. Together with the only 18 year old Charles Gray, in 1847 Kerr was a founder of the Architectural Association (AA), becoming its first President, 1847–48. The aim of the AA was to offer an alternative for the education of architects through a systematic course of training provided by the students themselves, rather than having to settle with the existing highly unreliable custom where young men were articled to established architects. Kerr had been elected a Fellow of the Royal Institute of British Architects (RIBA) in 1857, where he served as an examiner and as a council member. Between 1860–1902, Kerr was District Surv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
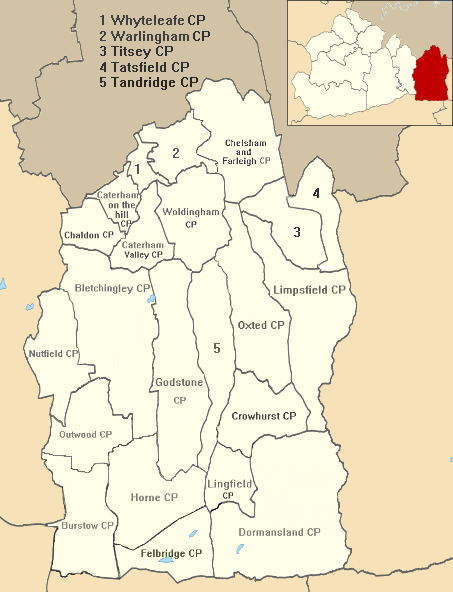
Dormansland, Surrey
Dormansland is a large village and civil parish with a low population approximately one mile south of Lingfield in Surrey, England. It was founded in the 19th century and is bordered on the east by the county of Kent and on the south by West Sussex and East Sussex, the only area of the county which borders East Sussex. The nearest town is the small town of East Grinstead, immediately across the West Sussex border. Geography Dormansland is a rural and semi-rural village of a largely cleared, flat area of the Weald save for the woodlands covering most of Greathed's private park, which is in Dormansland and scattered woodlands of Dormans Park, a housing estate toward the southern border. It is a large civil parish approximately one mile south of Lingfield. It is a recent village relative to the average age of an English village, and is bordered on the east by Kent and on the south by West Sussex and East Sussex, the only area of the county which borders East Sussex. The neares ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surrey
Surrey () is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in South East England, bordering Greater London to the south west. Surrey has a large rural area, and several significant urban areas which form part of the Greater London Built-up Area. With a population of approximately 1.2 million people, Surrey is the 12th-most populous county in England. The most populated town in Surrey is Woking, followed by Guildford. The county is divided into eleven districts with borough status. Between 1893 and 2020, Surrey County Council was headquartered at County Hall, Kingston-upon-Thames (now part of Greater London) but is now based at Woodhatch Place, Reigate. In the 20th century several alterations were made to Surrey's borders, with territory ceded to Greater London upon its creation and some gained from the abolition of Middlesex. Surrey is bordered by Greater London to the north east, Kent to the east, Berkshire to the north west, West Sussex to the south, East Sussex to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gothic Revival Architecture
Gothic Revival (also referred to as Victorian Gothic, neo-Gothic, or Gothick) is an architectural movement that began in the late 1740s in England. The movement gained momentum and expanded in the first half of the 19th century, as increasingly serious and learned admirers of the neo-Gothic styles sought to revive medieval Gothic architecture, intending to complement or even supersede the neoclassical styles prevalent at the time. Gothic Revival draws upon features of medieval examples, including decorative patterns, finials, lancet windows, and hood moulds. By the middle of the 19th century, Gothic had become the preeminent architectural style in the Western world, only to fall out of fashion in the 1880s and early 1890s. The Gothic Revival movement's roots are intertwined with philosophical movements associated with Catholicism and a re-awakening of high church or Anglo-Catholic belief concerned by the growth of religious nonconformism. Ultimately, the "Anglo-Catholicism" t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Victorian Architecture
Victorian architecture is a series of architectural revival styles in the mid-to-late 19th century. ''Victorian'' refers to the reign of Queen Victoria (1837–1901), called the Victorian era, during which period the styles known as Victorian were used in construction. However, many elements of what is typically termed "Victorian" architecture did not become popular until later in Victoria's reign, roughly from 1850 and later. The styles often included interpretations and eclectic revivals of historic styles ''(see Historicism)''. The name represents the British and French custom of naming architectural styles for a reigning monarch. Within this naming and classification scheme, it followed Georgian architecture and later Regency architecture, and was succeeded by Edwardian architecture. Although Victoria did not reign over the United States, the term is often used for American styles and buildings from the same period, as well as those from the British Empire. Victorian arc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Listed Building
In the United Kingdom, a listed building or listed structure is one that has been placed on one of the four statutory lists maintained by Historic England in England, Historic Environment Scotland in Scotland, in Wales, and the Northern Ireland Environment Agency in Northern Ireland. The term has also been used in the Republic of Ireland, where buildings are protected under the Planning and Development Act 2000. The statutory term in Ireland is " protected structure". A listed building may not be demolished, extended, or altered without special permission from the local planning authority, which typically consults the relevant central government agency, particularly for significant alterations to the more notable listed buildings. In England and Wales, a national amenity society must be notified of any work to a listed building which involves any element of demolition. Exemption from secular listed building control is provided for some buildings in current use for worship, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
St John's College, Nottingham
St John's College, Nottingham, founded as the London College of Divinity, was an Anglican and interdenominational theological college situated in Bramcote, Nottingham, England. The college stood in the open evangelical tradition and stated that its mission is "to inspire creative Christian learning marked by evangelical conviction, theological excellence and Spirit-filled life, that all who train with us might be equipped for mission in a world of change". St John's trained students for ministries in the Church of England and other denominations, independent students from a range of Christian contexts, and students for children's and youth ministries through its Midlands centre for the Institute for Children, Youth and Mission (MCYM). It offered a diversity of full-time, part-time, blended and distance learning courses, including specialist modules in pastoral care and counselling and church administration. Academic awards were validated by Durham University and Gloucester Univer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Country Houses Association
The Country Houses Association (CHA) was a British charity (a friendly society with charitable status) that converted country houses into retirement flats and maintained them from 1955 until its liquidation in 2004. History The Country Houses Association Ltd was an Industrial and Provident Society formed in 1955 by Rear Admiral Greathed, originally called the Mutual Households Association (MHA). Its stated aim was to preserve historic buildings for the benefit of the nation where those buildings were too large to support single household accommodation. During its lifetime, the Association acquired nine large country houses, and restored and preserved them until their sale in 2002–4. During their ownership by the Association, all the houses were converted into retirement apartments, with communal dining and drawing rooms, with the rental income helping to pay for the house's extensive renovations and repairs (residents also paid deposits of up to £140,000). The houses were ope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ian Nairn
Ian Douglas Nairn (24 August 1930 – 14 August 1983) was a British architectural critic who coined the word "Subtopia" to indicate drab suburbs that look identical through unimaginative town-planning. He published two strongly personalised critiques of London and Paris, and collaborated with Sir Nikolaus Pevsner, who considered his reports to be too subjective, but acknowledged him as the better writer. Early life Ian Nairn was born at 4 Milton Road, Bedford, England. Nairn's father was a draughtsman on the R101 airship programme based at Shortstown. The family moved in 1932 when the airship programme was terminated, and Nairn was brought up in Surrey. It was the balancing-act nature of this essentially suburban environment which he stated "produced a deep hatred of characterless buildings and places". Nairn had no formal architecture qualifications; he was a mathematics graduate (University of Birmingham) and a Royal Air Force pilot, flying Gloster Meteor aircraft.''The Man who ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mark Girouard
Mark Girouard (7 October 1931 – 16 August 2022) was a British architectural historian. He was an authority on the country house, and Elizabethan and Victorian architecture. Life and career Girouard was born on 7 October 1931. He was educated at Ampleforth College, read Classics at Christ Church, Oxford, and then worked for the magazine '' Country Life'' from about 1958 until 1967, firstly as a writer on architecture and then, from 1964, as its architectural editor. He was Slade Professor of Fine Art from 1975 to 1976 and elected a Fellow of the Society of Antiquaries of London in 1987. Girouard was elected a Fellow of the Royal Society of Literature in 2011. He was on the board of trustees of The Architecture Foundation from 1992 to 1999 and a founder, and the first chairman, of the Spitalfields Historic Buildings Trust. He was the grandson of Henry Beresford, 6th Marquess of Waterford through his mother, Lady Blanche Girouard. His ''Life in the English Country House'' wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bearwood House, Sindlesham
Bearwood or Bear Wood, Sindlesham, Berkshire, England is a Victorian country house built for John Walter, the owner of ''The Times''. The architect was Robert Kerr and the house was constructed between 1865 and 1874. The family fortune had been made by Walter's grandfather, John Walter I. Originally a coal merchant and underwriter, in 1785 John Walter had established ''The Daily Universal Register'', renamed as ''The Times'' in 1788. In 1816, Walter's father, John Walter II purchased the Bear Wood estate in Berkshire from the Crown Estate and in 1822 built a small villa on the site of the present house. Nothing remains of this first building, which was swept away in the gargantuan rebuilding undertaken by Kerr for John Walter III. The cost, £129,000, , was double the original estimate. In 1919, the house was sold and subsequently gifted to the Royal Merchant Navy School, which had been established in the City of London in 1827 to educate the sons of merchant sailors lost ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Porte-cochère
A porte-cochère (; , late 17th century, literally 'coach gateway'; plural: porte-cochères, portes-cochères) is a doorway to a building or courtyard, "often very grand," through which vehicles can enter from the street or a covered porch-like structure at a main or secondary entrance to a building through which originally a horse and carriage and today a motor vehicle can pass to provide arriving and departing occupants protection from the elements. Portes-cochères are still found on such structures as major public buildings and hotels, providing covered access for visitors and guests arriving by motorized transport. A porte-cochère, a structure for vehicle passage, is to be distinguished from a portico, a columned porch or entry for human, rather than vehicular, traffic. History The porte-cochère was a feature of many late 18th- and 19th-century mansions and public buildings. A well-known example is at Buckingham Palace in London. A portico at the White House in Wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |