|
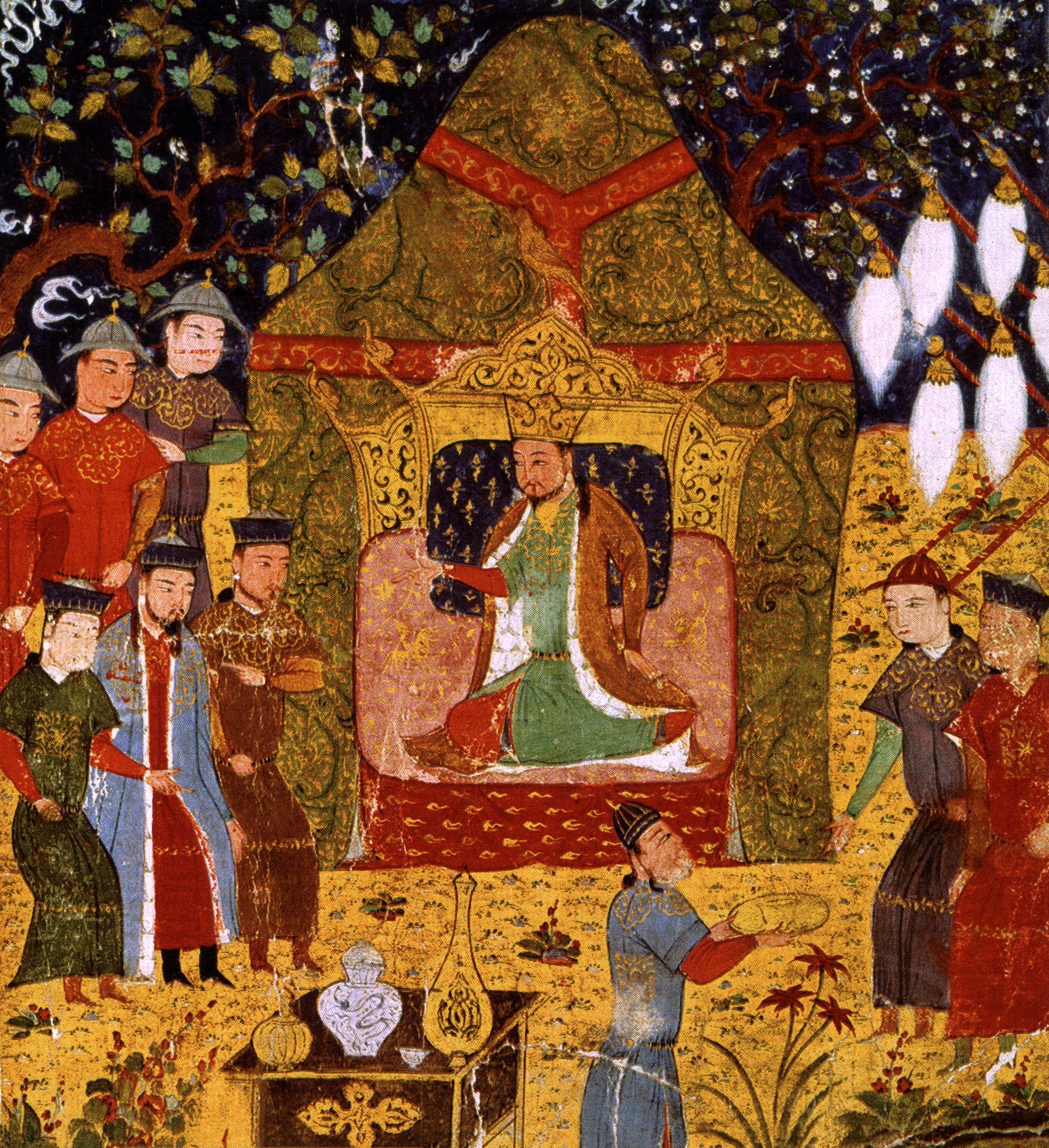
Great Horde
The Great Horde (''Uluğ Orda'') was a rump state of the Golden Horde that existed from the mid-15th century to 1502. It was centered at the core of the Golden Horde at Sarai. Both the Khanate of Astrakhan and the Khanate of Crimea broke away from the Great Horde throughout its existence, and were hostile to the Great Horde. The defeat of the forces of the Great Horde at the Great Stand on the Ugra River by Ivan III of Russia marked the end of the "Tatar yoke" over Russia. Decline of the Golden Horde The Golden Horde of Jochi had been showing cracks in the 14th century, with periods of chaos within the polity. It was united by Tokhtamysh in the 1390s, but the invasion of Timur during this time further weakened the Horde. The death of Edigu (the last person to ever unite the Horde) in 1419 marked one of the final steps of the decay of the Golden Horde, which fractured into the separate states of the Nogai Khanate, the Kazan Khanate, and later the Kasimov Khanate, which had sepa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khanate
A khaganate or khanate was a polity ruled by a khan, khagan, khatun, or khanum. That political territory was typically found on the Eurasian Steppe and could be equivalent in status to tribal chiefdom, principality, kingdom or empire. Mongol-ruled khanates Chagatai Khanate (1226–1347) After Genghis Khan established appanages for his family in the Mongol Empire during his rule (1206–1227), his sons, daughters, and grandsons inherited separate sections of the empire. The Mongol Empire and Mongolian khanates that emerged from those appanages are listed below. In 1226, the second son of Genghis Khan, Chagatai Khan established the Chagatai Khanate. At its height in the late 13th century, the khanate extended from the Amu Darya south of the Aral Sea to the Altai Mountains in the border of modern-day Mongolia and China, roughly corresponding to the defunct Qara Khitai Empire. Initially the rulers of the Chagatai Khanate recognized the supremacy of the Great Kh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jochi
Jochi Khan ( Mongolian: mn, Зүчи, ; kk, Жошы, Joşy جوشى; ; crh, Cuçi, Джучи, جوچى; also spelled Juchi; Djochi, and Jöchi c. 1182– February 1227) was a Mongol army commander who was the eldest son of Temüjin (aka Genghis Khan), and presumably one of the four sons by his principal wife Börte, though issues concerning his paternity followed him throughout his life. An accomplished military leader, he participated in his father's conquest of Central Asia, along with his brothers and uncles. Early life There is some question as to Jochi's true paternity. Shortly after Börte's marriage to Temüjin (later to become Genghis Khan), she was abducted by members of the Mergid confederation. She was given to a certain Chilger Bökh, who was the brother of the Yehe Chiledu, as a spoil of war. She remained in Chilger Bökh's captivity for a few months before she was recovered by Temüjin. Shortly afterwards she gave birth to Jochi. By all accounts, Temüji ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crimea
Crimea, crh, Къырым, Qırım, grc, Κιμμερία / Ταυρική, translit=Kimmería / Taurikḗ ( ) is a peninsula in Ukraine, on the northern coast of the Black Sea, that has been occupied by Russia since 2014. It has a population of 2.4 million. The peninsula is almost entirely surrounded by the Black Sea and the smaller Sea of Azov. The Isthmus of Perekop connects the peninsula to Kherson Oblast in mainland Ukraine. To the east, the Crimean Bridge, constructed in 2018, spans the Strait of Kerch, linking the peninsula with Krasnodar Krai in Russia. The Arabat Spit, located to the northeast, is a narrow strip of land that separates the Sivash lagoons from the Sea of Azov. Across the Black Sea to the west lies Romania and to the south is Turkey. Crimea (called the Tauric Peninsula until the early modern period) has historically been at the boundary between the classical world and the steppe. Greeks colonized its southern fringe and were absorbed b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sayid Ahmad I
Sayid Ahmad I ( fa, ) was a khan of the Golden Horde from 1427 or 1433 until 1455. Unlike the last five of six khans, Ahmad was a younger son of Tokhtamysh. Breakup of the Horde While he died before the Horde dissolved, historians believe that Sayid Ahmad was responsible for creating the conditions in the khanate which allowed it to happen. Paine, Sheila: ''The Golden Horde: From the Himalaya to the Mediterranean'', p. 80, Penguin Books, 1998. Genealogy *Genghis Khan *Jochi *Orda Khan *Sartaqtay * Köchü *Bayan * Sasibuqa * Ilbasan * Chimtay *Tuli Kwadja *Tokhtamysh Tokhtamysh ( kz, Тоқтамыс, tt-Cyrl, Тухтамыш, translit=Tuqtamış, fa, توقتمش),The spelling of Tokhtamysh varies, but the most common spelling is Tokhtamysh. Tokhtamısh, Toqtamysh, ''Toqtamış'', ''Toqtamıs'', ''Toktamy ... *Sayid Ahmad References Khans of the Golden Horde 15th-century monarchs in Europe Year of birth unknown 1455 deaths {{Europe-royal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Küchük Muhammad
Küchük Muḥammad or Kīchīk Muḥammad (; 28 June 1391 – 1459) was a Mongol Khan of the Golden Horde from 1433 until his death in 1459. He was the son of Tīmūr Khan, possibly by a daughter of the powerful beglerbeg Edigu. His name, "Little Muḥammad," was intended to distinguish him from a rival and older contemporary, Ulugh Muḥammad, "Big Muḥammad." Küchük Muḥammad started out as would-be khan at (old) Astrakhan from c. 1428, supported by his possible uncles, Ghāzī and Nawrūz, the sons of Edigu. A quarrel with the emir Nawrūz cost Küchük Muḥammad his desertion to Ulugh Muḥammad, and for a long time neither khan could eliminate his rival. However, Ulugh Muḥammad alienated more of his leading emirs, like Tekne and Ḥaydar, who deserted him to set up their own khan, Sayyid Aḥmad, son of Beg Ṣūfī, in 1432. Weakened by this, Ulugh Muḥammad came to terms with Küchük Muḥammad in 1432 or 1433, dividing the Golden Horde along the Volga, Ulugh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qonqirat
The Khongirad ( Mongolian: ᠬᠣᠩᠭᠢᠷᠠᠳ; Хонгирад; Khonghirad; ), also known as Qongirat (Qoŋğırat/Қоңғырат), was one of the major divisions of the Mongol tribes. Variations on the name include Onggirat, Ongirat, Qongrat, Khungirat,''The Chinese Social and Political Science Review'', Volume 20, pub Chinese Social and Political Science Association, 1937, p494. Kungrad,Central Asia: Foundations of Change'', by R. D. McChesney, pub Darwin Press, 1996, p202. Qunghrãt, Wangjila (王紀剌), Yongjilie (雍吉烈), Qungrat, and Guangjila (廣吉剌) in Chinese sources. Their homeland was located in the vicinity of Lake Hulun in Inner Mongolia and Khalkha River in Mongolia,M. Sanjdorj, History of the Mongolian People's Republic, Volume I, 1966 where they maintained close ties with the ruling dynasties of northern China. Because the various Hongirad clans never united under a single leader, the tribe never rose to great military glory. Their greatest fame c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manghud
The Mangghud, or Manghud ( mn, Мангуд, ''Mangud''), were a Mongol tribe of the Urud-Manghud federation. They established the Nogai Horde in the 14th century and the Manghit dynasty to rule the Emirate of Bukhara in 1785. They took the Islamic title of Emir instead of the title of Khan, since they were not descendants of Genghis Khan and rather based their legitimacy to rule on Islam. The clan name was used for Mongol vanguards as well. Their descendants live in several regions of the former Mongol Empire. Manghuds in the Mongol Empire According to ancient sources, they were derived from the Khiyad Mongols. The Manghuds and the Uruuds were war-like people from the Mongolian plateau. Some notable Manghud warriors supported Genghis Khan (1162–1227), while a body of them resisted his rise to power. When the Mongol Empire began to expand westward, the Manghud people were spread westward into the Middle East along with many other Mongol tribes. In the Golden Horde, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qiyat
A Borjigin, ; ; russian: Борджигин, Bordžigin; English plural: Borjigins or Borjigid (from Middle Mongolian);''Histoire des campagnes de Gengis Khan'', p. 119. Manchu plural: is a member of the Mongol sub-clan, which started with Bodonchar Munkhag of the Kiyat clan. Yesugei's descendants were thus said to be Kiyat-Borjigin. The senior Borjigids provided ruling princes for Mongolia and Inner Mongolia until the 20th century.Humphrey & Sneath, p. 27. The clan formed the ruling class among the Mongols and some other peoples of Central Asia and Eastern Europe. Today, the Borjigid are found in most of Mongolia, Inner Mongolia and Xinjiang, and additionally genetic research has shown that descent from Genghis Khan and Amir Timur Barlas is common throughout Central Asia and other regions. Origin and name The patrilineage began with Blue-grey Wolf (Börte Chino) and Fallow Doe (Gua Maral). According to ''The Secret History of the Mongols'', their 11th generation desce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kasimov Khanate
Qasim Khanate or Kingdom of Qasim or Khanate of Qasım ( tt-Cyrl, Касыйм ханлыгы/Касыйм патшалыгы; russian: Касимовское ханство/Касимовское царство, ''Kasimovskoye khanstvo/Kasimovskoye tsarstvo'') was a Tatar-ruled khanate, a vassal of Russia, which existed from 1452 until 1681 in the territory of modern Ryazan Oblast in Russia with its capital Kasimov, in the middle course of the Oka River. It was established in the lands which Grand Prince Vasily II of Moscow (reigned 1425–1462) presented in 1452 to the Kazan prince Qasim Khan (d. 1469), son of the first Kazan khan Olug Moxammat. Pre-history The original populations were Finnic tribes Meshchyora and Muroma, Mordvins. The land was under Kievan Rus' and Volga Bulgaria's influence. Local tribes were tributaries of Ruthenian dukes. Later, the area was incorporated into Vladimir-Suzdal. In 1152, Duke of Vladimir Yuri Dolgoruky founded Gorodets-Meshchyorskiy. Aft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kazan Khanate
The Khanate of Kazan ( tt, Казан ханлыгы, Kazan xanlıgı; russian: Казанское ханство, Kazanskoye khanstvo) was a medieval Tatar Turkic state that occupied the territory of former Volga Bulgaria between 1438 and 1552. The khanate covered contemporary Tatarstan, Mari El, Chuvashia, Mordovia, and parts of Udmurtia and Bashkortostan; its capital was the city of Kazan. It was one of the successor states of the Golden Horde (Kipchak Khanate), and it came to an end when it was conquered by the Tsardom of Russia. Geography and population The territory of the khanate comprised the Muslim Bulgar-populated lands of the Bolğar, Cükätäw, Kazan, and Qaşan duchies and other regions that originally belonged to Volga Bulgaria. The Volga, Kama and Vyatka were the main rivers of the khanate, as well as the major trade ways. The majority of the population were Kazan Tatars. Their self-identity was not restricted to Tatars; many identified themselves simply as M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nogai Khanate
The Nogai Horde was a confederation founded by the Nogais that occupied the Pontic–Caspian steppe from about 1500 until they were pushed west by the Kalmyks and south by the Russians in the 17th century. The Mongol tribe called the Manghuds constituted a core of the Nogai Horde. In the 13th century, the leader of the Golden Horde, Nogai Khan, a direct descendant of Genghis Khan through Jochi, formed an army of the Manghits joined by numerous Turkic tribes. A century later the Nogays were led by Edigu, a commander of Manghit paternal origin and Jochid maternal origin, who founded the Nogai dynasty. In 1557, Nogai ''Nur-al-Din'' Qazi Mirza quarreled with Ismael Beg and founded the Lesser Nogai Horde on the steppe of the North Caucasus. The Nogais north of the Caspian were thereafter called the Great Nogai Horde. In the early 17th century, the Horde broke down further under the onslaught of the Kalmyks. The Nogais north of the Black Sea were nominally subject to the Crimean Khanat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |