|
Graigue, Dorrha
Graigue (''An Ghráig'' in Irish) a townland in the civil parish of Dorrha in the Barony of Ormond Lower, County Tipperary, Ireland. It is located in the extreme north of the county, east of Rathcabbin and is one of 12 townlands in County Tipperary known as Graigue in English. The Church of Ireland church building (1832) was financed by the Board of First Fruits. It and its graveyard are located within the enclosure of an early Christian monastic settlement. The Dáil constituency of Offaly County Offaly (; ga, Contae Uíbh Fhailí) is a county in Ireland. It is part of the Eastern and Midland Region and the province of Leinster. It is named after the ancient Kingdom of Uí Failghe. It was formerly known as King's County, in hono ... includes Graigue along with twenty four other electoral divisions within County Tipperary. References {{coord missing, County Tipperary Townlands of County Tipperary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irish Language
Irish ( Standard Irish: ), also known as Gaelic, is a Goidelic language of the Insular Celtic branch of the Celtic language family, which is a part of the Indo-European language family. Irish is indigenous to the island of Ireland and was the population's first language until the 19th century, when English gradually became dominant, particularly in the last decades of the century. Irish is still spoken as a first language in a small number of areas of certain counties such as Cork, Donegal, Galway, and Kerry, as well as smaller areas of counties Mayo, Meath, and Waterford. It is also spoken by a larger group of habitual but non-traditional speakers, mostly in urban areas where the majority are second-language speakers. Daily users in Ireland outside the education system number around 73,000 (1.5%), and the total number of persons (aged 3 and over) who claimed they could speak Irish in April 2016 was 1,761,420, representing 39.8% of respondents. For most of recorded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Townland
A townland ( ga, baile fearainn; Ulster-Scots: ''toonlann'') is a small geographical division of land, historically and currently used in Ireland and in the Western Isles in Scotland, typically covering . The townland system is of Gaelic origin, pre-dating the Norman invasion, and most have names of Irish origin. However, some townland names and boundaries come from Norman manors, plantation divisions, or later creations of the Ordnance Survey.Connolly, S. J., ''The Oxford Companion to Irish History, page 577. Oxford University Press, 2002. ''Maxwell, Ian, ''How to Trace Your Irish Ancestors'', page 16. howtobooks, 2009. The total number of inhabited townlands in Ireland was 60,679 in 1911. The total number recognised by the Irish Place Names database as of 2014 was 61,098, including uninhabited townlands, mainly small islands. Background In Ireland a townland is generally the smallest administrative division of land, though a few large townlands are further divided into h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Civil Parishes In Ireland
Civil parishes () are units of territory in the island of Ireland that have their origins in old Gaelic territorial divisions. They were adopted by the Anglo-Norman Lordship of Ireland and then by the Elizabethan Kingdom of Ireland, and were formalised as land divisions at the time of the Plantations of Ireland. They no longer correspond to the boundaries of Roman Catholic or Church of Ireland parishes, which are generally larger. Their use as administrative units was gradually replaced by Poor_law_union#Ireland, Poor Law Divisions in the 19th century, although they were not formally abolished. Today they are still sometimes used for legal purposes, such as to locate property in deeds of property registered between 1833 and 1946. Origins The Irish parish was based on the Gaelic territorial unit called a ''túath'' or ''Trícha cét''. Following the Norman invasion of Ireland, the Anglo-Normans, Anglo-Norman barons retained the ''tuath'', later renamed a parish or manor, as a un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dorrha
Dorrha () is a civil parish in the historical barony of Ormond Lower, County Tipperary, Ireland. It is located in the extreme north of County Tipperary and includes the settlement of Rathcabbin Rathcabbin (''Ráth Cabáin'' in Irish) often Rathcabban is a small village and an electoral district situated at the very north of County Tipperary in Ireland. The village is located off the R489 regional road between Portumna, County Galway .... See also * List of civil parishes of County Tipperary References Civil parishes of Ormond Lower {{Tipperary-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
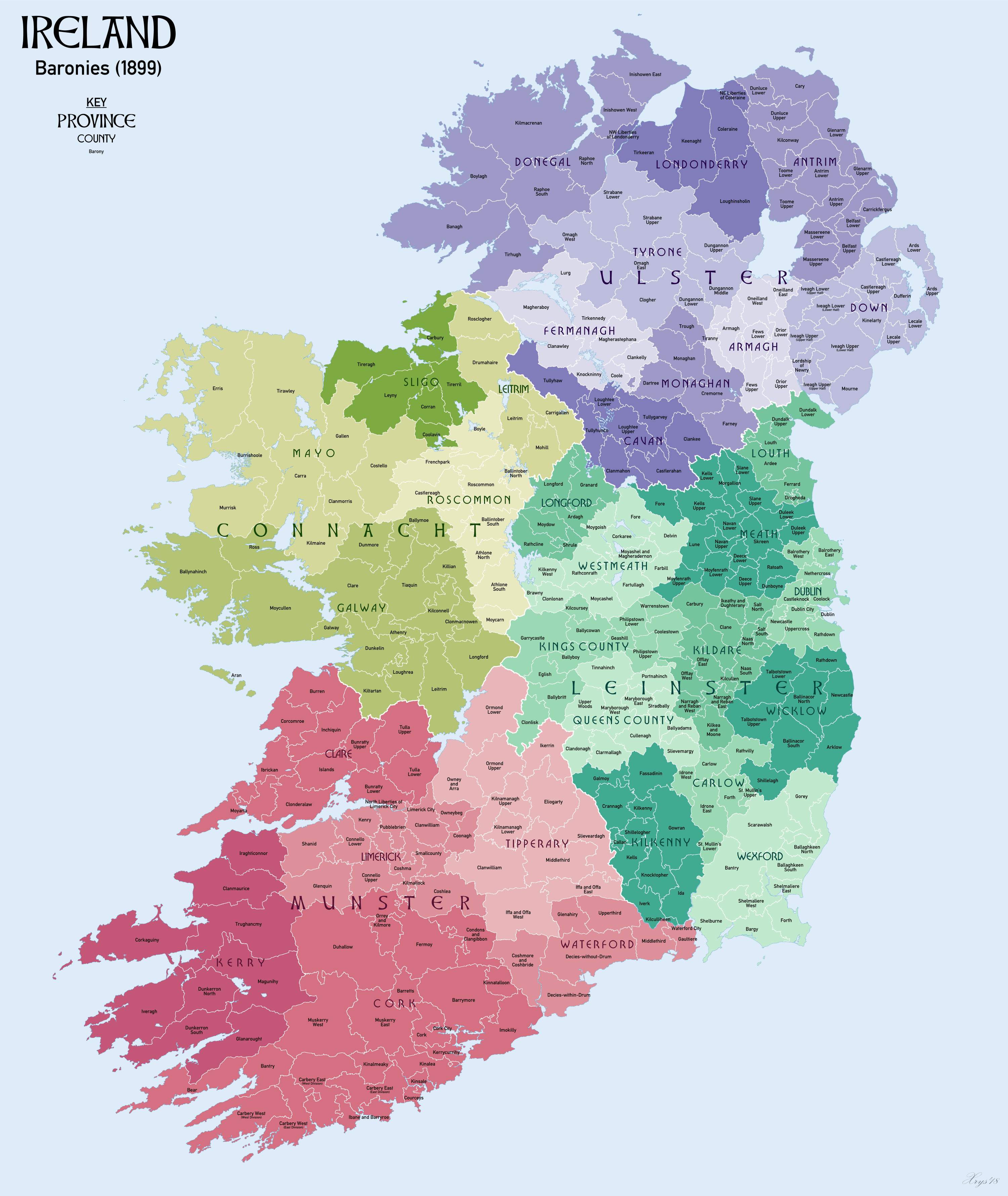
Baronies Of Ireland
In Ireland, a barony ( ga, barúntacht, plural ) is a historical subdivision of a county, analogous to the hundreds into which the counties of England were divided. Baronies were created during the Tudor reconquest of Ireland, replacing the earlier cantreds formed after the original Norman invasion.Mac Cotter 2005, pp.327–330 Some early baronies were later subdivided into half baronies with the same standing as full baronies. Baronies were mainly cadastral rather than administrative units. They acquired modest local taxation and spending functions in the 19th century before being superseded by the Local Government (Ireland) Act 1898. Subsequent adjustments of county boundaries mean that some baronies now straddle two counties. The final catalogue of baronies numbered 331, with an average area of ; therefore, each county was divided, on average, into 10 or 11 baronies. Creation The island of Ireland was "shired" into counties in two distinct periods: the east and south durin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ormond Lower
Ormond Lower (Irish: ''Urumhain Íochtarach'') is a barony in County Tipperary, Ireland. This geographical unit of land is one of 12 baronies in County Tipperary. Its chief town is Nenagh. The barony lies between Ormond Upper to the south-east (whose chief town is Toomevara) and Owney and Arra to the south-west (whose chief town is Newport). As a "peninsula", it is surrounded on three sides by counties Galway and Offaly. Legal context Baronies were created after the Norman invasion of Ireland as divisions of counties and were used the administration of justice and the raising of revenue. While baronies continue to be officially defined units, they have been administratively obsolete since 1898. However, they continue to be used in land registration and in specification, such as in planning permissions. In many cases, a barony corresponds to an earlier Gaelic túath which had submitted to the Crown. The Earl of Ormond wrongly applied the name "Ormond" to two baronies as they wer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
County Tipperary
County Tipperary ( ga, Contae Thiobraid Árann) is a county in Ireland. It is in the province of Munster and the Southern Region. The county is named after the town of Tipperary, and was established in the early 13th century, shortly after the Norman invasion of Ireland. It is Ireland's largest inland county and shares a border with 8 counties, more than any other. The population of the county was 159,553 at the 2016 census. The largest towns are Clonmel, Nenagh and Thurles. Tipperary County Council is the local authority for the county. In 1838, County Tipperary was divided into two ridings, North and South. From 1899 until 2014, they had their own county councils. They were unified under the Local Government Reform Act 2014, which came into effect following the 2014 local elections on 3 June 2014. Geography Tipperary is the sixth-largest of the 32 counties by area and the 12th largest by population. It is the third-largest of Munster's 6 counties by both size and popul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Church Of Ireland
The Church of Ireland ( ga, Eaglais na hÉireann, ; sco, label= Ulster-Scots, Kirk o Airlann, ) is a Christian church in Ireland and an autonomous province of the Anglican Communion. It is organised on an all-Ireland basis and is the second largest Christian church on the island after the Roman Catholic Church. Like other Anglican churches, it has retained elements of pre-Reformation practice, notably its episcopal polity, while rejecting the primacy of the Pope. In theological and liturgical matters, it incorporates many principles of the Reformation, particularly those of the English Reformation, but self-identifies as being both Reformed and Catholic, in that it sees itself as the inheritor of a continuous tradition going back to the founding of Christianity in Ireland. As with other members of the global Anglican communion, individual parishes accommodate different approaches to the level of ritual and formality, variously referred to as High and Low Church. Overvie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Board Of First Fruits
The Board of First Fruits () was an institution of the Church of Ireland that was established in 1711 by Anne, Queen of Great Britain to build and improve churches and glebe houses in Ireland. This was funded from taxes collected on clerical incomes which were in turn funded by tithes. The board was replaced in 1833 by the Board of Ecclesiastical Commissioners. History From the English Reformation in the 16th century, most Irish people chose to remain Roman Catholic and had by now to pay tithes valued at about 10% of an area's agricultural produce, to maintain and fund the established state church, the Anglican Church of Ireland, to which only a small minority of the population converted. Protests against this situation led to the Tithe war in the early 19th century. In 1711, Queen Anne agreed that the tax on clerical incomes be given to the Church of Ireland for the building of new churches and Glebe Houses. To that effect, with Jonathan Swift's influence, the Board of First ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dáil Éireann
Dáil Éireann ( , ; ) is the lower house, and principal chamber, of the Oireachtas (Irish legislature), which also includes the President of Ireland and Seanad Éireann (the upper house).Article 15.1.2º of the Constitution of Ireland reads: "The Oireachtas shall consist of the President and two Houses, viz.: a House of Representatives to be called Dáil Éireann and a Senate to be called Seanad Éireann." It consists of 160 members, each known as a (plural , commonly abbreviated as TDs). TDs represent 39 constituencies and are directly elected for terms not exceeding five years, on the system of proportional representation by means of the single transferable vote (PR-STV). Its powers are similar to those of lower houses under many other bicameral parliamentary systems and it is by far the dominant branch of the Oireachtas. Subject to the limits imposed by the Constitution of Ireland, it has power to pass any law it wishes, and to nominate and remove the Taoiseach (head of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Offaly (Dáil Constituency)
Offaly was a parliamentary constituency represented in Dáil Éireann, the lower house of the Irish parliament or Oireachtas, from 2016 to 2020. The constituency elected three deputies ( Teachtaí Dála, commonly known as TDs). The method of election was proportional representation by means of the single transferable vote (PR-STV). History and boundaries The Constituency Commission proposed in its 2012 report that at the next general election a new constituency called Offaly be created. The report proposed changes to the constituencies of Ireland so as to reduce the total number of TDs from 166 to 158. It was established by the Electoral (Amendment) (Dáil Constituencies) Act 2013. The constituency incorporated all of County Offaly from the previous Laois–Offaly constituency, and additionally twenty-four electoral divisions from Tipperary North. The 2013 Act defined the constituency as: "The county of Offaly; and in the county of North Tipperary the electoral divisions o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constituency Commission
The Constituency Commission ( ga, An Coimisiún um Thoghlaigh) is an independent commission in Ireland which advises on redrawing of constituency boundaries of Dáil constituencies for the election of members to Dáil Éireann (the lower house of the Oireachtas, the national parliament) and the European Parliament. Each commission is established by the Minister for Housing, Local Government and Heritage after the census, submits a non-binding report to the Oireachtas, and is dissolved. A separate but similar Local Electoral Area Boundary Committee fulfils the same function for local electoral area boundaries of local government areas. History Constituency revision is effected by an act of the Oireachtas (parliament) which enumerates the areas included within each constituency. Historically the act was drafted by the government of the day to favour its own party or parties, leading to allegations of gerrymandering by the opposition. The Electoral (Amendment) Act 1959 was struc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |