|
Goudbloem
The Goudbloem (marigold) was a chamber of rhetoric, a society to promote poetry and drama, that dated back to the 15th century in Antwerp.A. A. Keersmaekers, ''Geschiedenis van de Antwerpse Rederijkerskamers in de jaren 1585–1635'' (Aalst, 1952) It was one of three drama guilds in the city, the other two being the ''Violieren'' and the ''Olyftack''. It ceased to exist around 1654. The Violieren and Olyftack merged in 1660, and survived until 1762. History The Goudbloem had particular links to the urban aristocracy (patricians) and officeholders, while the Violieren was associated with artists and intellectuals (and had ties to the Guild of St Luke) and the Olyftack primarily consisted of merchants and tradesmen. The earliest mention of the society is of a performance in 1490, after which the city magistrates granted the chamber an annual subsidy of £3 Brabant (the same amount received by the Violieren). The chamber competed in the ''Landjuweel'' (a rhetoric competition open to c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chamber Of Rhetoric
Chambers of rhetoric ( nl, rederijkerskamers) were dramatic societies in the Low Countries. Their members were called Rederijkers (singular Rederijker), from the French word 'rhétoricien', and during the 15th and 16th centuries were mainly interested in dramas and lyrics. These societies were closely connected with local civic leaders and their public plays were a form of early public relations for the city.Reformers on stage: popular drama and religious propaganda in the low countries by Gary Waite on History The first chambers of rhetoric were founded in |
Chamber Of Rhetoric
Chambers of rhetoric ( nl, rederijkerskamers) were dramatic societies in the Low Countries. Their members were called Rederijkers (singular Rederijker), from the French word 'rhétoricien', and during the 15th and 16th centuries were mainly interested in dramas and lyrics. These societies were closely connected with local civic leaders and their public plays were a form of early public relations for the city.Reformers on stage: popular drama and religious propaganda in the low countries by Gary Waite on History The first chambers of rhetoric were founded in |
Violieren
The Violieren (wallflower or gillyflower) was a chamber of rhetoric that dates back to the 15th century in Antwerp, when it was a social drama society with close links to the Guild of Saint Luke.A. A. Keersmaekers, ''Geschiedenis van de Antwerpse Rederijkerskamers in de jaren 1585–1635'' (Aalst, 1952) It was one of three drama guilds in the city, the other two being the ''Goudbloem'' and the ''Olyftack''. In 1660 the Violieren merged with former rival Olyftack, and in 1762 the society was dissolved altogether. History Much of what is known today about Antwerp's chambers of rhetoric comes from the city and guild archives. According to a note by the year 1480 in the early records of the Guild of St. Luke, the chamber's first victory was at a "Landjuweel" (a rhetoric competition open to contenders from throughout the Duchy of Brabant) in Leuven that took place that year. Their motto was "Wt ionsten versaemt"(united in friendship). From 1490, the chamber received an annual grant from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
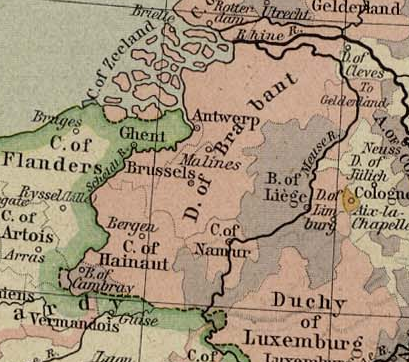
Antwerp
Antwerp (; nl, Antwerpen ; french: Anvers ; es, Amberes) is the largest city in Belgium by area at and the capital of Antwerp Province in the Flemish Region. With a population of 520,504,Statistics Belgium; ''Loop van de bevolking per gemeente'' (Excel file) Population of all municipalities in Belgium, . Retrieved 1 November 2017. it is the most populous municipality in Belgium, and with a metropolitan population of around 1,200,000 people, it is the second-largest metrop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duchy Of Brabant
The Duchy of Brabant was a State of the Holy Roman Empire established in 1183. It developed from the Landgraviate of Brabant and formed the heart of the historic Low Countries, part of the Burgundian Netherlands from 1430 and of the Habsburg Netherlands from 1482, until it was partitioned after the Dutch revolt. Present-day North Brabant (''Noord-Brabant'') was ceded to the Generality Lands of the Dutch Republic according to the 1648 Peace of Westphalia, while the reduced duchy remained part of the Habsburg Netherlands until it was conquered by French Revolutionary forces in 1794, which was recognized by treaty in 1797. Today all the duchy's former territories, apart from exclaves, are in Belgium except for the Dutch province of North Brabant. Geography The Duchy of Brabant (adjective: ''Brabantian'' or '' Brabantine'') was historically divided into four parts, each with its own capital. The four capitals were Leuven, Brussels, Antwerp and 's-Hertogenbosch. Before 's-Hertogenb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olyftack
De Olijftak (The Olive Branch), or in full (Confraternity of the Holy Spirit called the Olive Branch) was a chamber of rhetoric that dates back to the early 16th century in Antwerp, when it was a social drama society drawing its membership primarily from merchants and tradesmen.A. A. Keersmaekers, ''Geschiedenis van de Antwerpse Rederijkerskamers in de jaren 1585–1635'' (Aalst, 1952) In 1660 it merged with its former rival the Violieren (which was more closely associated with artists and intellectuals), and in 1762 the society was dissolved altogether. History The chamber took part in the ''landjuweel'' (a rhetoric competition for the whole Duchy of Brabant) at Mechelen in 1515, at Diest in 1521, at Brussels in 1532, at Mechelen in 1535, at Diest in 1541, and the final such competition, at Antwerp in 1561. The chamber also provided public entertainment at such events as the triumphal entry into Antwerp of Alexander Farnese, Duke of Parma. During the 1590s there were no regular p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guild Of St Luke
The Guild of Saint Luke was the most common name for a city guild for painters and other artists in early modern Europe, especially in the Low Countries. They were named in honor of the Evangelist Luke, the patron saint of artists, who was identified by John of Damascus as having painted the Virgin's portrait. One of the most famous such organizations was founded in Antwerp. It continued to function until 1795, although by then it had lost its monopoly and therefore most of its power. In most cities, including Antwerp, the local government had given the Guild the power to regulate defined types of trade within the city. Guild membership, as a master, was therefore required for an artist to take on apprentices or to sell paintings to the public. Similar rules existed in Delft, where only members could sell paintings in the city or have a shop. The early guilds in Antwerp and Bruges, setting a model that would be followed in other cities, even had their own showroom or market sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fall Of Antwerp
The Fall of Antwerp on 17 August 1585 took place during the Eighty Years' War, after a siege lasting over a year from July 1584 until August 1585. The city of Antwerp was the focal point of the Protestant-dominated Dutch Revolt, but was forced to surrender to the Spanish forces. Under the terms agreed, all Protestants were given four years to settle their affairs and leave the city. Many migrated north, especially to Amsterdam, which became the capital of the Dutch Republic. Apart from losing a high proportion of its mercantile population, Antwerp's trade suffered for two centuries as Dutch forts blockaded the River Scheldt up to 1795. Background At the time Antwerp, in modern Belgium, was not only the largest Dutch city, but was also the cultural, economic, and financial centre of the Seventeen Provinces and of north-western Europe. On 4 November 1576, unpaid Spanish soldiery mutinied: they plundered and burnt the city during what was called the Spanish Fury. Thousands of c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peoene
The Peoene (Peony), also known as the Sint-Jansgilde (Guild of St John), was a chamber of rhetoric dating back to the 15th century in Mechelen. History The oldest mention of the Peoene is in a city accounts book from 1472. The guild took part in ''landjuweel'' competitions in Leuven (1478), Antwerp (1496), Herentals (1510), Leuven (1518), Diest (1521), Brussels (1532), Antwerp (1561), and Brussels (1562). The guild hosted such competitions in Mechelen in 1515 and 1535. Activities were suspended in 1585, in the midst of the Habsburg reconquest of the Spanish Netherlands. An application to recommence activities in 1593 was rejected, but in 1617 the chamber received a charter from the Archdukes Albert and Isabella. A rhetoric competition drawing participants from across the Low Countries was hosted by the Peoene in Mechelen on 3 May 1620. Plays written by the guild's dean, the silversmith Jan Thieullier, and factor, Hendrik Faydherbe, were performed to entertain the participants. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mechelen
Mechelen (; french: Malines ; traditional English name: MechlinMechelen has been known in English as ''Mechlin'', from where the adjective ''Mechlinian'' is derived. This name may still be used, especially in a traditional or historical context. The city's French name ' had also been used in English in the past (in the 19th and 20th century) however this has largely been abandoned. Meanwhile, the Dutch derived ' began to be used in English increasingly from late 20th century onwards, even while ''Mechlin'' remained still in use (for example a ''Mechlinian'' is an inhabitant of this city or someone seen as born-and-raised there; the term is also the name of the city dialect; as an adjective ''Mechlinian'' may refer to the city or to its dialect.) is a city and municipality in the province of Antwerp in the Flemish Region of Belgium. The municipality comprises the city of Mechelen proper, some quarters at its outskirts, the hamlets of (adjacent) and (a few kilometers away), as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jan Thieullier
Jan Thieullier (active in the early 17th century) was a Flemish poet, residing in Mechelen, about whom very little is known. Life Thieullier was a silversmith who has been said to have been born in Mechelen, but the evidence for this is unclear.C. Debaive, "Thieullier (Jean)", ''Biographie Nationale de Belgique'', vol. 24 (Brussels, 1929), 920–923. In January 1617 he was dean of the Mechelen chamber of rhetoric the Peoene (the Peony). On 24 May 1619 his son, Wilhelmus, was baptized in St. Rumbold's Cathedral. As dean of the Peoene Thieullier was one of the organisers of the ''blazoenfeest'' (a rhetoric competition) hosted in Mechelen on 3 May 1620. Participants in the competition came from as far afield as Gouda and Haarlem. As part of the event, a play was performed which Thieullier had written for the occasion: ''Porphyre en Cyprine''. This was the first pastoral tragedy in the Netherlandish tradition of "rhetorical" drama. It was printed in 1621. Works ''Porphyre en Cyprine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Jaye
Henry Jaye (died 1643) was an English Catholic exile in the Southern Netherlands. He became printer to the city of Mechelen. Life The earliest record of Jaye is in 1606, when the English ambassador in Brussels, Sir Thomas Edmondes, had him summoned before Jean Richardot in an attempt to have him punished by the authorities in the Low Countries for slandering James I of England. He had allegedly spoken "certain very lewd and infamous words against his Majesty", namely: A pockes of god of the kinge of Ingland yf you terme him kinge I hope to see him hanged, he is none of my prince nether doe I knowledge him to be my prince. Nether a trewe anoyntted Prince nor never was or shalbe. In 1607 Jaye opened an account with the Plantin Office as a bookseller in Brussels. By 1609 he was married to Catharina vande Zetten, a daughter (or perhaps step-daughter) of Pieter Simons, and by November 1610 they were living in Mechelen, where their daughter was baptized in St Rumbold's Cathedral. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)