|
Gothia Restaurants
Gothia is a name given to various places where the Goths lived during their migrations: * Dacia, referred to as Gothia during the fourth century * Götaland, the traditionally assumed homeland of the Goths * the land of the Crimean Goths, referred to as Gothia by the Byzantines and Askuzai in Semitic sources (Hebrew: Ashkenaz). * Principality of Theodoro, deriving from the Crimean Goths * Septimania, land in southern France once inhabited by the Visigoths * Languedoc, larger modern provincial name for the Septimania land of Gothia. * ''Marca Hispanica'', land in northern Spain whose inhabitants were considered Goths and not Franks in the 8th–10th centuries * Catalonia, the name being possibly derived from "Gothic land" * Metropolitanate of Gothia, a diocese of the Patriarchate of Constantinople in the Middle Ages Gothia may also refer to: * Gothia Cup, the world's largest annual association football cup by number of contestants, held in Gothenburg * Gothia Towers The Gothia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goths
The Goths ( got, 𐌲𐌿𐍄𐌸𐌹𐌿𐌳𐌰, translit=''Gutþiuda''; la, Gothi, grc-gre, Γότθοι, Gótthoi) were a Germanic people who played a major role in the fall of the Western Roman Empire and the emergence of medieval Europe. In his book '' Getica'' (c. 551), the historian Jordanes writes that the Goths originated in southern Scandinavia, but the accuracy of this account is unclear. A people called the ''Gutones''possibly early Gothsare documented living near the lower Vistula River in the 1st century, where they are associated with the archaeological Wielbark culture. From the 2nd century, the Wielbark culture expanded southwards towards the Black Sea in what has been associated with Gothic migration, and by the late 3rd century it contributed to the formation of the Chernyakhov culture. By the 4th century at the latest, several Gothic groups were distinguishable, among whom the Thervingi and Greuthungi were the most powerful. During this time, Wulfila bega ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dacia
Dacia (, ; ) was the land inhabited by the Dacians, its core in Transylvania, stretching to the Danube in the south, the Black Sea in the east, and the Tisza in the west. The Carpathian Mountains were located in the middle of Dacia. It thus roughly corresponds to the present-day countries of Romania, as well as parts of Moldova, Bulgaria, Serbia, Hungary, Slovakia, and Ukraine. A Dacian Kingdom of variable size existed between 82 BC until the Roman conquest in AD 106, reaching its height under Burebista, King Burebista. As a result of the Trajan's Dacian Wars, two wars with Emperor Trajan, the population was dispersed and the central city, Sarmizegetusa Regia, was destroyed by the Romans, but was rebuilt by the latter to serve as the capital of the Roman Dacia, Roman province of Dacia. The Free Dacians, living the territory of modern-day Northern Romania disappeared with the start of the Migration Period. Nomenclature The Dacians are first mentioned in the writings of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
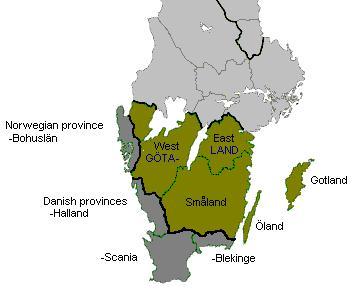
Götaland
Götaland (; also '' Geatland'', '' Gothia'', ''Gothland'', ''Gothenland'' or ''Gautland'') is one of three lands of Sweden and comprises ten provinces. Geographically it is located in the south of Sweden, bounded to the north by Svealand, with the deep woods of Tiveden, Tylöskog and Kolmården marking the border. Götaland once consisted of petty kingdoms, and their inhabitants were called ''Gautar'' in Old Norse. However, the term mainly referred to the population of modern Västergötland. It is agreed that these were the same as the ''Geats'', the people of the hero Beowulf in England's national epic, ''Beowulf''. The modern state of Sweden started forming when some provinces of Götaland gradually became more and more politically intertwined with those of Svealand. This process can be traced back to at least the 11th century, and would continue for several hundred years. Other parts of modern Götaland were at that time either Danish or Norwegian. The province of Smålan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
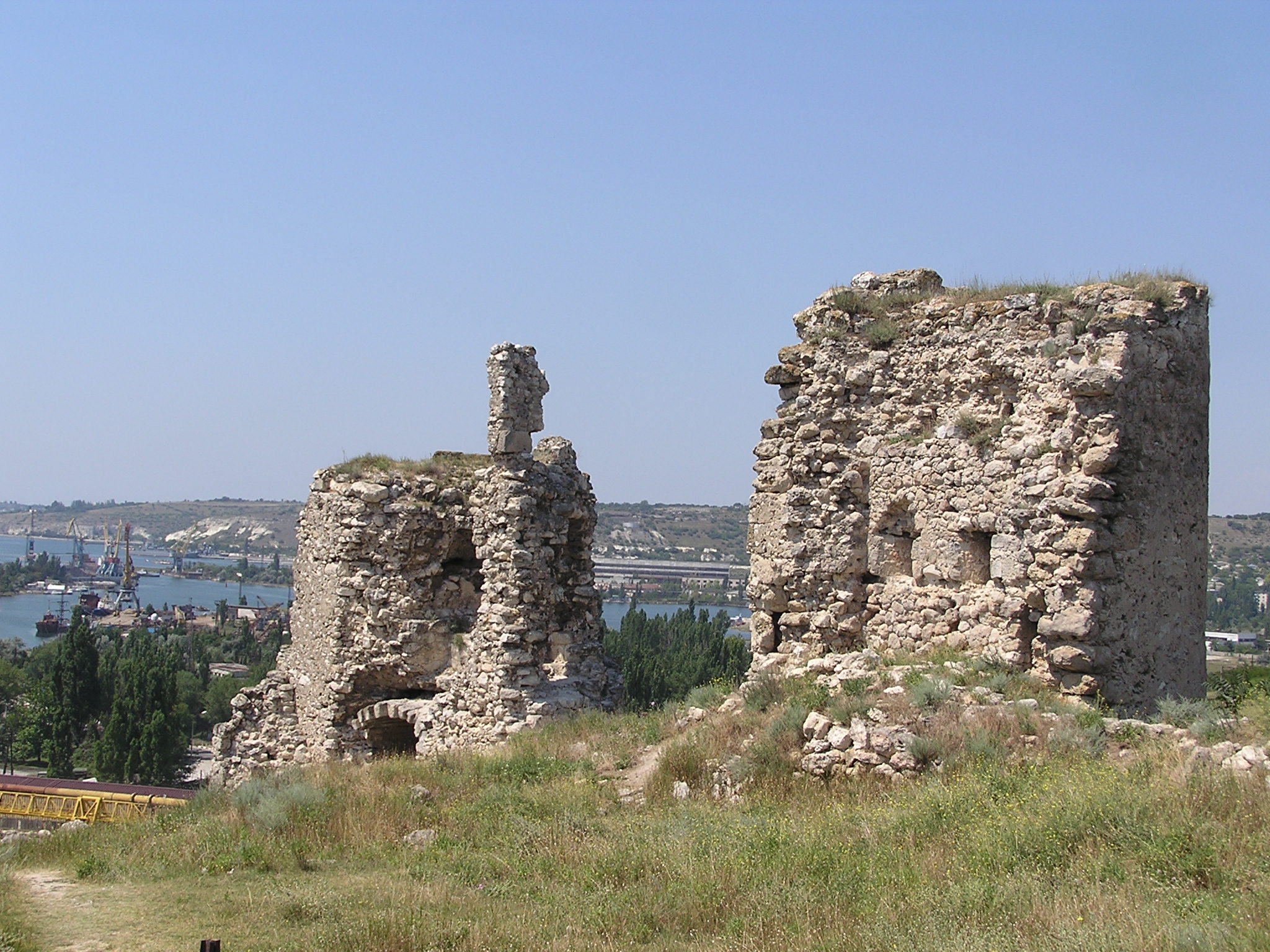
Crimean Goths
The Crimean Goths were Greuthungi-Gothic tribes who remained in the lands around the Black Sea, especially in Crimea. They were the longest-lasting of the Gothic communities. Their existence is well attested through the ages, though the exact period when they ceased to exist as a distinct culture is unknown; as with the Goths in general, they may have become diffused among the surrounding peoples. In his Fourth Turkish letter, Ogier Ghiselin de Busbecq (1522-1592) describes them as "a warlike people, who to this day inhabit many villages". However, in the 5th century, the Ostrogothic ruler Theodoric the Great failed to rouse Crimean Goths to support his 488-493 war in Italy. In medieval times it was customary to refer to a wide range of Germanic tribes as "Goths", so the exact ethnic nature of the Germanic peoples in Crimea is a subject of debate. Aside from textual reports of the existence of the Goths in Crimea, both first- and second-hand, from as early as 850, numerous arch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Principality Of Theodoro
The Principality of Theodoro ( el, Αὐθεντία πόλεως Θεοδωροῦς καὶ παραθαλασσίας), also known as Gothia ( el, Γοτθία) or the Principality of Theodoro-Mangup, was a Greek principality in the southern part of Crimea, specifically on the foothills of the Crimean Mountains. It represented one of the final rump states of the Eastern Roman Empire and the last territorial vestige of the Crimean Goths until its conquest by the Ottoman Empire by the Ottoman Albanian Gedik Ahmed Pasha in 1475. Its capital was Doros, also sometimes called Theodoro and now known as Mangup. The state was closely allied with the Empire of Trebizond. History In the late 12th century, the Crimean peninsula had seceded from the Byzantine Empire, but soon after the sack of Constantinople in 1204 parts of it were included in the Trapezuntine '' Gazarian Perateia''. This dependence was never very strong and was eventually replaced by the invading Mongols, who in 1238 po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Septimania
Septimania (french: Septimanie ; oc, Septimània ) is a historical region in modern-day Southern France. It referred to the western part of the Roman province of Gallia Narbonensis that passed to the control of the Visigoths in 462, when Septimania was ceded to their king, Theodoric II. The region was also variously known as Gallia, Arbuna or Narbonensis. The territory of Septimania roughly corresponds with the modern French former administrative region of Languedoc-Roussillon that merged into the new administrative region of Occitania (administrative region), Occitanie. Septimania was conquered by the Muslims in the 8th century, when it was known as Arbuna and was made part of Al-Andalus. It passed briefly to the Emirate of Córdoba, which had been expanding from the south during the eighth century, before its subsequent conquest by the Franks, who by the end of the ninth century termed it Gothia or the Gothic March (''Marca Gothica''). Septimania became a March (territorial ent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Languedoc
The Province of Languedoc (; , ; oc, Lengadòc ) is a former province of France. Most of its territory is now contained in the modern-day region of Occitanie in Southern France. Its capital city was Toulouse. It had an area of approximately 42,700 square kilometers (16,490 square miles). History The Roman province of Gallia Narbonensis fell to the Visigothic Kingdom from the 5th to the 8th centuries. Occupied briefly by the Emirate of Córdoba between 719 and 759, it was conquered and incorporated into the Kingdom of the Franks by Pippin the Short in 759 following the Siege of Narbonne. Under the Carolingians, the counts of Toulouse were appointed by the royal court. Later, this office became hereditary. Part of the territory where Occitan was spoken came to be called ''langue d'oc'', ''Lengadòc'' or Languedoc. In the 13th century, the spiritual beliefs of the area were challenged by the See of Rome and the region became attached to the Kingdom of France following the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marca Hispanica
The Hispanic March or Spanish March ( es, Marca Hispánica, ca, Marca Hispànica, Aragonese and oc, Marca Hispanica, eu, Hispaniako Marka, french: Marche d'Espagne), was a military buffer zone beyond the former province of Septimania, established by Charlemagne in 795 as a defensive barrier between the Umayyad Moors of Al-Andalus and the Frankish Carolingian Empire (Duchy of Gascony, the Duchy of Aquitaine and Carolingian Septimania). In its broader meaning, ''Hispanic March'' sometimes refers to a group of early Iberian and trans-Pyrenean lordships or counts coming under Frankish rule. As time passed, these lordships merged or gained independence from Frankish imperial rule. Geographical context The area broadly corresponds to the eastern regions between the Pyrenees and the Ebro River. The local population of the March was diverse. It included Basques in its north-western valleys, Jews, and a large Occitano-Romance-speaking Hispano-Roman population ( Occitans and Catal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catalonia
Catalonia (; ca, Catalunya ; Aranese Occitan: ''Catalonha'' ; es, Cataluña ) is an autonomous community of Spain, designated as a ''nationality'' by its Statute of Autonomy. Most of the territory (except the Val d'Aran) lies on the northeast of the Iberian Peninsula, to the south of the Pyrenees mountain range. Catalonia is administratively divided into four provinces: Barcelona, Girona, Lleida, and Tarragona. The capital and largest city, Barcelona is the second-most populated municipality in Spain and the fifth-most populous urban area in the European Union.Demographia: World Urban Areas – Demographia, April 2018 Current day Catalonia comprises most of the medieval and early modern Principality o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metropolitanate Of Gothia
:''See Archdiocese of the Goths and the Northlands for the 1994 establishment in Sweden.'' The Metropolitanate of Gothia (also ''of Gothia and Caffa''), also known as the Eparchy of Gothia or Metropolitanate of Doros, was a metropolitan diocese of the Patriarchate of Constantinople in the Middle Ages. The 9th-century Metropolitanate of Doros was centered in the Crimea, but it seems to have had dioceses further afield, as far east as the Caspian coast, but they were probably short-lived, as the Khazars converted to Judaism. From the 13th century until the Ottoman conquest in 1475, the Metropolitanate of Gothia was within the Principality of Theodoro (known in Greek as Γοτθία, ''Gothia''). In 1779, it was transferred to the Russian Orthodox Church and disestablished a few years later. Early history The Goths came into contact with Christianity from the late 3rd century, and were Christianized in the course of the 4th century. Theophilus, the first known bishop of the G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gothia Cup
The Gothia Cup () is an international youth association football tournament organized by professional football club BK Häcken, which has been held annually since 1975 in Gothenburg, Sweden. Considered the biggest tournament in the world in terms of participating teams, competing youth teams throughout the world enter the competition. The Gothia Cup is also Sweden's largest annual event. The Jamie Johnson (TV series) in Series 4 displays Phoenix FC, a grassroots football club competing in the Gothia Cup. Overview Spanning one week the Gothia Cup is a youth association football tournament held annually in Gothenburg, Sweden, open for both boys and girls of ages 11 to 18. In terms of participants, it is the world's second largest youth football tournament with only the Norway Cup being bigger. In 2017, 1730 teams from 82 nations participated. The Gothia Cup started in 1975 with 275 participating teams. In July each year, the event becomes the dominant event in Gothenburg, with (as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gothia Towers
The Gothia Towers, in Gothenburg, Sweden, is the largest hotel in the Nordic countries. Part of the Swedish Exhibition and Congress Centre The Swedish Exhibition & Congress Centre ( sv, Svenska Mässan) is an exhibition and convention centre in Gothenburg, Sweden and one of Scandinavia's largest assembly points, which attracts around 1.8 million visitors a year. It is one of Euro ..., it has 1,200 rooms and eleven suites and offers a variety of restaurants and bars. Construction The first tower was built in 1984, and the second in 2001. The third tower was built between 2011 and 2014. The third tower is the tallest building () in Gothenburg and the sixth tallest building in Sweden. Facilities In 2014, the Upper House was inaugurated in the second tower, a five-star hotel within the hotel. The Upper House has an awarded restaurant and an exclusive 3-floor spa with an outdoor glass bottom pool on the 19th floor. Also inaugurated in 2014, was the show arena the Theatre. He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)