|
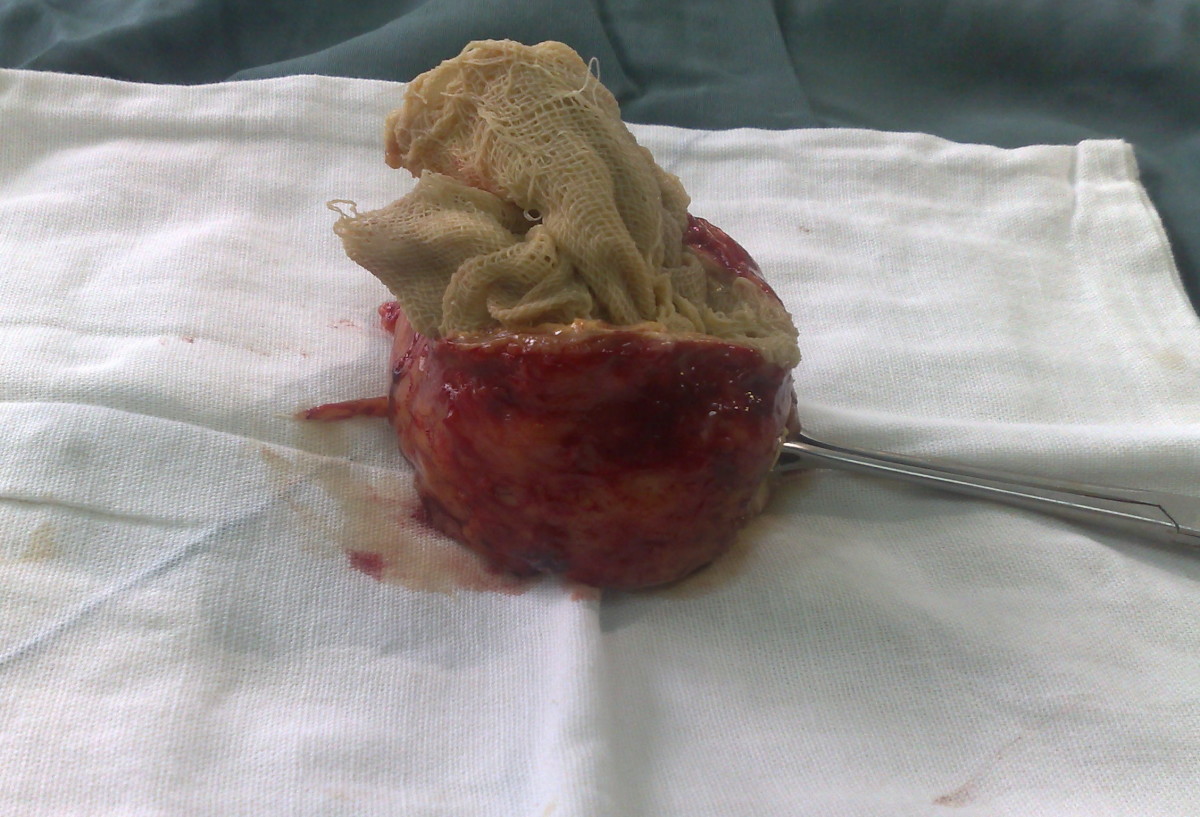
Gossypiboma 01
Gossypiboma, textiloma or more broadly Retained Foreign Object (RFO) is the technical term for surgical complications resulting from foreign materials, such as a surgical sponge, accidentally left inside a patient's body. Etymology Gossypiboma is derived from Latin ''gossypium'' (cotton) and Swahili "boma" (place of concealment), meaning a tumor or growth. Gossypiboma describes a mass within a patient's body comprising a cotton matrix surrounded by a foreign body granuloma. Textiloma is derived from textile (surgical sponges have historically been made of cloth), and is used in place of gossypiboma due to the increasing use of synthetic materials in place of cotton. Incidence and clinical presentation The actual incidence of gossypiboma is difficult to determine, possibly due to a reluctance to report occurrences arising from fear of legal repercussions, but retained surgical sponges is reported to occur once in every 3000 to 5000 abdominal operations and are most frequentl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gossypiboma 01
Gossypiboma, textiloma or more broadly Retained Foreign Object (RFO) is the technical term for surgical complications resulting from foreign materials, such as a surgical sponge, accidentally left inside a patient's body. Etymology Gossypiboma is derived from Latin ''gossypium'' (cotton) and Swahili "boma" (place of concealment), meaning a tumor or growth. Gossypiboma describes a mass within a patient's body comprising a cotton matrix surrounded by a foreign body granuloma. Textiloma is derived from textile (surgical sponges have historically been made of cloth), and is used in place of gossypiboma due to the increasing use of synthetic materials in place of cotton. Incidence and clinical presentation The actual incidence of gossypiboma is difficult to determine, possibly due to a reluctance to report occurrences arising from fear of legal repercussions, but retained surgical sponges is reported to occur once in every 3000 to 5000 abdominal operations and are most frequentl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Secondary Infection
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable disease, is an illness resulting from an infection. Infections can be caused by a wide range of pathogens, most prominently bacteria and viruses. Hosts can fight infections using their immune system. Mammalian hosts react to infections with an innate response, often involving inflammation, followed by an adaptive response. Specific medications used to treat infections include antibiotics, antivirals, antifungals, antiprotozoals, and antihelminthics. Infectious diseases resulted in 9.2 million deaths in 2013 (about 17% of all deaths). The branch of medicine that focuses on infections is referred to as infectious disease. Types Infections are caused by infectious agents (pathogens) including: * Bacteria (e.g. ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X-ray
An X-ray, or, much less commonly, X-radiation, is a penetrating form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. Most X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 picometers to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30 petahertz to 30 exahertz ( to ) and energies in the range 145 eV to 124 keV. X-ray wavelengths are shorter than those of UV rays and typically longer than those of gamma rays. In many languages, X-radiation is referred to as Röntgen radiation, after the German scientist Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen, who discovered it on November 8, 1895. He named it ''X-radiation'' to signify an unknown type of radiation.Novelline, Robert (1997). ''Squire's Fundamentals of Radiology''. Harvard University Press. 5th edition. . Spellings of ''X-ray(s)'' in English include the variants ''x-ray(s)'', ''xray(s)'', and ''X ray(s)''. The most familiar use of X-rays is checking for fractures (broken bones), but X-rays are also used in other ways. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiographic
Radiography is an imaging technique using X-rays, gamma rays, or similar ionizing radiation and non-ionizing radiation to view the internal form of an object. Applications of radiography include medical radiography ("diagnostic" and "therapeutic") and industrial radiography. Similar techniques are used in airport security (where "body scanners" generally use backscatter X-ray). To create an image in conventional radiography, a beam of X-rays is produced by an X-ray generator and is projected toward the object. A certain amount of the X-rays or other radiation is absorbed by the object, dependent on the object's density and structural composition. The X-rays that pass through the object are captured behind the object by a detector (either photographic film or a digital detector). The generation of flat two dimensional images by this technique is called projectional radiography. In computed tomography (CT scanning) an X-ray source and its associated detectors rotate around the su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiodensity
Radiodensity (or radiopacity) is opacity to the radio wave and X-ray portion of the electromagnetic spectrum: that is, the relative inability of those kinds of electromagnetic radiation to pass through a particular material. Radiolucency or hypodensity indicates greater passage (greater transradiancy) to X-ray photonsNovelline, Robert. ''Squire's Fundamentals of Radiology''. Harvard University Press. 5th edition. 1997. . and is the analogue of transparency and translucency with visible light. Materials that inhibit the passage of electromagnetic radiation are called radiodense or radiopaque, while those that allow radiation to pass more freely are referred to as radiolucent. Radiopaque volumes of material have white appearance on radiographs, compared with the relatively darker appearance of radiolucent volumes. For example, on typical radiographs, bones look white or light gray (radiopaque), whereas muscle and skin look black or dark gray, being mostly invisible (radiolucent). Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joint Commission
The Joint Commission is a United States-based nonprofit tax-exempt 501(c) organization that accredits more than 22,000 US health care organizations and programs. The international branch accredits medical services from around the world. A majority of US state governments recognize Joint Commission accreditation as a condition of licensure for the receipt of Medicaid and Medicare reimbursements. The Joint Commission is based in the Chicago suburb of Oakbrook Terrace, Illinois. History The Joint Commission was formerly the Joint Commission on Accreditation of Healthcare Organizations (JCAHO) and previous to that the Joint Commission on Accreditation of Hospitals (JCAH). The Joint Commission was renamed The Joint Commission on Accreditation of Hospitals in 1951, but it was not until 1965, when the federal government decided that a hospital meeting Joint Commission accreditation met the Medicare Conditions of Participation, that accreditation had any official impact. However, Se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American College Of Surgeons
The American College of Surgeons is an educational association of surgeons created in 1913.American College of Surgeons Online "What is the American College of Surgeons?"/ref> See also *American College of Physicians The American College of Physicians (ACP) is a national organization of internists, who specialize in the diagnosis, treatment, and care of adults.Sokanu "What is an Internist?" Retrieved October 20, 2014 With 161,000 members, ACP is the largest ... References External links *ACS Foundation [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agency For Healthcare Research And Quality
The Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ; pronounced "ark" by initiates and often "A-H-R-Q" by the public) is one of twelve agencies within the United States Department of Health and Human Services (HHS). The agency is headquartered in North Bethesda, Maryland, a suburb of Washington, D.C. (with a Rockville mailing address). It was established as the Agency for Health Care Policy and Research (AHCPR) in 1989 as a constituent unit of the Public Health Service (PHS) to enhance the quality, appropriateness, and effectiveness of health care services and access to care by conducting and supporting research, demonstration projects, and evaluations; developing guidelines; and disseminating information on health care services and delivery systems. History AHRQ's earliest predecessor was the National Center for Health Services Research and Development, established in 1968 within the PHS Health Services and Mental Health Administration. When that administration was split up ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Association Of PeriOperative Registered Nurses
The Association of periOperative Registered Nurses (AORN) represents more than 41,000 registered nurses in the United States and abroad who facilitate the management, teaching, and practice of perioperative nursing, or who are enrolled in nursing education or engaged in perioperative research. Its members also include perioperative nurses who work in related business and industry sectors. History The first groups of organized OR nurses were concerned with many of the same issues AORN and the profession of OR nursing face today, including standardizing OR techniques and education programs and promoting friendship among OR nurses. Between 1916 and 1949, several OR nursing groups formed in various parts of the United States, leading to the formal recognition of AORN as a national association. Major milestones in the association's history include: * The first national conference in 1954 * The establishment of a constitution, bylaws, and national officers, the AORN Board of Directors ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tissue Adhesion
Adhesions are fibrous bands that form between tissues and organs, often as a result of injury during surgery. They may be thought of as internal scar tissue that connects tissues not normally connected. Pathophysiology Adhesions form as a natural part of the body's healing process after surgery in a similar way that a scar forms. The term "adhesion" is applied when the scar extends from within one tissue across to another, usually across a virtual space such as the peritoneal cavity. Adhesion formation post-surgery typically occurs when two injured surfaces are close to one another. According to the "classical paradigm" of adhesion formation, the pathogenesis starts with inflammation and activation of the coagulation system which causes fibrin deposits onto the damaged tissues. The fibrin then connects the two adjacent structures where damage of the tissues occurred. The fibrin acts like a glue to seal the injury and builds the fledgling adhesion, said at this point to be "fibrinou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aseptic
Asepsis is the state of being free from disease-causing micro-organisms (such as pathogenic bacteria, viruses, pathogenic fungi, and parasites). There are two categories of asepsis: medical and surgical. The modern day notion of asepsis is derived from the older antiseptic techniques, a shift initiated by different individuals in the 19th century who introduced practices such as the sterilizing of surgical tools and the wearing of surgical gloves during operations. The goal of asepsis is to eliminate infection, not to achieve sterility. Ideally, a surgical field is sterile, meaning it is free of all biological contaminants (e.g. fungi, bacteria, viruses), not just those that can cause disease, putrefaction, or fermentation. Even in an aseptic state, a condition of sterile inflammation may develop. The term often refers to those practices used to promote or induce asepsis in an operative field of surgery or medicine to prevent infection. History The modern concept of asepsis evol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |