|
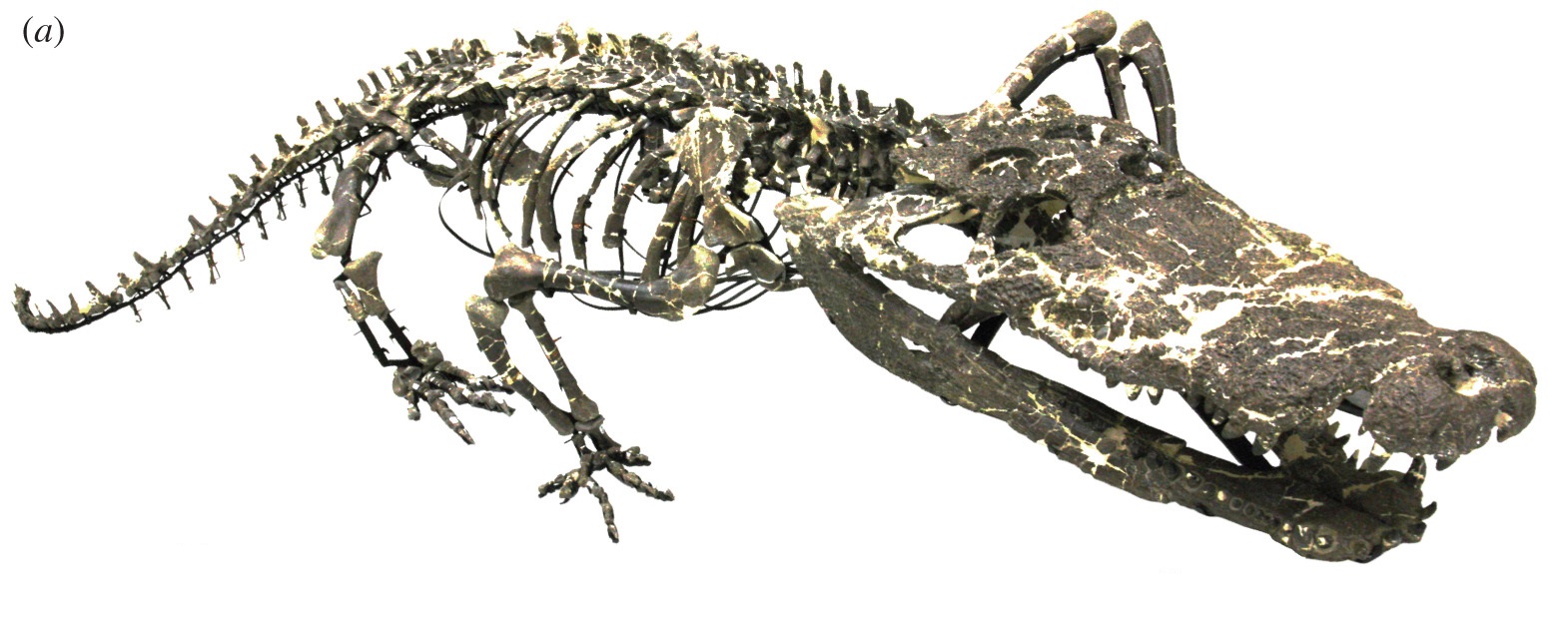
Goniopholididae
Goniopholididae is an extinct family of moderate-sized semi-aquatic neosuchian crocodyliformes. Their bodyplan and morphology are convergent on living crocodilians. They lived across Laurasia (Asia, Europe and North America) between the Middle Jurassic (possibly Early Jurassic, see below) and the Late Cretaceous. Description Compared to modern crocodilians, goniopholidids are very unusual in several respects. They possessed two rows of rectangular, interlocking osteoderms like those of terrestrial crocodilymorphs like atoposaurids, that are relatively simple, do not extend far in their necks, as opposed to the ornate armours of modern crocodilians; likewise, unlike modern crocodilians but like many extinct forms like phytosaurs, they have ventral osteoderms as well. Their forelimbs are also proportionally very long, particularly in the humeri and wrist bones, being as long or longer than the hindlimbs, the opposite of the condition seen in modern crocodilians. Some like ''Anteoph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eutretauranosuchus
''Eutretauranosuchus'' is an extinct genus of goniopholidid crocodyliform. ''E. delfsi'' is the only known species within the genus. Discovery and history The holotype, ''Eutretauranosuchus delfsi'', was discovered by Edwin Delfs in 1957 among remains recovered from the Morrison Formation in Canon City, Colorado. It was first described in detail by Charles Mook in 1967. The fossil remains consisted of an almost-complete skull as well as some limb bones. The name ''Eutretauranosuchus'' was given by Delfs upon its discovery in reference to its "doubly pierced palate". The holotype specimen was named ''E. delfsi'' by Mook in tribute to Delfs. Mook found ''E. delfsi'' differs significantly from previously described Mesosuchian crocodiles. This specimen was deemed part of a new species because of its extremely elongated internal narial aperture, which was notably longer than those of previously described specimens of similar size. Mook also described an additional, smaller op ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neosuchian
Neosuchia is a clade within Mesoeucrocodylia that includes all modern extant crocodilians and their closest fossil relatives. It is defined as the most inclusive clade containing all crocodylomorphs more closely related to ''Crocodylus niloticus'' (the Nile Crocodile) than to ''Notosuchus terrestris''. Members of Neosuchia generally share a crocodilian-like bodyform adapted to freshwater aquatic life, as opposed to the terrestrial habits of more basal crocodylomorph groups. The earliest neosuchian is suggested to be the Early Jurassic ''Calsoyasuchus'', which lived during the Sinemurian and Pliensbachian stages in North America. It is often identified as a member of Goniopholididae, though this is disputed, and the taxon may lie outside Neosuchia, which places the earliest records of the group in the Middle Jurassic. Characteristics A tooth notch between the maxilla and premaxilla is a basal characteristic of the Neosuchia, although it is lost in some more derived forms, most nota ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amphicotylus Milesi
''Amphicotylus'' is an extinct genus of goniopholidid mesoeucrocodylian from the Tithonian of Colorado, Wyoming, and Oklahoma. It was species description, described in 1878.E. D. Cope. 1878. Descriptions of new extinct Vertebrata from the Upper Tertiary and Dakota Formations. 'Bulletin of the United States Geological and Geographical Survey of the Territories'', 4(2):379-396 Discovery and species ''Amphicotylus'' was first described by Edward Drinker Cope in 1878 based on dorsal and lumbar vertebrae, ribs and osteoderms. Based on these remains, found in the same locality as Camarasaurus, ''Camarasaurus supremus'', Cope determined the animal to have been smaller in size than the extant American Alligator and named the species ''A. lucasii'' after Superintendent Lucas who initially made the discovery. Cope also collected skull material from the same locality and level, however did not refer it to ''Amphicotylus''. The cranial material was examined by Charles C. Mook in 1942 who refer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amphicotylus
''Amphicotylus'' is an extinct genus of goniopholidid mesoeucrocodylian from the Tithonian of Colorado, Wyoming, and Oklahoma. It was species description, described in 1878.E. D. Cope. 1878. Descriptions of new extinct Vertebrata from the Upper Tertiary and Dakota Formations. 'Bulletin of the United States Geological and Geographical Survey of the Territories'', 4(2):379-396 Discovery and species ''Amphicotylus'' was first described by Edward Drinker Cope in 1878 based on dorsal and lumbar vertebrae, ribs and osteoderms. Based on these remains, found in the same locality as Camarasaurus, ''Camarasaurus supremus'', Cope determined the animal to have been smaller in size than the extant American Alligator and named the species ''A. lucasii'' after Superintendent Lucas who initially made the discovery. Cope also collected skull material from the same locality and level, however did not refer it to ''Amphicotylus''. The cranial material was examined by Charles C. Mook in 1942 who refer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anteophthalmosuchus
''Anteophthalmosuchus'' (meaning "forward-pointing eye crocodile") is an extinct genus of goniopholidid mesoeucrocodylian from the Early Cretaceous of southern England, eastern Spain, and western Belgium. Discovery The holotype specimen of ''Anteophthalmosuchus'', from the Wealden Group of the Isle of Wight, includes a well-preserved skull and partial skeleton. This specimen has been known since 1904 and was identified as the "Tie Pits specimen" or the "Hooley specimen" after Reginald Walter Hooley, an amateur paleontologist who had described it in 1905. Hooley had originally attributed the specimen to the previously named species '' Goniopholis crassidens''. Additional referred specimens include a partial disarticulated skeleton and a partial skull that may represent a juvenile specimen. In 2011, Hooley's specimen was redescribed as a distinct genus and species of goniopholidid called ''Anteophthalmosuchus hooleyi''. The genus name means "forward-pointing eye crocodile" becaus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calsoyasuchus
''Calsoyasuchus'' (meaning " r. KyrilCalsoyas' crocodile") is a genus of crocodylomorph that lived in the Early Jurassic. Its fossilized remains were found in the Sinemurian-Pliensbachian-age Kayenta Formation on Navajo Nation land in Coconino County, Arizona, United States. Formally described as ''C. valliceps'', it is known from a single incomplete skull which is unusually derived for such an early crocodile relative. This genus was described in 2002 by Ronald Tykoski and colleagues; the specific name means "valley head" and refers to a deep groove along the midline of the nasal bones and frontal bones. It has often been interpreted as the earliest diverging member of Goniopholididae, but other studies have recovered it in various other positions. Description The holotype skull ( TMM 43631-1) that would be named ''Calsoyasuchus'' was discovered in 1997 by members of an expedition composed of crews from Texas Memorial Museum of the University of Texas at Austin, the Museum of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sunosuchus
''Sunosuchus'' is an extinct genus of goniopholidid mesoeucrocodylian. Fossils are known from China, Kyrgyzstan, and Thailand and are Jurassic in age, although some may be Early Cretaceous. Four species are currently assigned to the genus: the type species ''S. miaoi'' and the species ''S. junggarensis'', ''S. shartegensis'', and ''S. shunanensis''. All species are from China. ''Goniopholis phuwiangensis'', also from Thailand, was reassigned to ''Sunosuchus'' by Andrade ''et al.'' (2011). The material from Kyrgyzstan has not been assigned to any species. Description ''Sunosuchus'' has a long, narrow snout and a small skull table. Several characters help diagnose ''Sunosuchus'' and distinguish it from other taxa. For example, there are wide pits on the back of the frontal bone. The frontal bone also has a distinctive ridge along part of its midline. The lower jaw has a long symphysis where the two halves come together. This symphysis is formed mostly from the mandibles, but als ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hulkepholis
''Hulkepholis'' is an extinct genus of goniopholidid mesoeucrocodylian from the Early Cretaceous of southern England and eastern Spain. It contains two species, the type species, ''Hulkepholis willetti'', and also ''H. plotos''. ''Hulkepholis'' is most closely related to both species of ''Anteophthalmosuchus'' (including "Dollo's goniopholidid"). Discovery ''H. willetti'' is known from a single holotype specimen, BMNHB 001876 from the Wealden Group of the Isle of Wight that includes a well-preserved nearly complete skull. It was collected by Edgar W. Willett at Cuckfield, West Sussex, from the Valanginian-aged Grinstead Clay Member, of the Hastings Group, Wealden Supergroup. Willett showed the specimen to the Geological Society of London in or around 1877 or 1878, and it was then Hulke (1878) described it as a specimen of '' Goniopholis crassidens'', an identification derived from a similar tooth form. The specimen was considered lost among the crocodyliform research communi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diplosaurus
''Diplosaurus'' is an extinct genus of goniopholidid mesoeucrocodylian. Fossils have been found from the Western United States and range from Late Jurassic to Early Cretaceous in age. The genus was first named and described in a paper written in 1877 by Othniel Charles Marsh.Marsh, O. C. (1877). Notice of some new vertebrate fossils. ''American Journal of Arts and Sciences'' 14:249-256 Discovery and etymology The generic name, derived from Greek διπλόος, ''diploos'', "double", probably refers to the "biconcave vertebrae" Marsh mentions as a distinctive trait compared to modern forms. The type species is ''Diplosaurus felix''.Williston, S. W. (1906). American amphicoelian crocodiles. ''The Journal of Geology'', ''14''(1), 1-17.Norell, M. A., & Storrs, G. W. (1989)Postilla Number 203 The species was named on a heavily eroded skull roof and several postcranial elements, including a partial humerus, though the fossils have yet to be properly diagnosed. The fossils had been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goniopholis
''Goniopholis'' (meaning "angled scale") is an extinct genus of goniopholidid crocodyliform that lived in Europe and Africa during the Late Jurassic and Early Cretaceous. Being semi-aquatic it is very similar to modern crocodiles. It ranged from 2–4 metres in length, and would have had a very similar lifestyle to the American alligator or Nile crocodile. Discovery and species The type species of the genus is ''G. crassidens'' which is known from the Berriasian of England, and the referable species ''G simus'' from the Berriasian of NW Germany, might be conspecific. Other species that are referable to ''Goniopholis'' include ''G. kiplingi'' from the Berriasian of England, and ''G. baryglyphaeus'' from the Late Jurassic (Kimmeridgian) of Portugal making it the oldest known ''Goniopholis'' species. The species ''G. kiplingi'' honors the author Rudyard Kipling, "in recognition for his enthusiasm for natural sciences". Eggs attributed to ''Goniopholis'' were found in the Late Jura ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pinacosuchus
''Pinacosuchus'' is an extinct genus of crocodylomorph. Its fossils were found in the Late Cretaceous-age North Horn Formation of Utah (United States). ''Pinacosuchus'' was a diminutive crocodylomorph with spiky armor, and is known only from meagre remains. History and description Charles W. Gilmore named ''Pinacosuchus'' in 1942 for USNM 16592, consisting of a fragment of upper jaw, seven partial vertebrae, a partial coracoid, a partial thigh bone, numerous pieces of bony armor, and other fragments. This specimen was discovered at the "Lizard Locality" in the Manti National Forest, Emery County, Utah. The type species is ''P. mantiensis''. Gilmore had difficulty classifying the specimen, due to its fragmentary nature. He ruled out all then-known orders of reptiles on anatomical ground except for Crocodilia (which had a more expansive definition at the time) and the nebulous thecodontia. He considered a pseudosuchian thecodont identity, but eliminated it because all ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dakotasuchus
''Dakotasuchus'' (meaning "Dakota andstonecrocodile") is a genus of goniopholidid mesoeucrocodylian. Its fossils have been recovered from the Cenomanian-age Upper Cretaceous Dakota Sandstone of Kansas. The type specimen was found in an iron-cemented sandstone concretion near Salina. This concretion was broken into two large pieces; more of the specimen was probably present originally, but by the time it was found only the torso and short portions of the neck and tail remained. Twenty pairs of bony scutes ran down the midline of the back. The vertebrae lacked the procoelous articulation (concave anterior and convex posterior faces) of more derived crocodyliforms. ''Dakotasuchus'' had short broad shoulder blades, suggesting it had stout powerful forelimbs and perhaps terrestrial habits. M. G. Mehl, who described the genus, estimated the length of the type individual when complete to have been . The type species is ''D. kingi'', named for Professor King, a former dean of Kansa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |