|
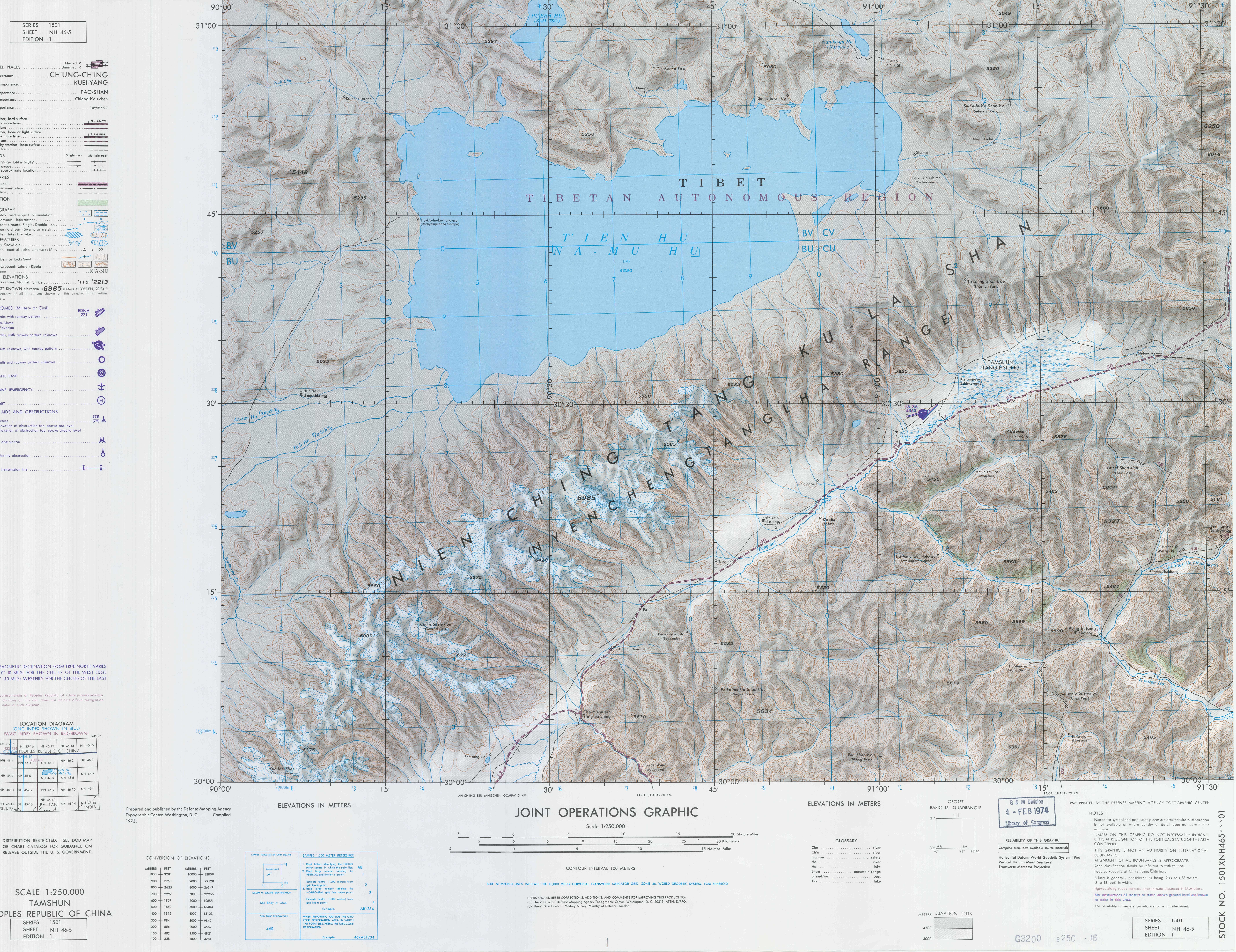
Gomang Co
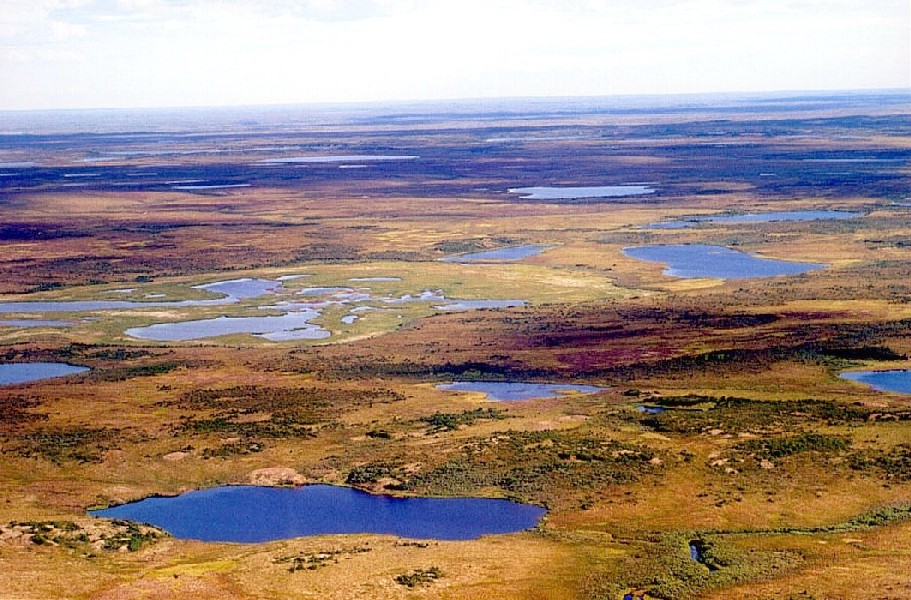
Gomang Co (Also spelled as Guomang Cuo and Guomangcuo) is a mountain graben basin lake on the Tibetan Plateau in Xainza County within Nagqu in the Tibet Autonomous Region of China. Gomang Co has a Köppen climate classification of existing in a tundra climate. The lake's water level is controlled by its outlet toward Siling Lake, which is north of Gomang Co. See also * Bangecuo * Dazecuo * Lake Urru * Namtso Namtso or Lake Nam (officially: Namco; mn, Tenger nuur; ; ; “Heavenly Lake” in European literature: Tengri Nor, ) is a mountain lake on the border between Damxung County of Lhasa prefecture-level city and Baingoin County of Nagqu Prefectu ... References Further reading * External links * Lakes of Tibet Xainza County {{Nagqu-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sentinel-2
Sentinel-2 is an Earth observation mission from the Copernicus Programme that systematically acquires optical imagery at high spatial resolution (10 m to 60 m) over land and coastal waters. The mission is currently a constellation with two satellites, Sentinel-2A and Sentinel-2B; a third satellite, Sentinel-2C, is currently undergoing testing in preparation for launch in 2024. The mission supports a broad range of services and applications such as agricultural monitoring, emergencies management, land cover classification or water quality. Sentinel-2 has been developed and is being operated by the European Space Agency, and the satellites were manufactured by a consortium led by Airbus Defence and Space in Friedrichshafen. Overview The Sentinel-2 mission has the following key characteristics: * Multi-spectral data with 13 bands in the visible, near infrared, and short wave infrared part of the spectrum * Systematic global coverage of land surfaces from 56° S to 84°&nb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Köppen Climate Classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen, notably in 1918 and 1936. Later, the climatologist Rudolf Geiger (1894–1981) introduced some changes to the classification system, which is thus sometimes called the Köppen–Geiger climate classification system. The Köppen climate classification divides climates into five main climate groups, with each group being divided based on seasonal precipitation and temperature patterns. The five main groups are ''A'' (tropical), ''B'' (arid), ''C'' (temperate), ''D'' (continental), and ''E'' (polar). Each group and subgroup is represented by a letter. All climates are assigned a main group (the first letter). All climates except for those in the ''E'' group are assigned a seasonal precipitation subgroup (the second letter). For example, ''Af'' indi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Namtso
Namtso or Lake Nam (officially: Namco; mn, Tenger nuur; ; ; “Heavenly Lake” in European literature: Tengri Nor, ) is a mountain lake on the border between Damxung County of Lhasa prefecture-level city and Baingoin County of Nagqu Prefecture in the Tibet Autonomous Region of China, approximately NNW of Lhasa. Geography Namtso (Namco) is a lake that first formed during the Paleogene age, as a result of Himalayan tectonic plate movements. The lake lies at an elevation of , and has a surface area of . This salt lake is the largest lake in the Tibet Autonomous Region. However, it is not the largest lake on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. That title belongs to Qinghai Lake (more than twice the size of Namtso); which lies more than to the north-east in Qinghai. Namtso has five uninhabited islands of reasonable size, in addition to one or two rocky outcrops. The islands have been used for spiritual retreat by pilgrims who walk over the lake's frozen surface at the end of winter, ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Urru
Urru Lake (; )is a plateau lake in Nagqu Prefecture, Tibet Autonomous Region, southwest of China, located between Nyima County and Xainza County. The lake, which is part of the Siling Lake drainage system, is fed by several rivers and drains eastward into Jargö Lake. It is 33.6 km long and 13.4 km wide and has an area of 342.7 square km. See also * Bangecuo * Gomang Co * Namtso * Notes {{reflist Lakes of Tibet, Urru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dazecuo
Dazecuo (, also known as Dagze Lake) is one of many inland lakes in Tibet. It is a salt lake on the Tibetan PlateauQin, Huayu; Wang, Shang; Feng, Kai; He, Zhili (May 2019)"Unraveling the diversity of sedimentary sulfate-reducing prokaryotes (SRP) across Tibetan saline lakes using epicPCR".''Microbiome'', 7(1). in Xainza County within Nagqu in the Tibet Autonomous Region of China. It was reported in 2021 that the lake receives "good environmental protection". It has an area of 260 km² (100 square miles) and an elevation of 4,459 meters above sea level."Plateau lakes in Tibet with an altitude of more than 4,400 meters Dazecuo: good ecology and beautiful scenery". China News Agency. July 29, 2021. Retrieved May 16, 2022. In 2021 the lake was 21.1 kilometers in length and 16.9 kilometers wide. In glacial times, the region was considerably wetter, and lakes were correspondingly much larger. Changes in climate have resulted in greater aridity on the Tibetan Plateau. The numerous co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bangecuo
Bangecuo (also spelled as Bangor Co) is a graben basin salt lakeWang, Can; Wang, Hailei; Song, Gao; Zheng, Mianping (February 2019)"Grain size of surface sediments in Selin Co (central Tibet) linked to water depth and offshore distance" ''Journal of Paleolimnology''. 61(2):1-13. DOI:10.1007/s10933-018-0054-8 on the Tibetan Plateau in Xainza County within Nagqu in the Tibet Autonomous Region of China. It was reported in 2003 that the water levels of Siling Lake and Bangecuo had increased by 19.34% since 1969. Siling Lake is another nearby salt lake located west of Bangecuo, around four miles away. See also * Dazecuo * Gomang Co * Lake Urru * Namtso References Further reading * Lv, P., Qu, Y. G., Li, W. Q., & Wang, H. S. (2003). "Shelincuo and Bangecuo extensional lake basins in the northern part of Tibet and present chasmic activities." Jilin Geol, 22, 15–19. External links * Li Pu, (1955)"Bangecuo Formation".''Chinese Science Bulletin ''Science Bulletin'' () is a multidi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siling Lake
Siling Lake (; ), (also known as Qilin) is a lake in the Tibet Autonomous Region, China to the north of Xainza. Doijiang is located near the lake. Administratively it belongs to Xainza County and Baingoin County of the Nagqu. Bangecuo is another nearby salt lake located east of Siling Lake, around four miles away. Overview The lake lies at an altitude of . It is a salt lake. It is fed by the rivers Za'gya Zangbo (or Tsagya Tsangpo) (扎加藏布) and the Boques Tsangpo (波曲藏布). With an area of , Siling Co is the second largest saltwater lake in the northern Tibetan Plateau and forms part of the Siling Co National Nature Reserve (also Selincuo Reserve or Xainza Nature Reserve). The reserve was established in 1993 and contains significant populations of black-necked cranes and some 120 species of birds in total. The lake only has a single species of fish, '' Gymnocypris selincuoensis'', exploited by fishermen. The prairie on the banks of the lake is traditionally used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tundra
In physical geography, tundra () is a type of biome where tree growth is hindered by frigid temperatures and short growing seasons. The term ''tundra'' comes through Russian (') from the Kildin Sámi word (') meaning "uplands", "treeless mountain tract". There are three regions and associated types of tundra: Arctic tundra, alpine tundra, and Antarctic tundra. Tundra vegetation is composed of dwarf shrubs, sedges, grasses, mosses, and lichens. Scattered trees grow in some tundra regions. The ecotone (or ecological boundary region) between the tundra and the forest is known as the tree line or timberline. The tundra soil is rich in nitrogen and phosphorus. The soil also contains large amounts of biomass and decomposed biomass that has been stored as methane and carbon dioxide in the permafrost, making the tundra soil a carbon sink. As global warming heats the ecosystem and causes soil thawing, the permafrost carbon cycle accelerates and releases much of these soil-contained g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mindat
Mindat may refer to: Places in Burma/Myanmar *Mindat, Chin State, in Burma *Mindat Township, in Burma *Mindat District in Chin State, Burma Other uses *Mindat Min Kanaung Mintha ( my, ကနောင်မင်းသား; 31 January 1820 – 2 August 1866) was crown prince of Burma and son of King Tharrawaddy and younger brother of King Mindon of Burma. Towards the end of the Second Anglo-Burmese Wa ..., a Burmese prince * Mindat.org, an online mineralogy database {{dab, geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xainza County
Xainza County, also Shantsa, Shentsa, (; ) is a county within Nagqu of the Tibet Autonomous Region of China. In 1999 the county had a population of 16,190. Geography The capital lies at Naktsang Town or Xainza. The county covers an area of . Until recent times the County extended all the way from the borders of Xinjiang in the north to the Brahmaputra River in the south, covering a larger area than the United Kingdom. It has since been split into two, Shentsa (Xainza) County and the new Nyima County to the east.Dorje (2009), p. 396. "In this region there are 67 lakes, including some of Tibet's largest: Serling Lake, Serling, Dangra Yutso, Ngangtse-tso, Kering-tso, Taktse-tse and Uru-tso. In the northeast there are a number of 6,000 m peaks including Purok Gangri and Norla Gangri , not to mention the Kunlun mountains on the Xinjiang border further north. The entire northern region forms part of the Jangtang Nature Reserve. Ten large salt fields testify to the importance of this r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tibetan Plateau
The Tibetan Plateau (, also known as the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau or the Qing–Zang Plateau () or as the Himalayan Plateau in India, is a vast elevated plateau located at the intersection of Central, South and East Asia covering most of the Tibet Autonomous Region, most of Qinghai, western half of Sichuan, Southern Gansu provinces in Western China, southern Xinjiang, Bhutan, the Indian regions of Ladakh and Lahaul and Spiti (Himachal Pradesh) as well as Gilgit-Baltistan in Pakistan, northwestern Nepal, eastern Tajikistan and southern Kyrgyzstan. It stretches approximately north to south and east to west. It is the world's highest and largest plateau above sea level, with an area of (about five times the size of Metropolitan France). With an average elevation exceeding and being surrounded by imposing mountain ranges that harbor the world's two highest summits, Mount Everest and K2, the Tibetan Plateau is often referred to as "the Roof of the World". The Tibetan Plateau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Depression (geology)
In geology, a depression is a landform sunken or depressed below the surrounding area. Depressions form by various mechanisms. Types Erosion-related: * Blowout: a depression created by wind erosion typically in either a partially vegetated sand dune ecosystem or dry soils (such as a post-glacial loess environment). * Glacial valley: a depression carved by erosion by a glacier. * River valley: a depression carved by fluvial erosion by a river. * Area of subsidence caused by the collapse of an underlying structure, such as sinkholes in karst terrain. * Sink: an endorheic depression generally containing a persistent or intermittent (seasonal) lake, a salt flat (playa) or dry lake, or an ephemeral lake. * Panhole: a shallow depression or basin eroded into flat or gently sloping, cohesive rock.Twidale, C.R., and Bourne, J.A., 2018Rock basins (gnammas) revisited.''Géomorphologie: Relief, Processus, Environnement,'' Vol. 24, No. 2. January 2018. Retrieved 9 June 2020. Coll ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |