|
Gold Lottery Of 1832
The Gold Lottery of 1832 was the seventh lottery of the Georgia Land Lotteries, a lottery system used by the State of Georgia between the years 1805 and 1833 to redistribute stolen Cherokee land. It was authorized by the Georgia General Assembly by an act of December 24, 1831 a few years after the start of the Georgia Gold Rush. The act specified that approximately one third of the land districts to be distributed by lottery under the act of December 21, 1830 (the sixth land lottery), be designated as gold districts of each and to be distributed in a separate lottery. The drawings for the Gold Lottery of 1832 occurred between October 22, 1832 and May 1, 1833 and applied to land that had been owned by the Cherokee Nation. Those successful in the lottery had to pay a grant fee of $10.00 per lot. Those eligible were: bachelors over the age of 18 who were 3 year residents of Georgia and citizens of United States; widows who were 3 year residents of Georgia; families of orphans w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1820 Land Lottery
The 1820 Land Lottery was the third lottery of the Georgia Land Lotteries, a lottery system used by the U.S. state of Georgia between the years 1805 and 1833 to steal and redistribute Cherokee and Muscogee land. The 1820 lottery was authorized by the Georgia General Assembly by acts of December 15, 1818, and December 16, 1819. The lottery redistributed land in Baldwin and Wilkinson counties. The 1820 lottery were used to steal Muscogee land and redistribute it to white settlers. Following the Creek War (1813–1814), President Andrew Jackson demanded from the Muscogee an immense area of land which would become the southern third of the entire state of Georgia. A second section of land in northeast Georgia was included. This other, smaller section defined the eastern end of the Cherokee Nation for 12 years. Muscogee land was stolen and redistributed in Appling, Early, Gwinnett, Habersham, Hall, Irwin, Rabun, and Walton counties. The size of stolen lots were either 250 acres or 490 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1832 In Georgia (U
Year 183 ( CLXXXIII) was a common year starting on Tuesday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Aurelius and Victorinus (or, less frequently, year 936 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 183 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Roman Empire * An assassination attempt on Emperor Commodus by members of the Senate fails. Births * January 26 – Lady Zhen, wife of the Cao Wei state Emperor Cao Pi (d. 221) * Hu Zong, Chinese general, official and poet of the Eastern Wu state (d. 242) * Liu Zan (Zhengming), Chinese general of the Eastern Wu state (d. 255) * Lu Xun Zhou Shuren (25 September 1881 – 19 October 1936), better known by his pen name Lu Xun (or Lu Sun; ; Wade–Giles: Lu Hsün), was a Chinese writer, essayist, poet, and literary critic. He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georgia Resolutions 1827
The Georgia Resolutions of 1827 were a response to the Cherokee's refusal to cede their territory within the U.S. state of Georgia. The resolutions declared the state's right to title, jurisdiction, and authority over all the land within its borders. They also stipulated that Indigenous people were tenants of Georgia at the state's will, and Georgia reserved the right to coerce obedience from all of its tenants, white, red or black. The resolutions were intended to pressure the federal government to prioritize its responsibility to Georgia over its responsibility to the Cherokee Nation, although it did not achieve its desired effect until the Jackson administration came into power.Robertson, Lindsay Gordon. ''Conquest by Law: How the Discovery of America Dispossessed Indigenous Peoples of Their Lands.''Oxford University Press, 2005:124-25. See also *Cherokee removal *Georgia Land Lotteries **1805 Land Lottery **1807 Land Lottery ** 1820 Land Lottery **1821 Land Lottery ** 1827 Land ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1833 Fractions Lottery
The 1833 Fractions Lottery was the eight and final lottery of the Georgia Land Lotteries, a lottery system used by the U.S. state of Georgia between the years 1805 and 1833 to redistribute stolen Cherokee and Muscogee land to white settlers. The 1833 fractions lottery was authorized by the Georgia General Assembly by an act of December 24, 1832. The lottery redistributed land from the original Cherokee territory and twenty-two lots that were not placed into prize wheels during previous lotteries. The lots varied in size, but the fractional lots left over from the 1832 Land Lottery were smaller than 100 acres and were taken from the 60 land districts and 33 gold districts in Georgia. The fractional lots resulted from irregular boundaries that had prevented measurements of square lots of land. Drawings for the lottery occurred on December 6 and 7 of 1833 for the land lots and on December 9-13 of that year for the gold lots. See also *Cherokee removal *Georgia Land Lotteries **1805 La ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1832 Land Lottery
The 1832 Land Lottery was the sixth lottery of the Georgia Land Lotteries, a lottery system used by the U.S. state of Georgia between the years 1805 and 1833 to redistribute stolen Cherokee and Muscogee land to white settlers. The 1832 lottery was authorized by the Georgia General Assembly by acts of December 21, 1830 and December 24, 1831. The lottery redistributed Cherokee land in Cass (renamed Bartow), Cherokee, Cobb, Floyd, Forsyth, Gilmer, Lumpkin, Murray, Paulding, and Union counties. The lots were 160 acres in size. Registration for the lottery occurred in the four months after the Governor's proclamation of February 20, 1832, with drawings occurring in 1832. Fortunate drawers from the previous Georgia land lotteries were excluded, as well as any person who had mined for gold or other metals in Georgia since 1 June 1830, any person who had taken up residence in Cherokee territory, any member or associate of "a horde of Thieves known as the Pony Club", and any person who ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1827 Land Lottery
The 1827 Land Lottery was the fifth lottery of the Georgia Land Lotteries, a lottery system used by the U.S. state of Georgia between the years 1805 and 1833 to redistribute stolen Cherokee and Muscogee land to white settlers. The 1827 lottery was authorized by the Georgia General Assembly by an act of June 9, 1825. The lottery redistributed confiscated Muscogee land in Carroll, Coweta, Lee, Muscogeee, and Troup counties. The lots were 202.5 acres in size. Registration for the lottery occurred in the two months after the Act's publication on December 7, 1824, with drawings occurring in 1827. Fortunate drawers from the previous Georgia land lotteries were excluded, as well as draft resisters who refused to fight in the War of 1812 or the Indian Wars, people who deserted from military service, imprisoned convicts, tax defaulters, and absconders for debt. See also *Georgia Land Lotteries **1805 Land Lottery **1807 Land Lottery ** 1820 Land Lottery **1821 Land Lottery **1832 Land ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1821 Land Lottery
The 1821 Land Lottery was the fourth lottery of the Georgia Land Lotteries, a lottery system used by the U.S. state of Georgia between the years 1805 and 1833 to steal Cherokee and Muscogee land and redistribute it to white settlers. The 1821 lottery was authorized by the Georgia General Assembly by an act of May 16, 1821. The lottery redistributed land in Dooly, Fayette, Henry, Houston, and Monroe counties. The 1821 lottery was used to confiscate Muscogee land and redistribute it to white settlers. The stolen lots were 202.5 acres in size. Registration for the lottery occurred in the two months after the Act's publication on May 16 1821, with drawings occurring between November 7 and December 12, 1821. Fortunate drawers from the previous Georgia land lotteries were excluded, as well as draft resisters who refused to fight in the War of 1812 or the Indian Wars, criminals, tax defaulters, and absconders for debt. List of fortunate drawers See also * Georgia Land Lotteries ** ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1807 Land Lottery
The 1807 Land Lottery was the second lottery of the Georgia Land Lotteries, a lottery system used by the U.S. state of Georgia between the years 1805 and 1833 to steal and redistribute Cherokee and Muscogee land. The 1807 lottery was authorized by the Georgia General Assembly by an act of June 26, 1806. The lottery redistributed land in Baldwin and Wilkinson counties. 202.5 acre lots were redistributed in both counties. The 1807 lottery were used to steal Muscogee land and redistribute it to white settlers. Registrations for the lottery took place between June 26 and September 26, 1806, with drawings occurring between August 10 and September 23, 1807. Fortunate drawers from the previous 1805 lottery were excluded. See also *Georgia Land Lotteries **1805 Land Lottery ** 1820 Land Lottery **1821 Land Lottery ** 1827 Land Lottery ** 1832 Land Lottery **Gold Lottery of 1832 ** 1833 Fractions Lottery * Georgia resolutions 1827 *Indian removal References {{Reflist External linksGeorgi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
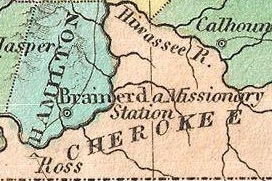
Georgia Land Lotteries
The Georgia land lotteries were an early nineteenth century system of land redistribution in Georgia. Under this system, white male citizens could register for a chance to win lots of land that had (and in most cases recently) been taken from the Muscogee and the Cherokee Nation. The lottery system was utilized by the State of Georgia between the years 1805 and 1833 “to strengthen the state and increase the population in order to increase Georgia's power in the House of Representatives.” Although some other states used land lotteries, none were implemented at the scale of the Georgia contests. Land Spaces Land lots were surveyed in five different sizes based on the perceived quality of the land. In 1805, land lots were and . In 1807, land lots were . In 1820, land lots were and . In 1821, land lots were . In the 1832 Land Lottery area, land lots were , while in the 1832 Gold Lottery area, land lots were . History of system Prior to 1803, Georgia distributed land via a headri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1805 Land Lottery
The 1805 Land Lottery was the first lottery of the Georgia Land Lotteries, a lottery system used by the U.S. state of Georgia between the years 1805 and 1833 to steal and redistribute Cherokee and Muscogee land. The lottery was authorized by the Georgia General Assembly by an act of May 11, 1803, with drawings occurring in 1805. The lottery redistributed land in Baldwin, Wayne, and Wilkinson counties. 490-acre plots were redistributed in Wayne County and 202.5-acre plots were redistributed in Baldwin and Wilkinson counties. The 1805 lottery were used to steal Muscogee land and redistribute it to white settlers. The John Rountree Log House in Twin City, Georgia, was built by John Rountree on land he won in the lottery. See also *Georgia Land Lotteries ** 1807 Land Lottery ** 1820 Land Lottery **1821 Land Lottery ** 1827 Land Lottery ** 1832 Land Lottery **Gold Lottery of 1832 ** 1833 Fractions Lottery * Georgia resolutions 1827 *Indian removal References {{Reflist External link ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cherokee Removal
Cherokee removal, part of the Trail of Tears, refers to the forced relocation between 1836 and 1839 of an estimated 16,000 members of the Cherokee Nation and 1,000–2,000 of their slaves; from their lands in Georgia, South Carolina, North Carolina, Tennessee, and Alabama to the Indian Territory (present day Oklahoma) in the then Western United States, and the resultant deaths along the way and at the end of the movement of an estimated 4,000 Cherokee and unknown number of slaves. The Cherokee have come to call the event ''Nu na da ul tsun yi'' (the place where they cried); another term is ''Tlo va sa'' (our removal)—both phrases not used at the time, and seems to be of Choctaw origin. Removal actions (voluntary, reluctantly or forcibly) occurred to other American Indian groups in the American South, North, Midwest, Southwest, and the Plains regions. The Chickasaw, Choctaw, Muskogee ( Creek), and Cherokee were removed reluctantly. The Seminole in Florida resisted removal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |