|
Godhra
Godhra is a municipality in Panchmahal district in Indian state of Gujarat. It is the administrative headquarters of the Panchmahal district. Originally the name came from ''gou'' which means "cow" and ''dhara''- which have two meanings depending on how you pronounce the word: 'dharaa' means a feminine thing or person that "holds" something and it usually means"land", and the other pronunciation is 'dhaaraa' in which means "flow". However, the second pronunciation is not popular nor is usually associated with this word. Hence, 'Godhra or Godharaa' means the Land of the Cow. Godhra is widely known in India and internationally for being the starting point of the 2002 Gujarat riots. Statewide religious riots between Hindus and Muslims began after the Godhra train burning incident near the Godhra railway station on 27 February 2002, where about 59 Hindu train passengers were burnt alive. It was in Godhra that Vallabhbhai Patel first met Gandhi in 1917 and was subsequently drawn into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Godhra Train Burning
The Godhra train burning occurred on the morning of 27 February 2002, in which 59 Hindu pilgrims and '' karsevaks'' returning from Ayodhya were killed in a fire inside the Sabarmati Express train near the Godhra railway station in the Indian state of Gujarat. The commission set up by the Government of Gujarat to investigate the train burning spent 6 years going over the details of the case, and concluded that the fire was arson committed by a Muslim mob of 1,000 to 2,000 people. A commission appointed by the central government, whose appointment was later held to be unconstitutional, stated that the fire had been an accident. A court convicted a group of 31 Muslim individuals for the incident and the conspiracy for the crime. The conviction was later upheld by the Gujarat High Court. The causes of the fire are frequently disputed.: "The cause of the initial fire has not been determined, but it was almost certainly not deliberately set by Muslims on the station platform, as Hin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2002 Gujarat Riots
The 2002 Gujarat riots, also known as the 2002 Gujarat violence, was a three-day period of inter-communal violence in the western Indian state of Gujarat. The burning of a train in Godhra on 27 February 2002, which caused the deaths of 58 Hindu pilgrims and karsevaks returning from Ayodhya, is cited as having instigated the violence. Following the initial riot incidents, there were further outbreaks of violence in Ahmedabad for three months; statewide, there were further outbreaks of violence against the minority Muslim population of Gujarat for the next year. According to official figures, the riots ended with 1,044 dead, 223 missing, and 2,500 injured. Of the dead, 790 were Muslim and 254 Hindu. The Concerned Citizens Tribunal Report, estimated that as many as 1,926 may have been killed. Other sources estimated death tolls in excess of 2,000. Many brutal killings and rapes were reported on as well as widespread looting and destruction of property. Narendra Modi, then Chief ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
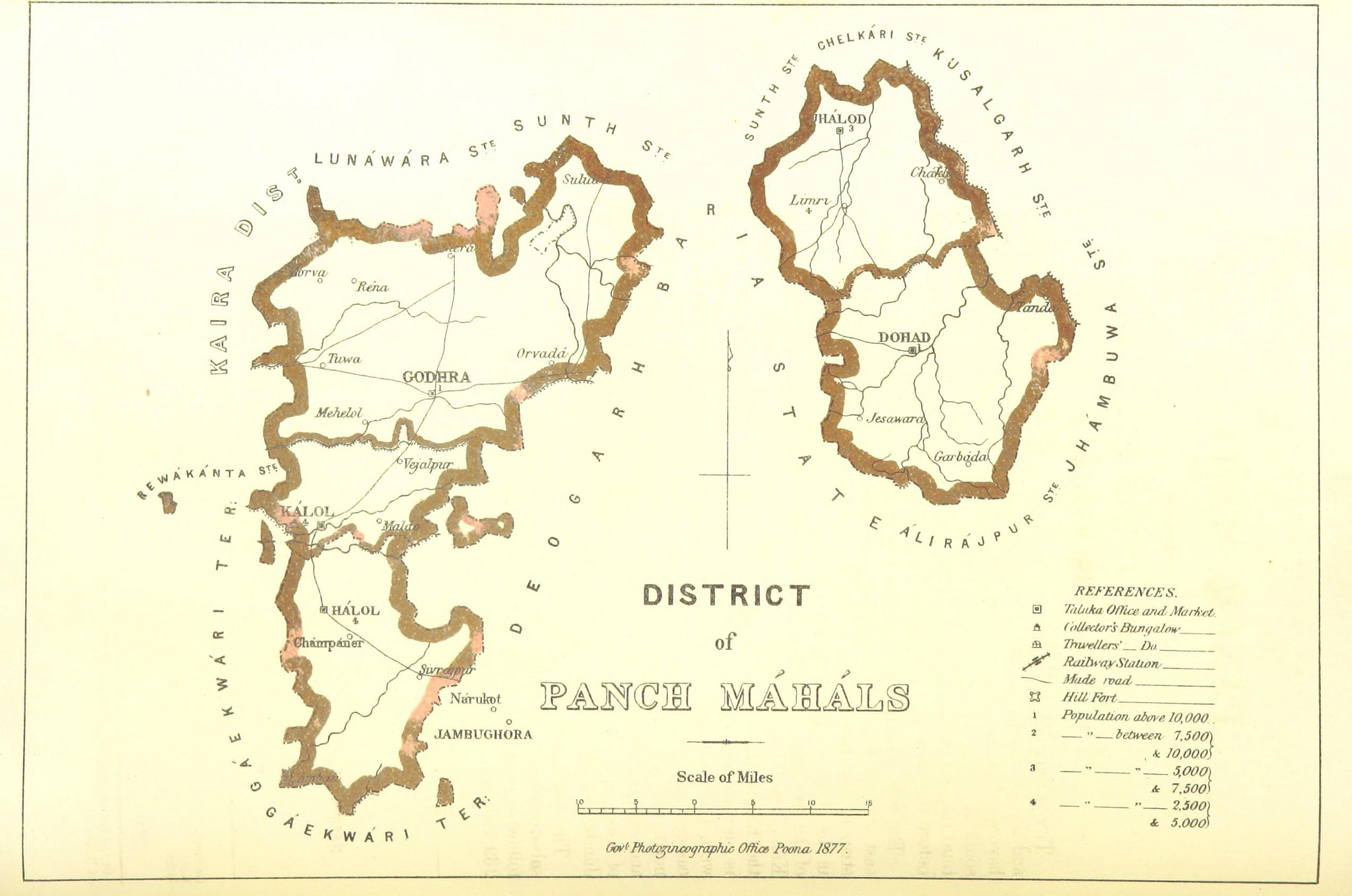
Panchmahal District
Panchmahal, also known as Panch Mahals, is a district in the eastern portion of Gujarat State western India. ''Panch-mahal'' means "five tehsils/talukas" (5 sub-divisions), and refers to the five sub-divisions that were transferred by the Maharaja Jivajirao Scindia of Gwalior State to the British: Godhra, Dahod, Halol, Kalol and Jhalod, Devgadh Baria. The district had a population of 2,390,776 of which 12.51% were urban as of 2001. The district is located on eastern end of the state. It is bordered by Dahod district to the north-east & east, Vadodara district to the southwest and Chhota Udaipur district to southeast, Kheda district to the west and Mahisagar district to the north. Name ''Panch-mahal'' is a Hindustani or Gujarati word derived from Panch ("five") and Mahal which adopted from its original usage in Arabic for a place or type of building, later adopted in Hindi to refer to a province, district or its division, an estate etc. The district was originally called the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panchmahal
Panchmahal, also known as Panch Mahals, is a district in the eastern portion of Gujarat State western India. ''Panch-mahal'' means "five tehsils/talukas" (5 sub-divisions), and refers to the five sub-divisions that were transferred by the Maharaja Jivajirao Scindia of Gwalior State to the British: Godhra, Dahod, Halol, Kalol and Jhalod, Devgadh Baria. The district had a population of 2,390,776 of which 12.51% were urban as of 2001. The district is located on eastern end of the state. It is bordered by Dahod district to the north-east & east, Vadodara district to the southwest and Chhota Udaipur district to southeast, Kheda district to the west and Mahisagar district to the north. Name ''Panch-mahal'' is a Hindustani or Gujarati word derived from Panch ("five") and Mahal which adopted from its original usage in Arabic for a place or type of building, later adopted in Hindi to refer to a province, district or its division, an estate etc. The district was originally called the P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vallabhbhai Patel
Vallabhbhai Jhaverbhai Patel (; ; 31 October 1875 – 15 December 1950), commonly known as Sardar, was an Indian lawyer, influential political leader, barrister and statesman who served as the first Deputy Prime Minister and Home Minister of India from 1947 to 1950. He was a barrister and a senior leader of the Indian National Congress, who played a leading role in the country's struggle for independence, guiding its integration into a united, independent nation. In India and elsewhere, he was often called ''Sardar'', meaning "chief" in Hindi, Urdu, Bengali and Persian. He acted as the Home Minister during the political integration of India and the Indo-Pakistani War of 1947. Patel was born in Nadiad, Kheda district, and raised in the countryside of the state of Gujarat. He was a successful lawyer. One of Mahatma Gandhi's earliest political lieutenants, he organised peasants from Kheda, Borsad, and Bardoli in Gujarat in non-violent civil disobedience against the British Raj ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Districts Of India
A district ('' zila'') is an administrative division of an Indian state or territory. In some cases, districts are further subdivided into sub-divisions, and in others directly into ''tehsils'' or ''talukas''. , there are a total of 766 districts, up from the 640 in the 2011 Census of India and the 593 recorded in the 2001 Census of India. District officials include: *District Magistrate or Deputy Commissioner or District Collector, an officer of the Indian Administrative Service, in charge of administration and revenue collection *Superintendent of Police or Senior Superintendent of Police or Deputy Commissioner of Police, an officer belonging to the Indian Police Service, responsible for maintaining law and order *Deputy Conservator of Forests, an officer belonging to the Indian Forest Service, entrusted with the management of the forests, environment and wildlife of the district Each of these officials is aided by officers from the appropriate branch of the state governme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gujarat
Gujarat (, ) is a state along the western coast of India. Its coastline of about is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the fifth-largest Indian state by area, covering some ; and the ninth-most populous state, with a population of 60.4 million. It is bordered by Rajasthan to the northeast, Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu to the south, Maharashtra to the southeast, Madhya Pradesh to the east, and the Arabian Sea and the Pakistani province of Sindh to the west. Gujarat's capital city is Gandhinagar, while its largest city is Ahmedabad. The Gujaratis are indigenous to the state and their language, Gujarati, is the state's official language. The state encompasses 23 sites of the ancient Indus Valley civilisation (more than any other state). The most important sites are Lothal (the world's first dry dock), Dholavira (the fifth largest site), and Gola Dhoro (where 5 uncommon seals were found). Lothal i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parmar
Parmar is a Rajput clan found in Northern and Central India, especially in Rajasthan, Punjab, Haryana, Kutch, Uttarakhand, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Madhya Pradesh and North Maharashtra. See also * Paramara Dynasty * Panwar Dynasty * Pawar * Panwar The Panwar is a Rajput clan found in Northern India, especially in Uttarakhand. See also * Panwar dynasty * Paramara dynasty The Paramara dynasty (IAST: Paramāra) was an Indian dynasty that ruled Malwa and surrounding areas in west-c ... References {{Rajput Groups of India Rajput clans Agnivansha Rajput clans of Uttarakhand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mohandas Gandhi
Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi (; ; 2 October 1869 – 30 January 1948), popularly known as Mahatma Gandhi, was an Indian lawyer, anti-colonial nationalist Quote: "... marks Gandhi as a hybrid cosmopolitan figure who transformed ... anti-colonial nationalist politics in the twentieth-century in ways that neither indigenous nor westernized Indian nationalists could." and political ethicist Quote: "Gandhi staked his reputation as an original political thinker on this specific issue. Hitherto, violence had been used in the name of political rights, such as in street riots, regicide, or armed revolutions. Gandhi believes there is a better way of securing political rights, that of nonviolence, and that this new way marks an advance in political ethics." who employed nonviolent resistance to lead the successful campaign for India's independence from British rule, and to later inspire movements for civil rights and freedom across the world. The honorific ''Mahātmā'' (Sanskrit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zaverchand Meghani
Jhaverchand or Zaverchand Kalidas Meghani ( – ) was an Indian poet, writer, social reformer and freedom fighter. He is a well-known name in the field of Gujarati literature. He was born in Chotila where the Government College has been renamed for this literary figure as Raashtreeya Shaayar Zaverchand Meghani College, Chotila. Mahatma Gandhi spontaneously gave him the title of ''Raashtreeya Shaayar'' (National Poet). Besides this he received many awards like Ranjitram Suvarna Chandrak and ''Mahida Paaritoshik'' in literature. He authored more than 100 books. His first book was a translation work of Rabindranath Tagore's called ''Kathaa-u-Kaahinee'' titled ''Kurbani Ni Katha'' (Stories of martyrdom) which was first published in 1922. He contributed widely to Gujarati folk literature. He went from village to village in search of folk-lores and published them in various volumes of ''Saurashtra Ni Rasdhar''. He was also the Editor of Phulchhab Newspaper of Janmabhoomi group (whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jainism
Jainism ( ), also known as Jain Dharma, is an Indian religions, Indian religion. Jainism traces its spiritual ideas and history through the succession of twenty-four tirthankaras (supreme preachers of ''Dharma''), with the first in the current time cycle being Rishabhadeva, whom the tradition holds to have lived millions of years ago, the twenty-third ''tirthankara'' Parshvanatha, whom historians date to the 9th century BCE, and the twenty-fourth ''tirthankara'' Mahāvīra, Mahavira, around 600 BCE. Jainism is considered to be an eternal ''dharma'' with the ''tirthankaras'' guiding every time cycle of the Jain cosmology, cosmology. The three main pillars of Jainism are ''Ahimsa in Jainism, ahiṃsā'' (non-violence), ''anekāntavāda'' (non-absolutism), and ''aparigraha'' (asceticism). Jain monks, after positioning themselves in the sublime state of soul consciousness, take five main vows: ''ahiṃsā'' (non-violence), ''satya'' (truth), ''Achourya, asteya'' (not stealing), ''b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)


