|
Glomus Spurcum , an anatomical term meaning "small ball"
{{disambig ...
Glomus (Latin for 'ball of thread or yarn') can refer to: * ''Glomus'' (fungus) * Glomus tumor * Coccygeal glomus * Carotid glomus, another name for the carotid body * Glomus cell * Glomerulus ''Glomerulus'' () is a common term used in anatomy to describe globular structures of entwined vessels, fibers, or neurons. ''Glomerulus'' is the diminutive of the Latin ''glomus'', meaning "ball of yarn". ''Glomerulus'' may refer to: * the filter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the Roman Republic it became the dominant language in the Italian region and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. Even after the fall of Western Rome, Latin remained the common language of international communication, science, scholarship and academia in Europe until well into the 18th century, when other regional vernaculars (including its own descendants, the Romance languages) supplanted it in common academic and political usage, and it eventually became a dead language in the modern linguistic definition. Latin is a highly inflected language, with three distinct genders (masculine, feminine, and neuter), six or seven noun cases (nominative, accusative, genitive, dative, ablative, and vocative), five declensions, four verb conjuga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glomus (fungus)
''Glomus'' is a genus of arbuscular mycorrhizal (AM) fungi, and all species form symbiotic relationships (mycorrhizae) with plant roots. ''Glomus'' is the largest genus of AM fungi, with ''ca.'' 85 species described, but is currently defined as non-monophyletic. Classification ''Glomus'' is one of the genera in the family Glomeraceae, in the division Glomeromycota. Some members of the genus were originally described as ''Sclerocystis'' species, but this genus has been entirely transferred to ''Glomus''. However, further taxonomic changes are likely as the phylogeny of AM fungi becomes better understood. ''Glomus'' is likely related to the fossil fungus '' Glomites'', discovered in the Rhynie chert deposits from the Early Devonian (400 million years ago). Ecology As with other AM fungi, all ''Glomus'' species are thought to be obligate symbionts, dependent on their mycorrhizal association with plant roots to complete their life cycle. They cannot be cultured in the laboratory i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glomus Tumor
:''Glomus tumor was also the name formerly (and incorrectly) used for a tumor now called a paraganglioma.'' A glomus tumor (also known as a "solitary glomus tumor," "solid glomus tumor,") is a rare neoplasm arising from the glomus body and mainly found under the nail, on the fingertip or in the foot.Freedberg, et al. (2003). ''Fitzpatrick's Dermatology in General Medicine''. (6th ed.). McGraw-Hill. . They account for less than 2% of all soft tissue tumors. The majority of glomus tumors are benign, but they can also show malignant features. Glomus tumors were first described by Hoyer in 1877 while the first complete clinical description was given by Masson in 1924. Histologically, glomus tumors are made up of an afferent arteriole, anastomotic vessel, and collecting venule. Glomus tumors are modified smooth muscle cells that control the thermoregulatory function of dermal glomus bodies. As stated above, these lesions should not be confused with paragangliomas, which were formerly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coccygeal Glomus
The coccygeal glomus (coccygeal gland or body; Luschka’s gland) is a vestigial structure placed in front of, or immediately below, the tip of the coccyx. Anatomy It is about 2.5 mm. in diameter and is irregularly oval in shape; several smaller nodules are found around or near the main mass. It consists of irregular masses of round or polyhedral cells epitheloid cells, which are grouped around a dilated sinusoidal capillary vessel. Each cell contains a large round or oval nucleus, the protoplasm surrounding which is clear, and is not stained by chromic salts. Since it is not stained by chromic salts, it is not truly a part of Chromafin system; viz. the system which includes cells stained by chromic salts, consisting of renal medulla, para ganglia, and para aortic bodies. It is situated near the ganglion impar in pelvis, and also at the termination of median sacral artery. Clinical significance It may appear similar to a glomus tumor :''Glomus tumor was also the name f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carotid Body
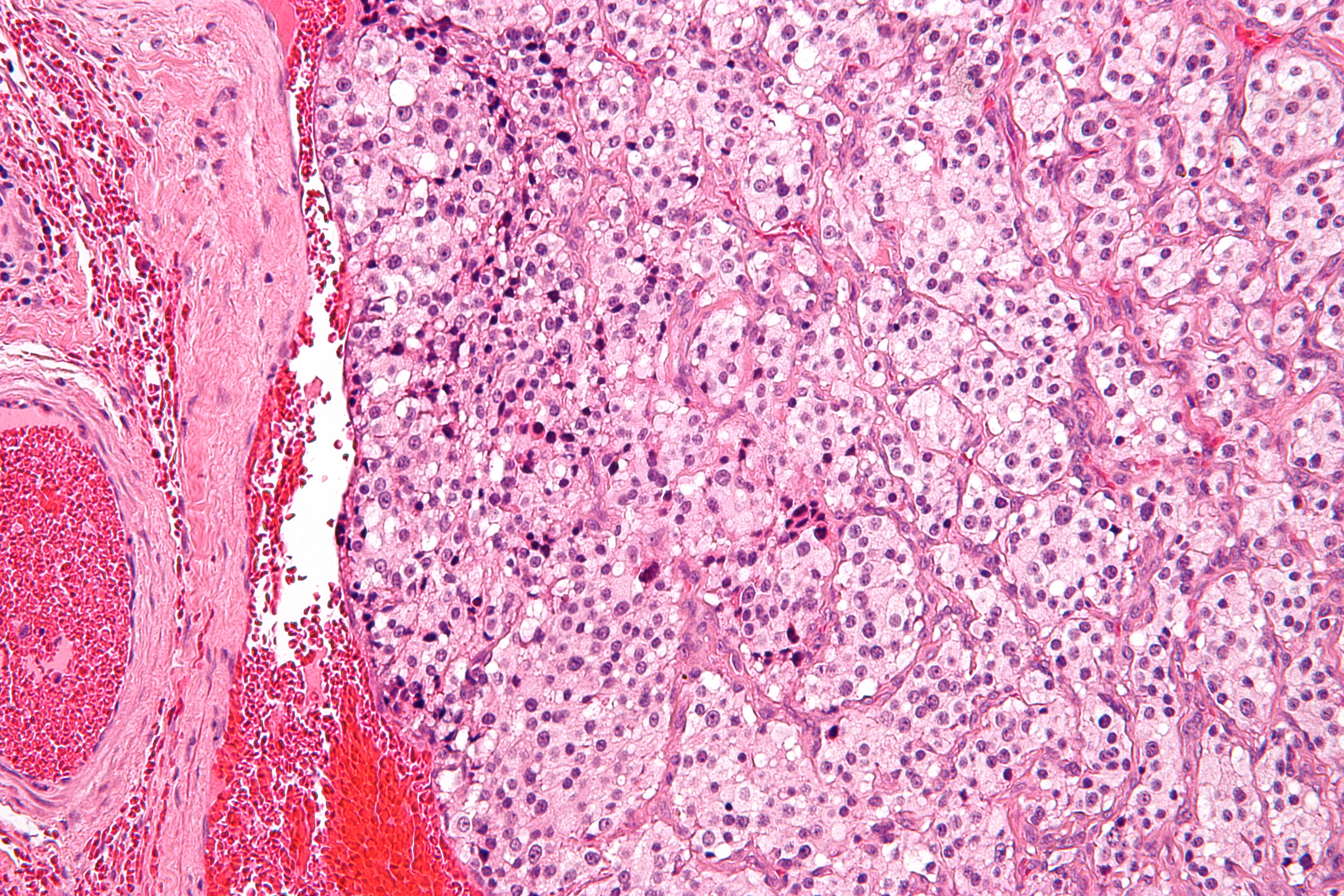
The carotid body is a small cluster of chemoreceptor cells, and supporting sustentacular cells. The carotid body is located in the adventitia, in the bifurcation (fork) of the common carotid artery, which runs along both sides of the neck. The carotid body detects changes in the composition of arterial blood flowing through it, mainly the partial pressure of arterial oxygen, but also of carbon dioxide. It is also sensitive to changes in blood pH, and temperature. Structure The carotid body is made up of two types of cells, called glomus cells: glomus type I cells are peripheral chemoreceptors, and glomus type II cells are sustentacular supportive cells. * Glomus type I cells are derived from the neural crest. They release a variety of neurotransmitters, including acetylcholine, ATP, and dopamine that trigger EPSPs in synapsed neurons leading to the respiratory center. They are innervated by axons of the glossopharyngeal nerve which collectively are called the carotid sinus ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glomus Cell
Glomus cells are the cell type mainly located in the carotid bodies and aortic bodies. Glomus type I cells are peripheral chemoreceptors which sense the oxygen, carbon dioxide and pH levels of the blood. When there is a decrease in the blood's pH, a decrease in oxygen (pO2), or an increase in carbon dioxide ( pCO2), the carotid bodies and the aortic bodies signal the dorsal respiratory group in the medulla oblongata to increase the volume and rate of breathing. The glomus cells have a high metabolic rate and good blood perfusion and thus are sensitive to changes in arterial blood gas tension. Glomus type II cells are sustentacular cells having a similar supportive function to glial cells. Structure The signalling within the chemoreceptors is thought to be mediated by the release of neurotransmitters by the glomus cells, including dopamine, noradrenaline, acetylcholine, substance P, vasoactive intestinal peptide and enkephalins. Vasopressin has been found to inhibit the response ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |