|
Glenn Cunningham (Nebraska Politician)
Glenn Clarence Cunningham (September 10, 1912 – December 18, 2003) was an American Republican politician. He was born in Omaha, Nebraska on September 10, 1912 and graduated from the University of Nebraska at Omaha in 1935. He sold insurance for a while. From 1946 to 1948 he was a member of the Omaha board of education and a member of Omaha city council from 1947 to 1948. He was elected Mayor of Omaha from 1949 to 1954. He was a delegate to the 1948 Republican National Convention and to the 1952 Republican National Convention. He was elected as a Republican to the Eighty-fifth United States Congress and to the six succeeding Congresses serving from January 3, 1957 to January 3, 1971. Cunningham voted in favor of the Civil Rights Acts of 1957, 1960, 1964, and 1968, and the Voting Rights Act of 1965, but did not vote on the 24th Amendment to the U.S. Constitution. He lost his bid for renomination to the Ninety-second United States Congress in 1970 to then Douglas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nebraska
Nebraska () is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States. It is bordered by South Dakota to the north; Iowa to the east and Missouri to the southeast, both across the Missouri River; Kansas to the south; Colorado to the southwest; and Wyoming to the west. It is the only triply landlocked U.S. state. Indigenous peoples, including Omaha, Missouria, Ponca, Pawnee, Otoe, and various branches of the Lakota ( Sioux) tribes, lived in the region for thousands of years before European exploration. The state is crossed by many historic trails, including that of the Lewis and Clark Expedition. Nebraska's area is just over with a population of over 1.9 million. Its capital is Lincoln, and its largest city is Omaha, which is on the Missouri River. Nebraska was admitted into the United States in 1867, two years after the end of the American Civil War. The Nebraska Legislature is unlike any other American legislature in that it is unicameral, and its members are elected ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Civil Rights Act Of 1957
The Civil Rights Act of 1957 was the first federal civil rights legislation passed by the United States Congress since the Civil Rights Act of 1875. The bill was passed by the 85th United States Congress and signed into law by President Dwight D. Eisenhower on September 9, 1957. The Supreme Court of the United States, Supreme Court's 1954 ruling in the case of ''Brown v. Board of Education'' brought the issue of school desegregation to the fore of public attention, as Southern Democratic leaders began a campaign of "massive resistance" against desegregation. In the midst of this campaign, President Eisenhower proposed a civil rights bill designed to provide federal protection for African Americans, African American voting rights; most African Americans in the Southern United States had been Disenfranchisement after the Reconstruction Era, disenfranchised by state and local laws. Though the civil rights bill passed Congress, opponents of the act were able to remove or weaken se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Congressional Delegations From Nebraska
These are tables of congressional delegations from Nebraska to the United States House of Representatives and the United States Senate. The current dean of the Nebraska delegation is Representative Adrian Smith (NE-3), having served in the House since 2007. U.S. House of Representatives Current members List of members, their terms in office, district boundaries, and the district political ratings according to the CPVI. The delegation has 3 members, all Republicans. Delegate from Nebraska Territory 1867–1883: One seat 1883–1893: Three seats 1893–1933: Six seats 1933–1943: Five seats 1943–1963: Four seats 1963–present: Three seats U.S. Senate Key See also *List of United States congressional districts *Nebraska's congressional districts * Political party strength in Nebraska References {{U.S. congressional delegations Nebraska Nebraska () is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Congress
The United States Congress is the legislature of the federal government of the United States. It is bicameral, composed of a lower body, the House of Representatives, and an upper body, the Senate. It meets in the U.S. Capitol in Washington, D.C. Senators and representatives are chosen through direct election, though vacancies in the Senate may be filled by a governor's appointment. Congress has 535 voting members: 100 senators and 435 representatives. The U.S. vice president has a vote in the Senate only when senators are evenly divided. The House of Representatives has six non-voting members. The sitting of a Congress is for a two-year term, at present, beginning every other January. Elections are held every even-numbered year on Election Day. The members of the House of Representatives are elected for the two-year term of a Congress. The Reapportionment Act of 1929 establishes that there be 435 representatives and the Uniform Congressional Redistricting Act requires ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biographical Directory Of The United States Congress
The ''Biographical Directory of the United States Congress'' (Bioguide) is a biographical dictionary of all present and former members of the United States Congress and its predecessor, the Continental Congress. Also included are Delegates from territories and the District of Columbia and Resident Commissioners from the Philippines and Puerto Rico. The online edition has a guide to the research collections of institutions where member's papers, letters, correspondence, and other items are archived, as well as an extended bibliography of published works concerning the member (a shorter bibliography is included with the member's biography). These additional resources, when available, can be accessed via links at the left side of the member's page on the website. History Charles Lanman, author, journalist, and former secretary to Daniel Webster, gathered the first collection of biographies of former and sitting members of Congress for his ''Dictionary of Congress'', published by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Political Graveyard
The Political Graveyard is a website and database that catalogues information on more than 277,000 American political figures and political families, along with other information. The name comes from the website's inclusion of burial locations of the deceased (when known). It is also a pun; where bodies are buried can refer to the politicians accused of crimes or touched by scandal. History The site was created in 1996 by Lawrence Kestenbaum, then an academic specialist at Michigan State University, and later on staff at the University of Michigan. Kestenbaum was formerly a county commissioner, and in 2004 was elected to be County Clerk/Register of Deeds of Washtenaw County, Michigan. The site and its underlying database were developed from a personal interest triggered by the ''Biographical Directory of the U.S. Congress'', which was its original data source. Since then his personal research, and the information contributions of hundreds of volunteers have greatly expanded the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glenn Cunningham Lake
Glenn Cunningham Lake is a reservoir located in Omaha, Nebraska, United States. The lake is located along 96th Street with entrances at State Highway 36, State Street, 96th Street and Rainwood Road. The lake is a part of Little Papillion Creek, which is part of the Papillion Creek watershed. Glenn Cunningham Lake, named for former Omaha mayor and U.S. Congressman Glenn C. Cunningham, is located in north central Omaha. The lake project was constructed by the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers for flood control and recreation and opened to the public in 1977. The lake has a surface area and a maximum depth of approximately 23 ft (7 m). More than of parkland surround the lake, including , north of Nebraska Highway 36 Nebraska Highway 36 is a highway in Nebraska. Its western terminus is southwest of U.S. Highway 275 near Fremont, and its eastern terminus is at U.S. Highway 75 in Omaha. Route description Nebraska Highway 36 begins in far northwestern Dougla ..., designated as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pi Kappa Alpha
Pi Kappa Alpha (), commonly known as PIKE, is a college fraternity founded at the University of Virginia in 1868. The fraternity has over 225 chapters and colonies across the United States and abroad with over 15,500 undergraduate members over 300,000 lifetime initiates. History Pi Kappa Alpha was founded on March 1, 1868, in Room 47 in West Range ( The Range) at the University of Virginia by six graduate students: Three of the Founders had been former cadets, having served on both sides of the recently concluded Civil War. One had been a Union hospital officer, another a Confederate veteran, and a third, a repatriate. Expansion was considered early in the fraternity's history; on March 1, 1869, exactly one year after the ''Alpha chapter'' at the University of Virginia was formed, the ''Beta chapter'' of Pi Kappa Alpha was founded at Davidson College. Its ''Gamma chapter'' was placed at William and Mary just two years later, and a total of seven chapters formed in the first d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Episcopal Church In The United States Of America
The Episcopal Church, based in the United States with additional dioceses elsewhere, is a member church of the worldwide Anglican Communion. It is a mainline Protestant denomination and is divided into nine provinces. The presiding bishop of the Episcopal Church is Michael Bruce Curry, the first African-American bishop to serve in that position. As of 2022, the Episcopal Church had 1,678,157 members, of whom the majority were in the United States. it was the nation's 14th largest denomination. Note: The number of members given here is the total number of baptized members in 2012 (cf. Baptized Members by Province and Diocese 2002–2013). Pew Research estimated that 1.2 percent of the adult population in the United States, or 3 million people, self-identify as mainline Episcopalians. The church has recorded a regular decline in membership and Sunday attendance since the 1960s, particularly in the Northeast and Upper Midwest. The church was organized after the Americ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ninety-second United States Congress
The 92nd United States Congress was a meeting of the legislative branch of the United States federal government, composed of the United States Senate and the United States House of Representatives. It met in Washington, DC from January 3, 1971, to January 3, 1973, during the third and fourth years of Richard Nixon's presidency. The apportionment of seats in this House of Representatives was based on the 1960 Census. Both chambers maintained a Democratic majority. Major events Passing legislation on revenue-sharing was a key event of the congress. President President most commonly refers to: *President (corporate title) *President (education), a leader of a college or university *President (government title) President may also refer to: Automobiles * Nissan President, a 1966–2010 Japanese ful ... Richard Nixon had it listed on his list of top policies to cover for the year. Nixon signed the bill into law at Independence Hall in Philadelphia. The law gained support ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
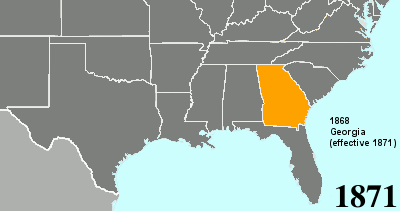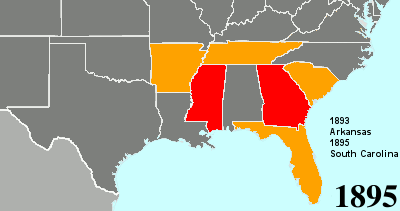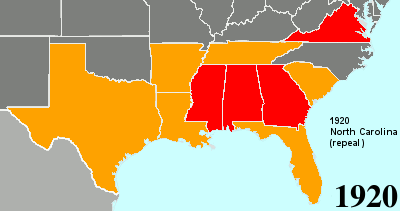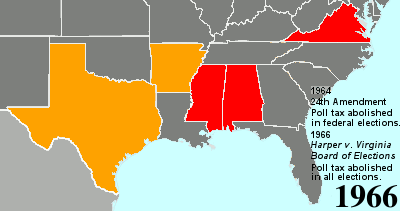
Twenty-fourth Amendment To The United States Constitution
The Twenty-fourth Amendment (Amendment XXIV) of the United States Constitution prohibits both Congress and the states from conditioning the right to vote in federal elections on payment of a poll tax or other types of tax. The amendment was proposed by Congress to the states on August 27, 1962, and was ratified by the states on January 23, 1964. Southern states of the former Confederate States of America adopted poll taxes in laws of the late 19th century and new constitutions from 1890 to 1908, after the Democratic Party had generally regained control of state legislatures decades after the end of Reconstruction, as a measure to prevent African Americans and often poor whites (and following passage of the Nineteenth Amendment, women) from voting. Use of the poll taxes by states was held to be constitutional by the Supreme Court of the United States in the 1937 decision ''Breedlove v. Suttles''. When the 24th Amendment was ratified in 1964, five states still retained a po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voting Rights Act Of 1965
The Voting Rights Act of 1965 is a landmark piece of federal legislation in the United States that prohibits racial discrimination in voting. It was signed into law by President Lyndon B. Johnson during the height of the civil rights movement on August 6, 1965, and Congress later amended the Act five times to expand its protections. Designed to enforce the voting rights guaranteed by the Fourteenth and Fifteenth Amendments to the United States Constitution, the Act sought to secure the right to vote for racial minorities throughout the country, especially in the South. According to the U.S. Department of Justice, the Act is considered to be the most effective piece of federal civil rights legislation ever enacted in the country. It is also "one of the most far-reaching pieces of civil rights legislation in U.S. history." The act contains numerous provisions that regulate elections. The act's "general provisions" provide nationwide protections for voting rights. Section 2 is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |