|
Glazkov Culture
Glazkov culture is an archaeological culture of possibly proto-Tunguses, Tungusic tribes in the Bronze Age (18th-13th centuries BCE), spread in the Baikal area. The Glazkov culture came to Siberia from the south, displacing Yukaghir people, Yukagir tribes. Glazkovs is a conditional name for the group of the ancient tribes inhabiting Siberia in the 2nd millennium BCE (Glazkov time) the headwaters of Angara river.Gumilev L.N., ''"History of Hun People"'', Moscow, 'Science', Ch.2, http://gumilevica.kulichki.net/HPH/hph02.htm (In Russian) Glazkov culture is named after a suburb of the city Irkutsk, where it was first found. Areal Archeologists distinguish in the 2nd millennium BCE Southern Siberia two synchronous independent cultures: Glazkov in the east and the Andronovo culture in the west. "In the Baikal territory lived a Glazkov group of related tribes, most likely the ancestors of modern Evenks, Evens or Yukagirs. Their culture was very close to the culture of the inhabitants ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeological Culture
An archaeological culture is a recurring assemblage of types of artifacts, buildings and monuments from a specific period and region that may constitute the material culture remains of a particular past human society. The connection between these types is an empirical observation, but their interpretation in terms of ethnic or political groups is based on archaeologists' understanding and interpretation and is in many cases subject to long-unresolved debates. The concept of the archaeological culture is fundamental to culture-historical archaeology. Concept Different cultural groups have material culture items that differ both functionally and aesthetically due to varying cultural and social practices. This notion is observably true on the broadest scales. For example, the equipment associated with the brewing of tea varies greatly across the world. Social relations to material culture often include notions of identity and status. Advocates of culture-historical archaeology u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Divaricate
Divaricate means branching, or having separation or a degree of separation. The angle between branches is wide. In botany In botany, the term is often used to describe the branching pattern of plants. Plants are said to be divaricating when their growth form is such that each internode diverges widely from the previous internode producing an often tightly interlaced shrub or small tree. Of the 72 small leaved shrubs found on the Banks Peninsula, for example, some 38 are divaricating. In medicine See also * Diastasis (pathology), a medical term for separation of parts * Laciniate The following is a list of terms which are used to describe leaf plant morphology, morphology in the description and taxonomy (biology), taxonomy of plants. Leaves may be simple (a single leaf blade or lamina) or compound (with several leaflet (bo ... References Plant morphology Medical terminology {{botany-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Russia
The history of Russia begins with the histories of the East Slavs. The traditional start-date of specifically Russian history is the establishment of the Rus' people, Rus' state in the north in 862, ruled by Varangians. Staraya Ladoga and Veliky Novgorod, Novgorod became the first major cities of the new union of immigrants from Scandinavia with the Slavs and Finnic peoples, Finns. In 882, Prince Oleg of Novgorod seized Kiev, thereby uniting the northern and southern lands of the Eastern Slavs under one authority, moving the governance center to Kiev by the end of the 10th century, and maintaining northern and southern parts with significant autonomy from each other. The state Christianization of Kievan Rus', adopted Christianity from the Byzantine Empire in 988, beginning the synthesis of Byzantine Empire, Byzantine and Slavs, Slavic cultures that defined Russia, Russian culture for the next millennium. Kievan Rus' ultimately disintegrated as a state due to the Mongol invasion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Mongolia
Various nomadic empires, including the Xiongnu (3rd century BC–1st century AD), the Xianbei state ( AD 93–234), the Rouran Khaganate (330–555), the First Turkic Khaganate, First (552–603) and Second Turkic Khaganates (682–744) and others, ruled the area of present-day Mongolia. The Khitan people, who used a para-Mongolic language, founded an empire known as the Liao dynasty (916–1125), and ruled Mongolia and portions of North China, northern Korea, and the present-day Russian Far East. In 1206, Genghis Khan was able to unite the Mongols, Mongol tribes, forging them into a fighting force which went on to establish the largest contiguous empire in world history, the Mongol Empire (1206–1368). After the Division of the Mongol Empire, fragmentation of the Mongol Empire, Mongolia came to be ruled by the Yuan dynasty (1271–1368) based in Khanbaliq (modern Beijing) and administered as part of the Mongolia under Yuan rule, Lingbei Province. Buddhism in Mongolia began wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Kyrgyzstan
The history of the Kyrgyz people and the land now called Kyrgyzstan goes back more than 3,000 years. Although geographically isolated by its mountainous location, it had an important role as part of the historical Silk Road trade route. Turkic nomads, who trace their ancestry to many Turkic states such as the First and Second Turkic Khaganates, have inhabited the country throughout its history. In the 13th century, Kyrgyzstan was conquered by the Mongols; subsequently it regained independence but was invaded by Kalmyks, Manchus, and Uzbeks. In 1876, it became part of the Russian Empire, remaining in the USSR as the Kirghiz Soviet Socialist Republic after the Russian Revolution. Following Mikhael Gorbachev's democratic reforms in the USSR, in 1990 pro-independence candidate Askar Akayev was elected president of the SSR. On 31 August 1991, Kyrgyzstan declared independence from Moscow, and a democratic government was subsequently established. Early history Stone implements f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, the largest country fully within the Eurasian Steppe, has been a historical crossroads and home to numerous different peoples, states and empires throughout history. Throughout history, peoples on the territory of modern Kazakhstan had nomadic lifestyle, which developed and influenced Kazakh culture. Human activity in the region began with the extinct ''Pithecanthropus'' and '' Sinanthropus'' one million–800,000 years ago in the Karatau Mountains and the Caspian and Balkhash areas. Neanderthals were present from 140,000 to 40,000 years ago in the Karatau Mountains and central Kazakhstan. Modern ''Homo sapiens'' appeared from 40,000 to 12,000 years ago in southern, central and eastern Kazakhstan. After the end of the last glacial period (12,500 to 5,000 years ago) human settlement spread across the country and led to the extinction of the mammoth and the woolly rhinoceros. Hunter-gatherer communes invented bows and boats and used domesticated wolves and traps ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of China
The earliest known written records of the history of China date from as early as 1250 BC, from the Shang dynasty (c. 1600–1046 BC), during the reign of king Wu Ding. Ancient historical texts such as the '' Book of Documents'' (early chapters, 11th century BC), the '' Bamboo Annals'' (c. 296 BC) and the ''Records of the Grand Historian'' (c. 91 BC) describe a Xia dynasty before the Shang, but no writing is known from the period, and Shang writings do not indicate the existence of the Xia. The Shang ruled in the Yellow River valley, which is commonly held to be the cradle of Chinese civilization. However, Neolithic civilizations originated at various cultural centers along both the Yellow River and Yangtze River. These Yellow River and Yangtze civilizations arose millennia before the Shang. With thousands of years of continuous history, China is among the world's oldest civilizations and is regarded as one of the cradles of civilization. The Zhou dynasty (1046–256 BC) supp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexey Okladnikov
Alexey Pavlovich Okladnikov (russian: Алексе́й Па́влович Окла́дников; 1908–1981) was a Soviet archaeologist, historian, and ethnographer, an expert in the ancient cultures of Siberia and the Pacific Basin. He was elected a full member of the Academy of Sciences of the USSR in 1968, and awarded the honorary title of the Hero of Socialist Labor (1978). The childhood of the scientist took place in Biryulka village in Siberia. In 1938–1961, Okladnikov worked in the Leningrad Division of the Archeology Institute of the USSR Academy of Sciences. Since 1961 Head of the Division of Human Research of the Economics Institute, Siberian Division of the USSR Academy of Sciences. Since 1966 Director of the Institute of History, Philology and Philosophy, Siberian Division of the USSR Academy of Sciences. Since 1962, Professor and Head, Department of History, of Novosibirsk State University. His works include research on ancient history of Siberia, Far East, Mon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haplogroup N (Y-DNA)
Haplogroup N (M231) is a Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup defined by the presence of the single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) marker M231. It is most commonly found in males originating from northern Eurasia. It also has been observed at lower frequencies in populations native to other regions, including parts of the Balkans, Central Asia, East Asia, and Southeast Asia. Origins Haplogroup NO-M214 – its most recent common ancestor with its sibling, haplogroup O-M175 – is estimated to have existed about 36,800–44,700 years ago.YFull Haplogroup YTree v6.05.11 at 25 September 2018. It is generally considered that N-M231 arose in approximately 19,400 (±4,80 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haplogroup Q (Y-DNA)
Haplogroup Q or Q-M242 is a Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup. It has one primary subclade, Haplogroup Q1 (L232/S432), which includes numerous subclades that have been sampled and identified in males among modern populations. Q-M242 is the predominant Y-DNA haplogroup among Native Americans and several peoples of Central Asia and Northern Siberia. Origins Haplogroup Q-M242 is one of the two branches of P1-M45, the other being R-M207. P1, as well as R* and Q* were observed among Ancient North Eurasians, a deeply European hunter-gatherer related population. Q-M242 is believed to have arisen around the Altai Mountains area (or South Central Siberia), approximately 17,000 to 31,700 years ago. However, the matter remains unclear due to limited sample sizes and changing definitions of Haplogroup Q: early definitions used a combination of the SNPs M242, P36.2, and MEH2 as defining mutations. Technical specification of mutation The polymorphism, “M242”, is a C→T transition resid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eurasia
Eurasia (, ) is the largest continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. Primarily in the Northern and Eastern Hemispheres, it spans from the British Isles and the Iberian Peninsula in the west to the Japanese archipelago and the Russian Far East to the east. The continental landmass is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean and Africa to the west, the Pacific Ocean to the east, the Arctic Ocean to the north, and by Africa, the Mediterranean Sea, and the Indian Ocean to the south. The division between Europe and Asia as two continents is a historical social construct, as many of their borders are over land; thus, in some parts of the world, Eurasia is recognized as the largest of the six, five, or four continents on Earth. In geology, Eurasia is often considered as a single rigid megablock. However, the rigidity of Eurasia is debated based on paleomagnetic data. Eurasia covers around , or around 36.2% of the Earth's total land area. It is also home to the largest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
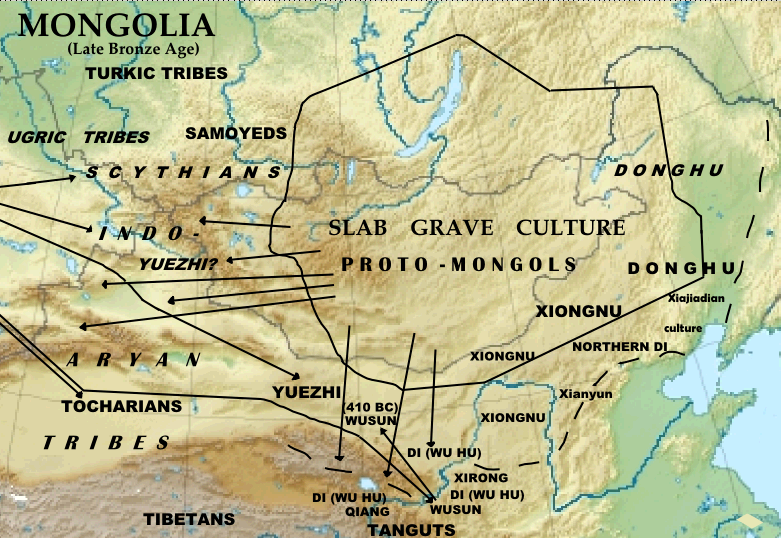
Slab Grave Culture
The Slab-Grave culture is an archaeological culture of the Late Bronze Age and Early Iron Age Mongols.Tumen D., "Anthropology of Archaeological Populations from Northeast Asipage 25,27 The ethnogenesis of modern Mongolian people is linked to the Slab-Grave culture by historical and archaeological evidence, and genetic research also links modern Mongolians to the Slab Grave culture. According to various sources, it is dated from 1,300 to 300 BC. The Slab-Grave culture became an eastern wing of a huge nomadic Eurasian world, which saw the emergence and hybridization of various cultures, such as Scythians and the Xiongnu. The anthropological type of the population is predominantly Mongoloid, while the western newcomers from the area of Tuva and north-western Mongolia were Caucasoids. "History of Buratia Cultu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |