|
Gift Aid
Gift Aid is a UK tax incentive that enables tax-effective giving by individuals to charities in the United Kingdom. Gift Aid was introduced in the Finance Act 1990 for donations given after 1 October 1990, but was originally limited to cash gifts of £600 or more. This threshold was successively reduced in April 2000 when the policy was substantially revised and the minimum donation limit removed entirely. A similar policy applies to charitable donations by companies that are subject to the UK corporation tax. Gift Aid was originally intended for cash donations only. However, since 2006, HMRC compliant systems have been introduced to allow tax on the income earned by charity shops, acting as an agent for a donor, to be reclaimed. In order for the charity to operate effectively they will need HMRC-approved systems to be able to record and track the progress of each item from receipt to sale and confirm with the donor that the donation should still go ahead. In the financial year ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tax Incentive
A tax incentive is an aspect of a government's taxation policy designed to incentivize or encourage a particular economic activity by reducing tax payments. Tax incentives can have both positive and negative impacts on an economy. Among the positive benefits, if implemented and designed properly, tax incentives can attract investment to a country. Other benefits of tax incentives include increased employment, higher number of capital transfers, research and technology development, and also improvement to less developed areas. Though it is difficult to estimate the effects of tax incentives, they can, if done properly, raise the overall economic welfare through increasing economic growth and government tax revenue (after the expiration of the tax holiday/incentive period). However, tax incentive can cause negative effects on a government's financial condition, among other negative effects, if they are not properly designed and implemented. There are four typical costs to tax incen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charitable Organization
A charitable organization or charity is an organization whose primary objectives are philanthropy and social well-being (e.g. educational, Religion, religious or other activities serving the public interest or common good). The legal definition of a charitable organization (and of charity) varies between countries and in some instances regions of the country. The Charity regulators, regulation, the tax treatment, and the way in which charity law affects charitable organizations also vary. Charitable organizations may not use any of their funds to profit individual persons or entities. (However, some charitable organizations have come under scrutiny for spending a disproportionate amount of their income to pay the salaries of their leadership). Financial figures (e.g. tax refund, revenue from fundraising, revenue from sale of goods and services or revenue from investment) are indicators to assess the financial sustainability of a charity, especially to charity evaluators. This ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland. The United Kingdom includes the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland, and many smaller islands within the British Isles. Northern Ireland shares a land border with the Republic of Ireland; otherwise, the United Kingdom is surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean, the North Sea, the English Channel, the Celtic Sea and the Irish Sea. The total area of the United Kingdom is , with an estimated 2020 population of more than 67 million people. The United Kingdom has evolved from a series of annexations, unions and separations of constituent countries over several hundred years. The Treaty of Union between the Kingdom of England (which included Wales, annexed in 1542) and the Kingdom of Scotland in 170 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finance Act 1990
A Finance Act is the headline fiscal (budgetary) legislation enacted by the UK Parliament, containing multiple provisions as to taxes, duties, exemptions and reliefs at least once per year, and in particular setting out the principal tax rates for each fiscal year. Overview In the UK, the Chancellor of the Exchequer delivers a Budget speech on Budget Day, outlining changes in spending, as well as tax and duty. The changes to tax and duty are passed as law, and each year form the respective Finance Act. Additional Finance Acts are also common and are the result of a change in governing party due to a general election, a pressing loophole or defect in the law of taxation, or a backtrack with regard to government spending or taxation. However, a repeal order can also be made by statutory instrument. The rules governing the various taxation methods are contained within the relevant taxation acts. Capital Gains Tax legislation, for example, is contained within Taxation of Chargeabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
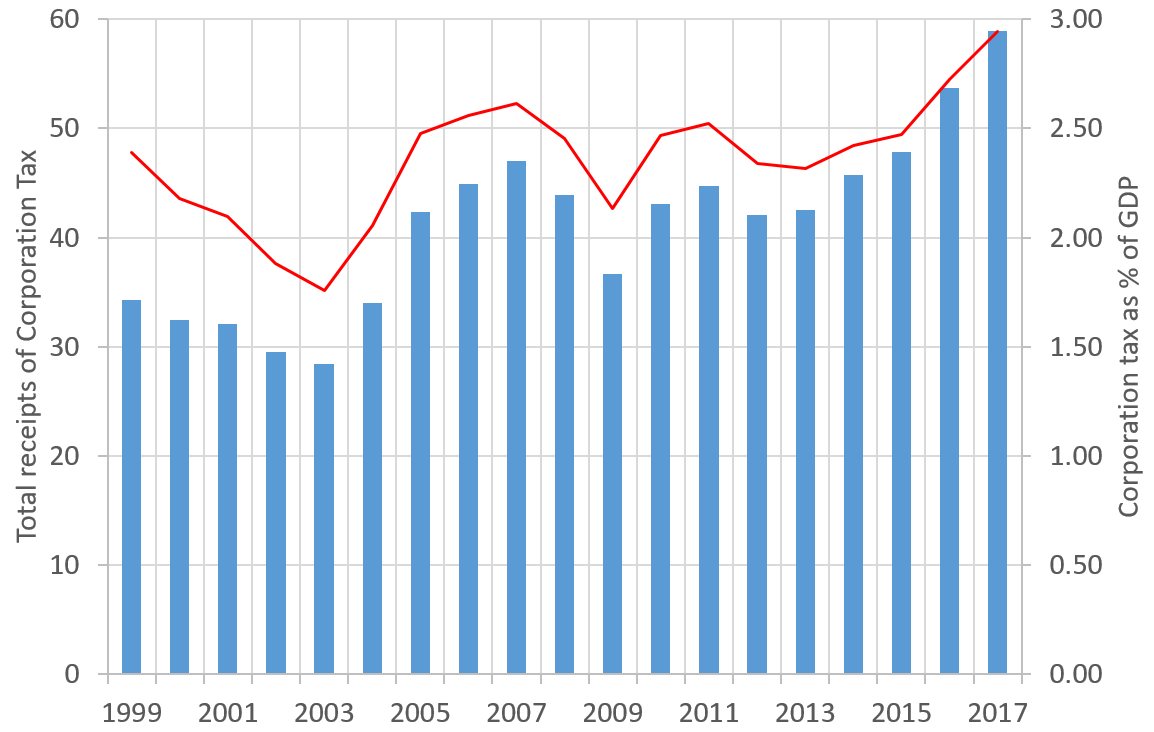
UK Corporation Tax
: ''Throughout this article, the term "pound" and the £ symbol refer to the Pound sterling.'' Corporation tax in the United Kingdom is a corporate tax levied in on the profits made by UK-resident companies and on the profits of entities registered overseas with permanent establishments in the UK. Until 1 April 1965, companies were taxed at the same income tax rates as individual taxpayers, with an additional profits tax levied on companies. Finance Act 1965 replaced this structure for companies and associations with a single corporate tax, which took its basic structure and rules from the income tax system. Since 1997, the UK's Tax Law Rewrite ProjectTax Law Rewrite , |
HMRC
, patch = , patchcaption = , logo = HM Revenue & Customs.svg , logocaption = , badge = , badgecaption = , flag = , flagcaption = , image_size = , commonname = , abbreviation = , motto = , formed = , preceding1 = Inland Revenue , preceding2 = HM Customs and Excise , dissolved = , superseding = , employees = 63,042 FTE , volunteers = , budget = (2018–2019) , country = United Kingdom , constitution1 = Commissioners for Revenue and Customs Act 2005 , speciality1 = customs , speciality2 = tax , headquarters = 100 Parliament Street, London, SW1A 2BQ , sworntype = , sworn = , unsworntype = , unsworn = , minister1name = Andrew Griffith MP , minister1pfo = Economic Secretary to the Treasury and mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finance Act 2010
The Finance Act 2010 is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom enacting the March 2010 United Kingdom Budget. The ''Chancellor of the Exchequer'' delivers the annual budget speech outlining changes in spending, tax, duty and other financial matters. However, in 2010 there was a second budget in June. The respective year's Finance Act is the mechanism to enact the changes. Levels of Excise Duties, Value Added Tax, Income Tax, Corporation Tax and Capital Gains Tax) are often modified. The rules governing the various taxation methods are contained within the relevant taxation acts. (For instance Capital Gains Tax Legislation is contained within Taxation of Chargeable Gains Act 1992). The Finance Act details amendments to be made to each one of these Acts. Provisions Charitable tax benefits (for example Gift Aid) were extended to charities A charitable organization or charity is an organization whose primary objectives are philanthropy and social well-being (e.g. educat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UK Income Tax
Taxation in the United Kingdom may involve payments to at least three different levels of government: central government ( HM Revenue & Customs), devolved governments and local government. Central government revenues come primarily from income tax, National Insurance contributions, value added tax, corporation tax and fuel duty. Local government revenues come primarily from grants from central government funds, business rates in England, Council Tax and increasingly from fees and charges such as those for on-street parking. In the fiscal year 2014–15, total government revenue was forecast to be £648 billion, or 37.7 per cent of GDP, with net taxes and National Insurance contributions standing at £606 billion. History A uniform Land tax, originally was introduced in England during the late 17th century, formed the main source of government revenue throughout the 18th century and the early 19th century. Stephen Dowell, ''History of Taxation and Taxes in England'' (Ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gross (economics)
A net (sometimes written nett) value is the resultant amount after accounting for the sum or difference of two or more variables. In economics, it is frequently used to imply the remaining value after accounting for a specific, commonly understood deduction. In these cases it is contrasted with the term gross, which refers to the pre-deduction value. For example, net income is the total income of a company after deducting its expenses—commonly known as profit—or the total income of an individual after deducting their income tax. Profit may be broken down further into pre-taxed or gross profit and profit after taxes or net profit. Similarly, an individual's net worth is the difference between their assets (what they own) and their liabilities (what they owe to others). Similarly, net investment in physical capital such as machinery equals gross (total) investment minus the dollar amount of replacement investment that offsets depreciation of pre-existing machinery, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tax Return (United Kingdom)
In the United Kingdom, a tax return is a document that must be filed with HM Revenue & Customs declaring liability for taxation. Different bodies must file different returns with respect to various forms of taxation. The main returns currently in use are: *SA100 for individuals paying income tax *SA800 for partnerships *SA900 for trusts and estates of deceased persons *CT600 for companies paying corporation tax *VAT100 for value added tax Income tax self-assessment Most employees paying tax under the PAYE system are not required to file a tax return, because the PAYE system operates to withhold the correct amount of tax from their wages or salaries. However, some tax payers, including employees, may have income that has not been taxed at source and needs to be declared to HMRC, usually by submitting a self assessment tax return. Legally, a tax payer is obliged to submit a tax return when HMRC request one by sending a notice to file a tax return, either because the tax payer has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Insurance
National Insurance (NI) is a fundamental component of the welfare state in the United Kingdom. It acts as a form of social security, since payment of NI contributions establishes entitlement to certain state benefits for workers and their families. Introduced by the National Insurance Act 1911 and expanded by the Labour government in 1948, the system has been subjected to numerous amendments in succeeding years. Initially, it was a contributory form of insurance against illness and unemployment, and eventually provided retirement pensions and other benefits. Currently, workers pay contributions from the age of 16 years, until the age they become eligible for the State pension. Contributions are due from employed people earning at or above a threshold called the Lower Earnings Limit, the value of which is reviewed each year. Self-employed people contribute partly through a fixed weekly or monthly payment and partly on a percentage of net profits above a threshold, which is revi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contactless Payment
Contactless payment systems are credit cards and debit cards, key fobs, smart cards, or other devices, including smartphones and other mobile devices, that use radio-frequency identification (RFID) or near-field communication (NFC, e.g. Samsung Pay, Apple Pay, Google Pay, Fitbit Pay, or any bank mobile application that supports contactless) for making secure payments. The embedded integrated circuit chip and antenna enable consumers to wave their card, fob, or handheld device over a reader at the point of sale terminal. Contactless payments are made in close physical proximity, unlike other types of mobile payments which use broad-area cellular or WiFi networks and do not involve close physical proximity. EMV is a common standard used by major credit card and smartphone companies for use in general commerce. Contactless smart cards that function as stored-value cards are becoming popular for use as transit system farecards, such as the Oyster card or RioCard. These can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)


