|
Ghior Upazila
Ghior ( bn, ঘিওর) is an upazila (sub-district) of Manikganj District of central Bangladesh, located in the Dhaka Division. It is located at and is named after the town of Ghior. It is home to the Tarra Bridge, an overpass above the Dhaleshwari River, which is one of the major bridges of the country. The 53 km R506 road is one of the main roads of Ghior connecting the upazila to Dhaka and Tangail. Md. Nazmul Islam, Upazila Nirbahi Officer is the present Executive Head of the Upazila. Geography Ghior Upazila has a total area of 145.95 km2. It is bounded by Daulatpur Upazila on the north, Manikganj Sadar on the east, Shivalaya & Harirampur Upazila on the south and Sibalay Upazila on the west. Annual average temperatures reach a maximum of 36 °C and a minimum of 12.7 °C with the annual rainfall total being 2,376 mm (93.5 in). The main rivers are the Dhaleshwari River, Kaliganga River, Gangdubi River and Ichamati River. Other water sources incl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upazilas Of Bangladesh
An ''upazila'' ( bn, উপজেলা, upôzela, lit=sub-district pronounced: ), formerly called ''thana'', is an administrative region in Bangladesh, functioning as a sub-unit of a district. It can be seen as an analogous to a county or a borough of Western countries. Rural upazilas are further administratively divided into union council areas (union parishads). Bangladesh ha495 upazilas(as of 20 Oct 2022). The upazilas are the second lowest tier of regional administration in Bangladesh. The administrative structure consists of divisions (8), districts (64), upazilas (495) and union parishads (UPs). This system of devolution was introduced by the former military ruler and president of Bangladesh, Lieutenant General Hossain Mohammad Ershad, in an attempt to strengthen local government. Below UPs, villages (''gram'') and ''para'' exist, but these have no administrative power and elected members. The Local Government Ordinance of 1982 was amended a year later, redesignatin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manikgonj Sadar Upazila
Manikgonj Sadar ( bn, মানিকগঞ্জ সদর) is an upazila of Manikgonj District in the division of Dhaka, Bangladesh. Geography Manikgonj Sadar is located at . It has a total area of 214.81 km2. Demographics According to the 2011 Bangladesh census, Manikganj Sadar Upazila had 71,202 households and a population of 309,413, 23.3% of whom lived in urban areas. 9.0% of the population was under the age of 5. The literacy rate (age 7 and over) was 56.0%, compared to the national average of 51.8%. Sports Manikganj Stadium is located by the Manikganj public library, Manikganj, Bangladesh. Administration Manikganj Sadar Upazila is divided into Manikganj Municipality and ten union parishads: Atigram, Bhararia, Betila-Mitra, Dighi Union, Garpara, Hatipara, Jagir, Krishnapur, Nabagram, Putail. The union parishads are subdivided into 270 mauzas and 315 villages. Manikganj Municipality is subdivided into 9 wards and 50 mahallas. Education Among the educational ins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bangladesh Liberation War
The Bangladesh Liberation War ( bn, মুক্তিযুদ্ধ, , also known as the Bangladesh War of Independence, or simply the Liberation War in Bangladesh) was a revolution and War, armed conflict sparked by the rise of the Bengali nationalism, Bengali nationalist and self-determination movement in East Pakistan, which resulted in the independence of Bangladesh. The war began when the Pakistani Military dictatorship, military junta based in West Pakistan—under the orders of Yahya Khan—launched Operation Searchlight against the people of East Pakistan on the night of 25 March 1971, initiating the 1971 Bangladesh genocide, Bangladesh genocide. In response to the violence, members of the Mukti Bahini—a guerrilla resistance movement formed by Bengali military, paramilitary and civilians—launched a mass Guerrilla warfare, guerrilla war against the Pakistani military, liberating numerous towns and cities in the initial months of the conflict. At first, the Pakis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcutta Gazette
''Calcutta Gazette'' was an English newspaper in Bengal founded by Francis Gladwin, a colonial officer, in 1784. It was one of the first newspapers in India. History The ''Calcutta Gazette'' was founded by Francis Gladwin, an officer in the British East India Company, and an orientalist. Its first issue was published on 4 March 1784. The newspaper became an important medium for the publication of public information. The ''Gazette'' initially charged the government for advertisements but stopped after the government provided the ''Gazette'' with free postal circulation and free postage. The government withdrew this in 1787. In January 1787, Francis Gladwin gave control of the company to Arthur Muir, Herbert H. Harrington and Edmond Morris. The three were civilians involved with the newspaper. In June 1815 the ''Government Gazette'' was created by the Bengal Military Orphan Society. All government advertisements were diverted to the ''Government Gazette'' from the ''Calcutta Gazett ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
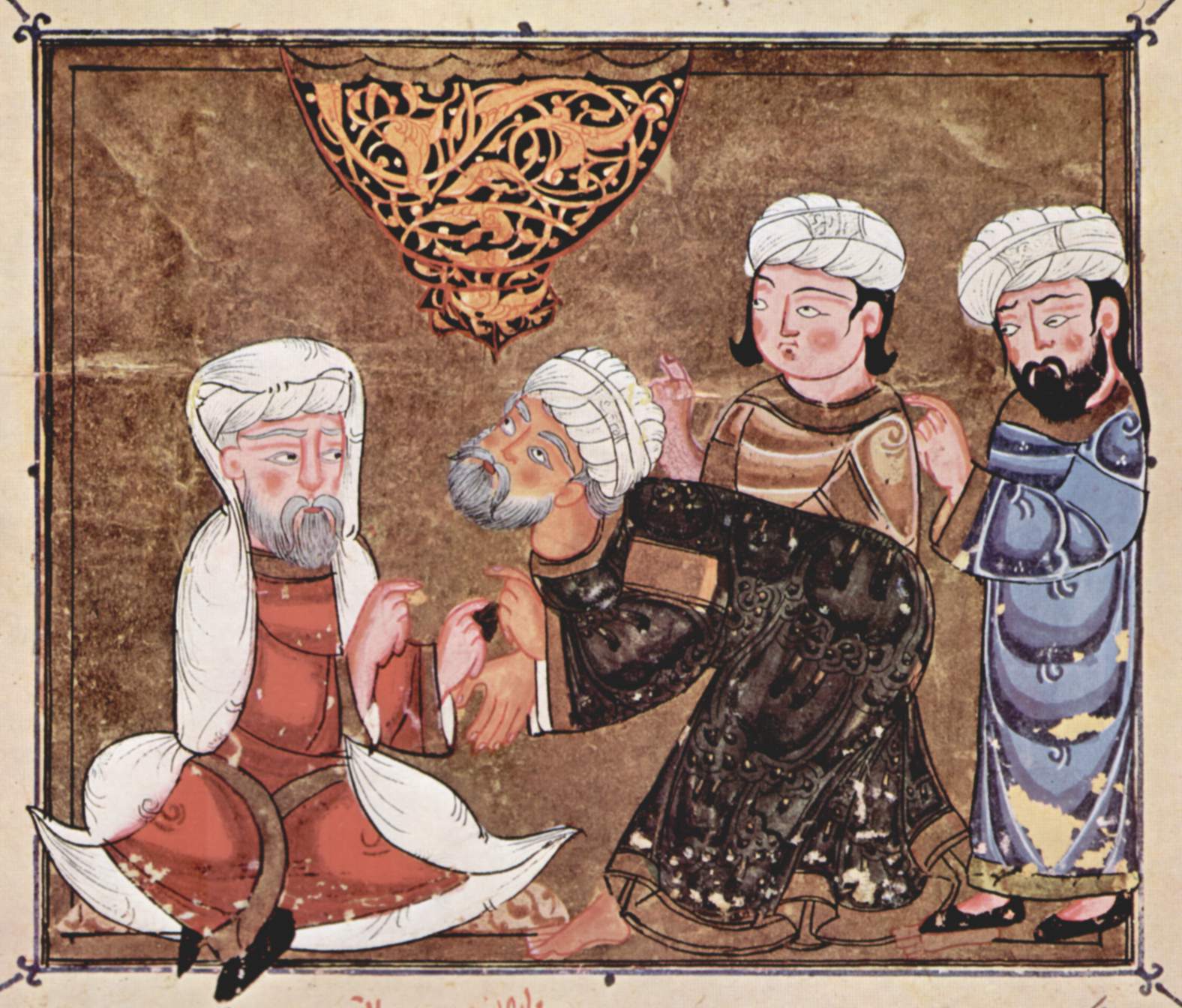
Qadi
A qāḍī ( ar, قاضي, Qāḍī; otherwise transliterated as qazi, cadi, kadi, or kazi) is the magistrate or judge of a '' sharīʿa'' court, who also exercises extrajudicial functions such as mediation, guardianship over orphans and minors, and supervision and auditing of public works. History The term ''qāḍī'' was in use from the time of Muhammad during the early history of Islam, and remained the term used for judges throughout Islamic history and the period of the caliphates. While the '' muftī'' and '' fuqaha'' played the role in elucidation of the principles of Islamic jurisprudence (''Uṣūl al-Fiqh'') and the Islamic law (''sharīʿa''), the ''qāḍī'' remained the key person ensuring the establishment of justice on the basis of these very laws and rules. Thus, the ''qāḍī'' was chosen from amongst those who had mastered the sciences of jurisprudence and law. The Abbasid caliphs created the office of "chief ''qāḍī''" (''qāḍī al-quḍāh''), who ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thana
Thana means "police station" in South Asian countries, and can also mean the district controlled by a police station. * Thanas of Bangladesh, former subdistricts in the administrative geography of Bangladesh; later renamed ''upazila'' * in (British) Indian history, a ''thana'' was a group of princely states deemed too small to perform all functions separately *Thane is a city named after the word ''thana'' (police station) because it was important for its barracks back in colonial era, it is located in Konkan division, a province of India *Thana Bhawan (), also known simply as Thana, is a town in Uttar Pradesh, India See also * * {{wikt-inline, thana * Tana (other) * Thaana Thaana, Taana or Tāna ( ) is the present writing system of the Maldivian language spoken in the Maldives. Thaana has characteristics of both an abugida (diacritic, vowel-killer strokes) and a true alphabet (all vowels are written), ..., also known as Tāna, the modern writing syste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indigo Dye
Indigo dye is an organic compound with a distinctive blue color. Historically, indigo was a natural dye extracted from the leaves of some plants of the ''Indigofera'' genus, in particular ''Indigofera tinctoria''; dye-bearing ''Indigofera'' plants were commonly grown and used throughout the world, in Asia in particular, as an important crop, with the production of indigo dyestuff economically important due to the previous rarity of some blue dyestuffs historically. Most indigo dye produced today is synthetic, constituting several thousand tons each year. It is most commonly associated with the production of denim cloth and blue jeans, where its properties allow for effects such as stone washing and acid washing to be applied quickly. Uses The primary use for indigo is as a dye for cotton yarn, mainly used in the production of denim cloth suitable for blue jeans; on average, a pair of blue jeans requires just to of dye. Smaller quantities are used in the dyeing of wool and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buddhist
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and gradually spread throughout much of Asia via the Silk Road. It is the world's fourth-largest religion, with over 520 million followers (Buddhists) who comprise seven percent of the global population. The Buddha taught the Middle Way, a path of spiritual development that avoids both extreme asceticism and hedonism. It aims at liberation from clinging and craving to things which are impermanent (), incapable of satisfying ('), and without a lasting essence (), ending the cycle of death and rebirth (). A summary of this path is expressed in the Noble Eightfold Path, a training of the mind with observance of Buddhist ethics and meditation. Other widely observed practices include: monasticism; " taking refuge" in the Buddha, the , and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
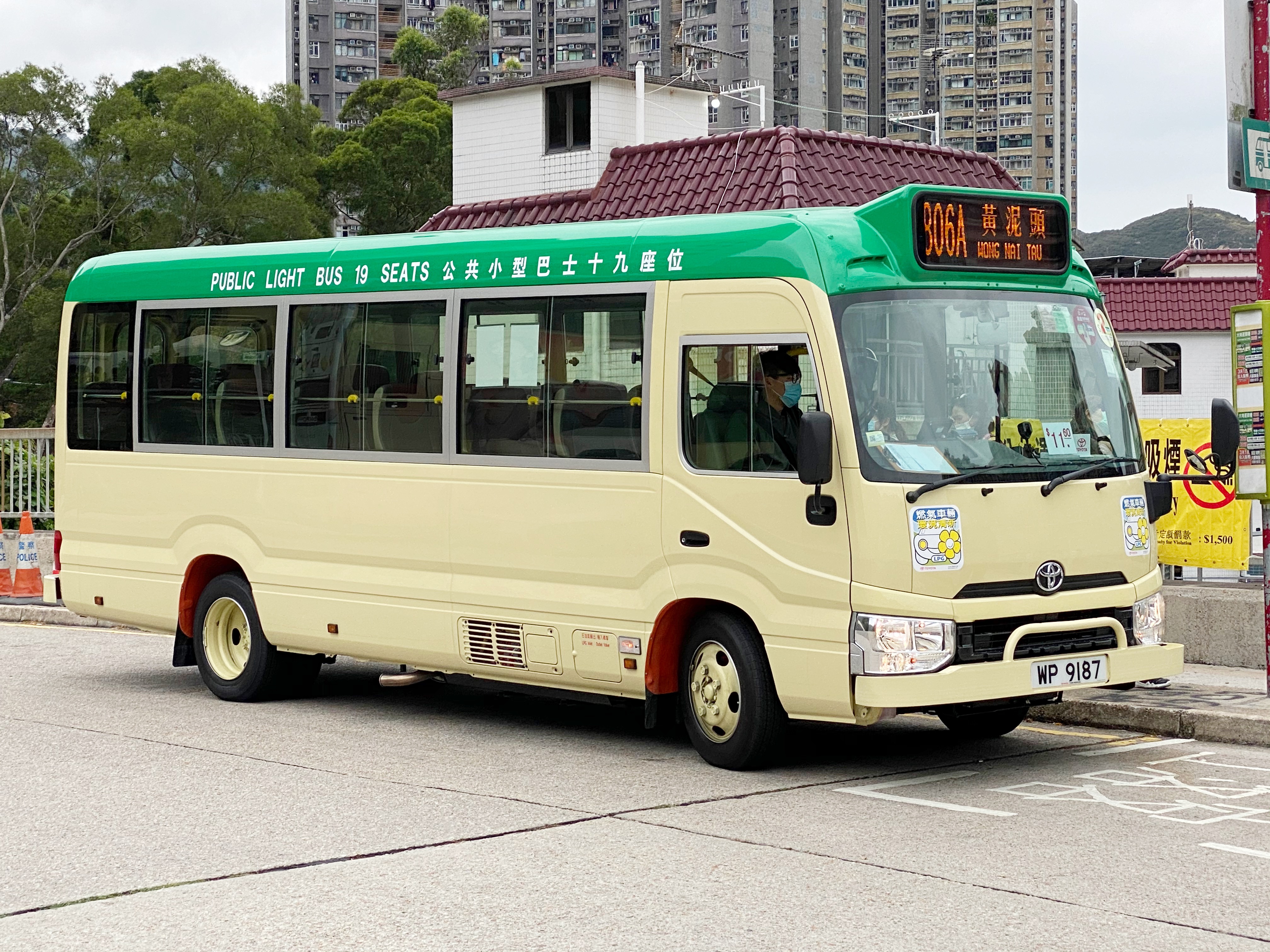
Microbus Wreckage - Dhaka-Cha-13-0302 - Mishuk Munier And Tareque Masud Memorial - University Of Dhaka Campus - Dhaka 2015-05-31 2493
A minibus, microbus, minicoach, or commuter (in Zimbabwe) is a passenger-carrying motor vehicle that is designed to carry more people than a multi-purpose vehicle or minivan, but fewer people than a full-size bus. In the United Kingdom, the word "minibus" is used to describe any full-sized passenger-carrying van or panel truck. Minibuses have a seating capacity of between 12 and 30 seats. Larger minibusses may be called midibuses. Minibuses are typically front engine step in vehicles, although low floor minibuses do exist and are particularly common in Japan. Minibuses may range in price from £2000 to nearly £100,000. History It is unknown when the first minibus vehicle was released but it is possible that the first one was the 1935-1955 Chevrolet Suburban or the Volkswagen Transporter, even though the Suburban is thought by most to be an SUV, the first generation to the third generation could have theoretically be classified as minibusses today. Usage Minibuses are used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beel
A beel (Bengali and Assamese: বিল) is a billabong or a lake-like wetland with static water (as opposed to moving water in rivers and canals - typically called in Bengali, in the Ganges - Brahmaputra flood plains of the Eastern Indian states of West Bengal, and Assam and in the country of Bangladesh. The term owes its origins to the word of the same pronunciation meaning "pond" and "lake" in the Bengali and Assamese languages. Formation Typically, beels are formed by inundation of low-lying lands during flooding, where some water gets trapped even after flood waters recede back from the flood plains. Beels may also be caused by filling up of low-lying areas during rains, especially during the monsoon season. There are different causes for the formation of beels. A string of beels is indicative of there being the remains of a great river that deserted its channel, moving to a new one elsewhere. Haor, baor In north eastern Bangladesh there are large water bodies called ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ichamati River
Ichamati River ( bn, ইছামতী নদী) (also spelt Ichhamati), is a trans-boundary river which flows through India and Bangladesh and also forms the boundary between the two countries. The river is facing the problem of siltation leading to thin flow of water in the dry season and floods in the rainy season. Experts are handling the situation and remedial matters are being discussed between the governments of India and Bangladesh. Ichamati flow Ichamati River is now in three parts: (1) The longer part flows from the Mathabhanga River, a distributary of the Padma, and after flowing for joins the Kalindi River near Hasnabad in North 24 Parganas and Debhata in Satkhira District. (2) Once the main river west of Dhaka and (3) Ichamati of Dinajpur. Rennel's map of 1764–66, shows the last two rivers as one. The second river marked above originates south of Jafarganj opposite to the mouth of the Hoorsagar near Nathpur factory and runs towards Joginighat in Munshigan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |