|
Gesalec
Gesalic (Gothic: ''*Gaisalaiks'', "dancing with spears"), ''Gesaleico'' in Spanish and Portuguese, ''Gesaleic'' in Catalan, ( – 513), was a king of the Visigoths from 507 to 511, and died in 513. Biography Although the illegitimate son of Alaric II, he had been elected king by the Visigoths after Alaric had been killed in battle by the Franks. Alaric's only legitimate son, Amalaric, was a child and too young to rule. Initially Gesalec was supported by the powerful Ostrogothic king Theodoric the Great, but this support eventually faded. Between 508 and 511, he had one important Visigothic noble executed - Goiaric.Peter Heather, ''The Goths'' (Oxford: Blackwell, 1996), p. 232 Gesalec's rule was dealt a decisive blow when the Burgundians, led by their king Gundobad, captured and plundered Narbonne, his capital. Gesalec fled to Barcelona, where he remained until Theodoric deposed him. Theodoric took over the rule of the Visigothic kingdom for the next 15 years, collecting its taxes a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amalaric
Amalaric ( got, *Amalareiks; Spanish and Portuguese: ''Amalarico''; 502–531) was king of the Visigoths from 522 until his death in battle in 531. He was a son of king Alaric II and his first wife Theodegotha, daughter of Theoderic the Great. Biography When Alaric II was killed while fighting Clovis I, king of the Franks, in the Battle of Vouillé (507), his kingdom fell into disarray. "More serious than the destruction of the Gothic army," writes Herwig Wolfram, "than the loss of both Aquitanian provinces and the capital of Toulose, was the death of the king." Alaric had made no provision for a successor, and although he had two sons, one was of age but illegitimate and the other, Amalaric, the offspring of a legal marriage but still a child. Amalaric was carried for safety into Spain, which country and Provence were thenceforth ruled by his maternal grandfather, Theodoric the Great, acting through his vice-regent, an Ostrogothic nobleman named Theudis. The older son, Gesalec, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alaric II
Alaric II ( got, 𐌰𐌻𐌰𐍂𐌴𐌹𐌺𐍃, , "ruler of all"; la, Alaricus; – August 507) was the King of the Visigoths from 484 until 507. He succeeded his father Euric as king of the Visigoths in Toulouse on 28 December 484; he was the great-grandson of the more famous Alaric I, who sacked Rome in 410. He established his capital at Aire-sur-l'Adour (''Vicus Julii'') in Aquitaine. His dominions included not only the majority of Hispania (excluding its northwestern corner) but also Gallia Aquitania and the greater part of an as-yet undivided Gallia Narbonensis. Reign Herwig Wolfram opens his chapter on the eighth Visigothic king, "Alaric's reign gets no full treatment in the sources, and the little they do contain is overshadowed by his death in the Battle of Vouillé and the downfall of the Toulosan kingdom."Wolfram, ''History of the Goths'', p. 191 One example is Isidore of Seville's account of Alaric's reign: consisting of a single paragraph, it is primarily ab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
513 Deaths
__NOTOC__ Year 513 ( DXIII) was a common year starting on Tuesday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Probus and Clementinus (or, less frequently, year 1266 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 513 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Europe * Revolt of Vitalian: Byzantine general Vitalian revolts against Emperor Anastasius I, and conquers a large part of the Diocese of Thrace. He gains the support of the local people, and assembles an army of 50,000–60,000 men. * Anastasius I reduces taxes in the provinces of Bithynia and Asia, to prevent them from joining the rebellion. Vitalian marches to Constantinople and encamps at the suburb of Hebdomon (modern Turkey). * Anastasius I sends an embassy under the former consul Patricius to start negotiations. V ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
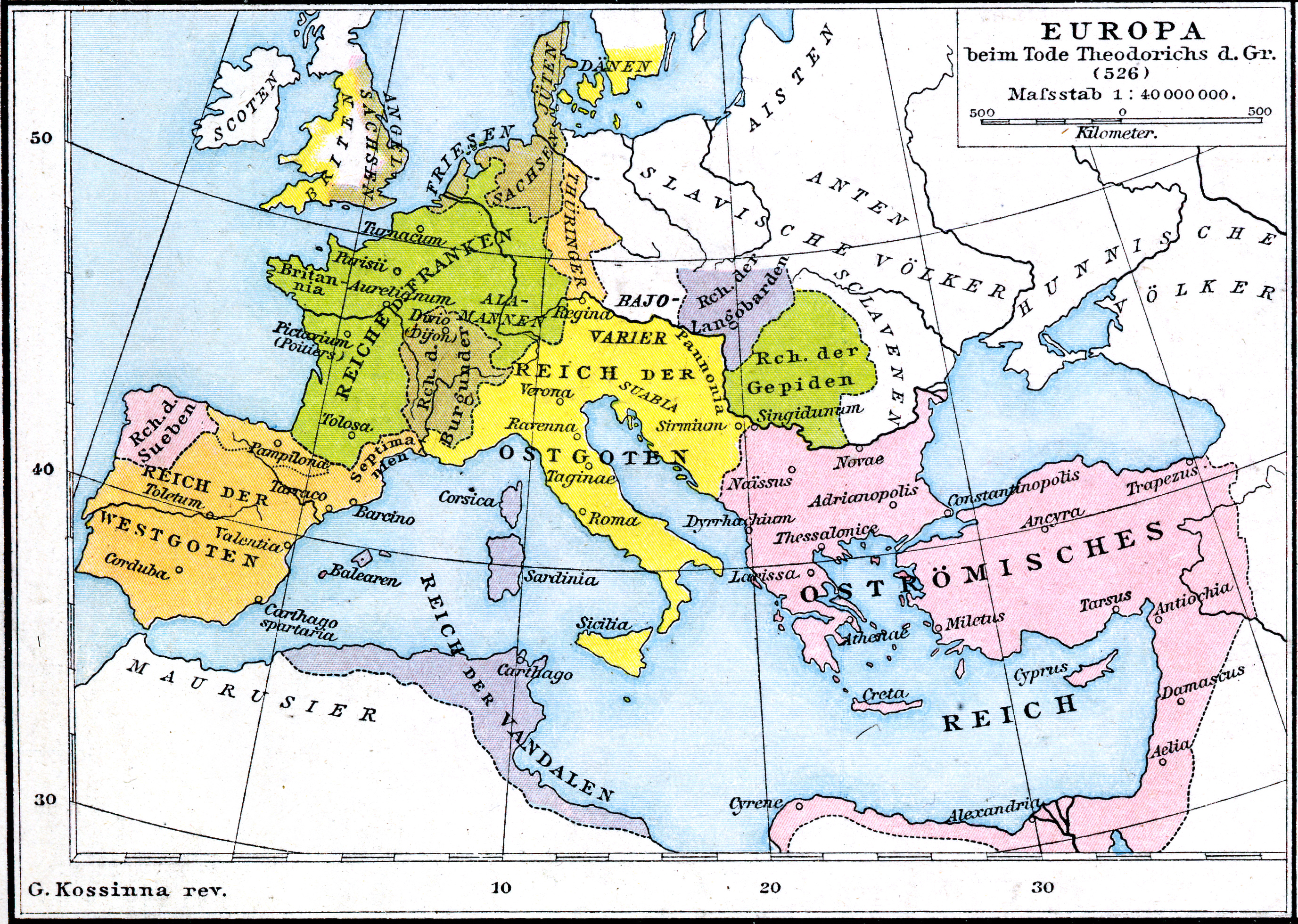
Theodoric The Great
Theodoric (or Theoderic) the Great (454 – 30 August 526), also called Theodoric the Amal ( got, , *Þiudareiks; Greek: , romanized: ; Latin: ), was king of the Ostrogoths (471–526), and ruler of the independent Ostrogothic Kingdom of Italy between 493 and 526, regent of the Visigoths (511–526), and a patrician of the Eastern Roman Empire. As ruler of the combined Gothic realms, Theodoric controlled an empire stretching from the Atlantic Ocean to the Adriatic Sea. Though Theodoric himself only used the title 'king' (''rex''), some scholars characterize him as a Western Roman Emperor in all but name, since he ruled large parts of the former Western Roman Empire, had received the former Western imperial regalia from Constantinople in 497, and was referred to by the title ''augustus'' by some of his subjects. As a young child of an Ostrogothic nobleman, Theodoric was taken as a hostage to Constantinople, where he spent his formative years and received an East Roman education (' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carthage
Carthage was the capital city of Ancient Carthage, on the eastern side of the Lake of Tunis in what is now Tunisia. Carthage was one of the most important trading hubs of the Ancient Mediterranean and one of the most affluent cities of the classical world. The city developed from a Canaanite Phoenician colony into the capital of a Punic empire which dominated large parts of the Southwest Mediterranean during the first millennium BC. The legendary Queen Alyssa or Dido, originally from Tyre, is regarded as the founder of the city, though her historicity has been questioned. According to accounts by Timaeus of Tauromenium, she purchased from a local tribe the amount of land that could be covered by an oxhide. As Carthage prospered at home, the polity sent colonists abroad as well as magistrates to rule the colonies. The ancient city was destroyed in the nearly-three year siege of Carthage by the Roman Republic during the Third Punic War in 146 BC and then re-developed as Roman Car ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
6th-century Visigothic Monarchs
The 6th century is the period from 501 through 600 in line with the Julian calendar. In the West, the century marks the end of Classical Antiquity and the beginning of the Middle Ages. The collapse of the Western Roman Empire late in the previous century left Europe fractured into many small Germanic kingdoms competing fiercely for land and wealth. From the upheaval the Franks rose to prominence and carved out a sizeable domain covering much of modern France and Germany. Meanwhile, the surviving Eastern Roman Empire began to expand under Emperor Justinian, who recaptured North Africa from the Vandals and attempted fully to recover Italy as well, in the hope of reinstating Roman control over the lands once ruled by the Western Roman Empire. In its second Golden Age, the Sassanid Empire reached the peak of its power under Khosrau I in the 6th century.Roberts, J: "History of the World.". Penguin, 1994. The classical Gupta Empire of Northern India, largely overrun by the Huna, ended in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balt Dynasty
The Balts or Baltic peoples ( lt, baltai, lv, balti) are an ethno-linguistic group of peoples who speak the Baltic languages of the Balto-Slavic branch of the Indo-European languages. One of the features of Baltic languages is the number of conservative or archaic features retained. Among the Baltic peoples are modern-day Lithuanians and Latvians (including Latgalians) — all Eastern Balts — as well as the Old Prussians, Yotvingians and Galindians — the Western Balts — whose languages and cultures are now extinct. Etymology Medieval German chronicler Adam of Bremen in the latter part of the 11th century AD was the first writer to use the term "Baltic" in reference to the sea of that name.Bojtár page 9. Before him various ancient places names, such as Balcia, were used in reference to a supposed island in the Baltic Sea. Adam, a speaker of German, connected ''Balt-'' with ''belt'', a word with which he was familiar. In Germanic languages there was some form of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balti Dynasty
Balti may refer to: Places * Bălți, a city in Moldova * Bălți County (Moldova), a former county of Moldova * Bălți County (Romania), a former county of Romania * Balti Power Plant, one of two Narva Power Plants in Estonia * Bălți Steppe, a grassland in northern Moldova * Balti Triangle, an area of Birmingham, England * Balti jaam (''Baltic station''), Tallinn railway station People * ''Balti'', Latin for the Balts * Bianca Balti, an Italian model *Balti (singer) (born 1980), Tunisian singer, rapper, composer and music producer Other uses * Balti (food), a northern Pakistan-style food believed to originate from the UK * Balti dynasty, a branch of the ancient Visigoths * Balti language spoken in Baltistan and Ladakh in Kashmir * Balti people, an ethnic group of Tibetan origin in Baltistan See also * Baltistan, a mountainous region in Gilgit-Baltistan, Pakistan-administered Kashmir *Baltic (other) Baltic may refer to: Peoples and languages * Baltic languages, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Durance
The Durance (; ''Durença'' in the Occitan classical norm or ''Durènço'' in the Mistralian norm) is a major river in Southeastern France. A left tributary of the Rhône, it is long. Its drainage basin is .Bassin versant : Durance (La) Observatoire Régional Eau et Milieux Aquatiques en PACA Its source is in the southwestern part of the , in the ski resort near ; it flows southwest through the following [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isidore Of Seville
Isidore of Seville ( la, Isidorus Hispalensis; c. 560 – 4 April 636) was a Spanish scholar, theologian, and archbishop of Seville. He is widely regarded, in the words of 19th-century historian Montalembert, as "the last scholar of the ancient world". At a time of disintegration of classical culture, aristocratic violence and widespread illiteracy, Isidore was involved in the conversion of the Arian Visigothic kings to Catholicism, both assisting his brother Leander of Seville and continuing after his brother's death. He was influential in the inner circle of Sisebut, Visigothic king of Hispania. Like Leander, he played a prominent role in the Councils of Toledo and Seville. His fame after his death was based on his ''Etymologiae'', an etymological encyclopedia that assembled extracts of many books from classical antiquity that would have otherwise been lost. This work also helped standardize the use of the period ( full stop), comma, and colon. Since the early ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |