|
Gerrit De Graeff (I.) Van Zuid-Polsbroek
Gerrit de Graeff (I.) van Zuid-Polsbroek (27 February 1711 in Amsterdam – 10 November 1752) was a member of the De Graeff – Family from the Dutch Golden Age. De Graeff was "known for his wealth and notorious for his stinginess." House at Herengracht 553, now called ''Tassenmuseum Hendrikje'' De Graeff belonged to the patrician class of Amsterdam and held the feudal titles Free Lord of Zuid-Polsbroek as those of 21st Purmerland and Ilpendam. Family Gerrit was the son of Johan de Graeff and his wife ''Johanna Hooft''. In 1734 he married Maria Elisabeth Sautijn, and in 1739, after his first had died, with Elizabeth Lestevenon (1716–1766). Mattheus Lestevenon, the Dutch ambassador to France, became his brother-in-law. With his first wife he had one child, Joan de Graeff (1735-1754), his succeeder as Lord of Zuid-Polsbroek, who died at the age of 19. With his second wife he had six children; Abraham (1743–1744), Pieter (1746–1762) and Elisabeth Jacoba de Graeff (1748–1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dutch East Indies Company
The United East India Company ( nl, Verenigde Oostindische Compagnie, the VOC) was a chartered company established on the 20th March 1602 by the States General of the Netherlands amalgamating existing companies into the first joint-stock company in the world, granting it a 21-year monopoly to carry out trade activities in Asia. Shares in the company could be bought by any resident of the United Provinces and then subsequently bought and sold in open-air secondary markets (one of which became the Amsterdam Stock Exchange). It is sometimes considered to have been the first multinational corporation. It was a powerful company, possessing quasi-governmental powers, including the ability to wage war, imprison and execute convicts, negotiate treaties, strike its own coins, and establish colonies. They are also known for their international slave trade. Statistically, the VOC eclipsed all of its rivals in the Asia trade. Between 1602 and 1796 the VOC sent almost a million Euro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Leiden
Leiden University (abbreviated as ''LEI''; nl, Universiteit Leiden) is a public research university in Leiden, Netherlands. The university was founded as a Protestant university in 1575 by William, Prince of Orange, as a reward to the city of Leiden for its defence against Spanish attacks during the Eighty Years' War. As the oldest institution of higher education in the Netherlands, it enjoys a reputation across Europe and the world. Known for its historic foundations and emphasis on the social sciences, the university came into particular prominence during the Dutch Golden Age, when scholars from around Europe were attracted to the Dutch Republic due to its climate of intellectual tolerance and Leiden's international reputation. During this time, Leiden became the home to individuals such as René Descartes, Rembrandt, Christiaan Huygens, Hugo Grotius, Baruch Spinoza and Baron d'Holbach. The university has seven academic faculties and over fifty subject departments while hou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kassel
Kassel (; in Germany, spelled Cassel until 1926) is a city on the Fulda River in northern Hesse, Germany. It is the administrative seat of the Regierungsbezirk Kassel and the district of the same name and had 201,048 inhabitants in December 2020. The former capital of the state of Hesse-Kassel has many palaces and parks, including the Bergpark Wilhelmshöhe, which is a UNESCO World Heritage Site. Kassel is also known for the '' documenta'' exhibitions of contemporary art. Kassel has a public university with 25,000 students (2018) and a multicultural population (39% of the citizens in 2017 had a migration background). History Kassel was first mentioned in 913 AD, as the place where two deeds were signed by King Conrad I. The place was called ''Chasella'' or ''Chassalla'' and was a fortification at a bridge crossing the Fulda river. There are several yet unproven assumptions of the name's origin. It could be derived from the ancient ''Castellum Cattorum'', a castle of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
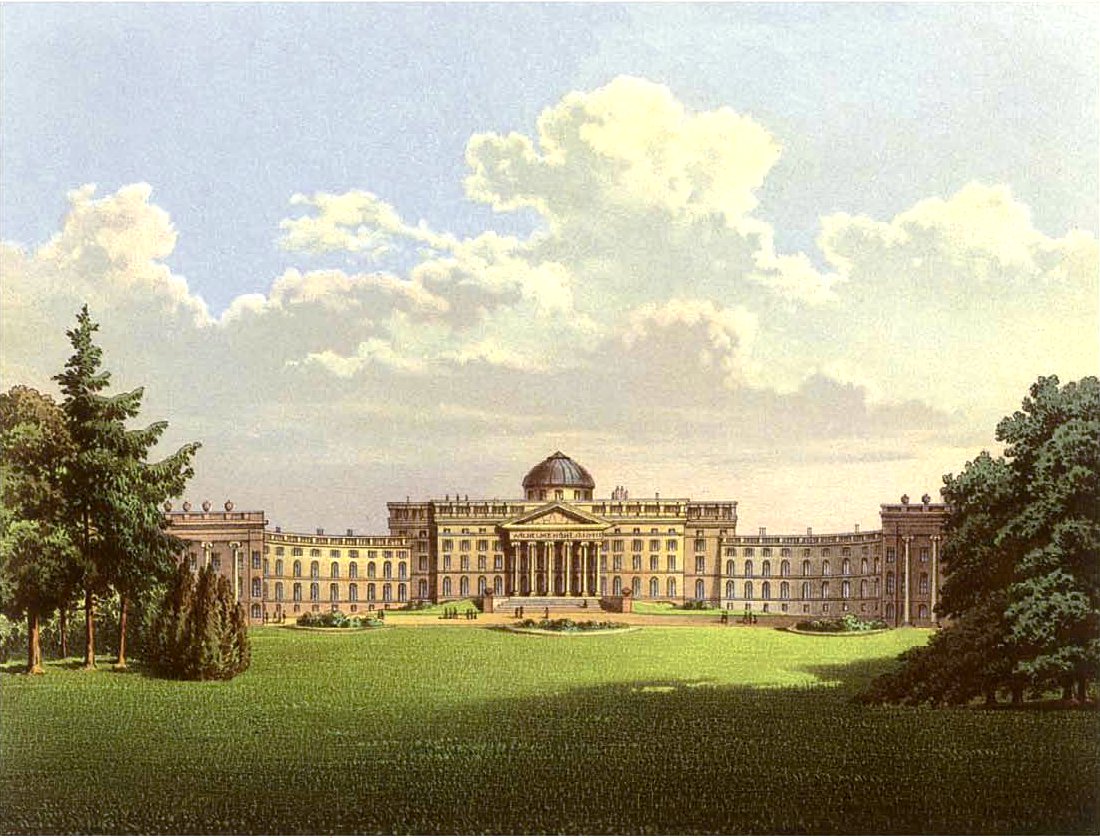
Schloss Wilhelmshöhe
Schloss Wilhelmshöhe is a Neoclassical palace located in , a part of Kassel, Germany. It was built for Landgrave Wilhelm (William) IX of Hesse in the late 18th century. Emperor Wilhelm II made extensive use of it as a summer residence and personal retreat. Today, the palace houses the art gallery Gemäldegalerie Alte Meister, part of ''Museumslandschaft Hessen Kassel''. Since 2013, ''Schloss Wilhelmshöhe'' has been part of the UNESCO World Heritage Site ''Bergpark Wilhelmshöhe'' because of its contribution to Baroque architecture and the outstanding water features that surround the palace. History Beginning in the 12th century the site was used as a monastery. Under Philip I, Landgrave of Hesse 1504-1567 it was secularised and used as a castle. This castle was replaced by a new one from 1606 to 1610 by Landgrave Moritz. The current Neoclassical ''Schloss Wilhelmshöhe'' was designed by architects Simon Louis du Ry and from 1786 to 1798 for Landgrave William IX of Hesse. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andries De Graeff
Andries de Graeff (19 February 1611 – 30 November 1678) was a powerful member of the Amsterdam branch of the De Graeff - family during the Dutch Golden Age. He became a mayor of Amsterdam and a powerful Amsterdam regent after the death of his older brother Cornelis de Graeff. Like him and their father Jacob Dircksz de Graeff he opposed the house of Orange. In the mid-17th century, during the First Stadtholderless Period, they controlled the finances and politics. Andries de Graeff followed in his father's and brother's footsteps and, between 1657 and 1672, was appointed mayor some seven times. He was a member of a family of regents who belonged to the republican political movement also referred to as the ‘state oriented’, the Dutch States Party, as opposed to the Royalists. Andries was called the last mayor from the dynasty of the "Graven", who was powerful and able enough to ruled the city of Amsterdam. De Graeff was an Imperial Knight of the Holy Roman Empire, an Ambac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William VIII, Landgrave Of Hesse-Cassel
William VIII (10 March 1682 – 1 February 1760) ruled the German Landgraviate Hesse-Kassel from 1730 until his death, first as regent (1730–1751) and then as landgrave (1751–1760). Life Born in Kassel, he was the seventh son of Charles I, Landgrave of Hesse-Kassel and Maria Amalia of Courland. After his elder brother Frederick became King of Sweden in 1720 and his father died in 1730, he became de facto ruler of Hesse-Kassel. He officially became landgrave after his brother's death on 25 March 1751. Five years later, the Seven Years' War began and William joined with the Prussian and British forces. Hesse-Kassel became an important battlefield and was occupied by France on several occasions. He had a deep, personal friendship with Frederick the Great, King of Prussia, and Holy Roman Emperor Charles VII. His second son and successor, Frederick, became a Catholic, which led to restrictions on Catholicism in the Calvinist landgraviate and the transfer of the Principality ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heemstede
Heemstede () is a town and a municipality in the Netherlands, in the province of North Holland. It is the fourth richest municipality of the Netherlands. History Heemstede formed around the Castle ''Heemstede'' that was built overlooking the Spaarne River around 1286. Before 1296, Floris V, Count of Holland, granted Heemstede as a fiefdom to Reinier of Holy. During the 14th century, a village formed near the castle, which was destroyed and rebuilt several times in this period. A resident of this castle was Adriaan Pauw, who bought it in 1620. In 1653, Bennebroek split off from Heemstede, becoming a separate fiefdom. Growth was slow, and in 1787 Heemstede counted 196 families. Even at that early date Heemstede had already gained the reputation it has today, of being primarily a "bedroom community" for the cities of Haarlem and Amsterdam. Wealthy city families left the cities in the summer, escaping "canal fever" which caused illness from the putrid canals. As a result, many e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis XIV Style
The Louis XIV style or ''Louis Quatorze'' ( , ), also called French classicism, was the style of architecture and decorative arts intended to glorify King Louis XIV and his reign. It featured majesty, harmony and regularity. It became the official style during the reign of Louis XIV (1643–1715), imposed upon artists by the newly established (Royal Academy of Painting and Sculpture) and the (Royal Academy of Architecture). It had an important influence upon the architecture of other European monarchs, from Frederick the Great of Prussia to Peter the Great of Russia. Major architects of the period included François Mansart, Jules Hardouin Mansart, Robert de Cotte, Pierre Le Muet, Claude Perrault, and Louis Le Vau. Major monuments included the Palace of Versailles, the Grand Trianon at Versailles, and the Church of Les Invalides (1675–1691). The Louis XIV style had three periods. During the first period, which coincided with the youth of the King (1643–1660) and the rege ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
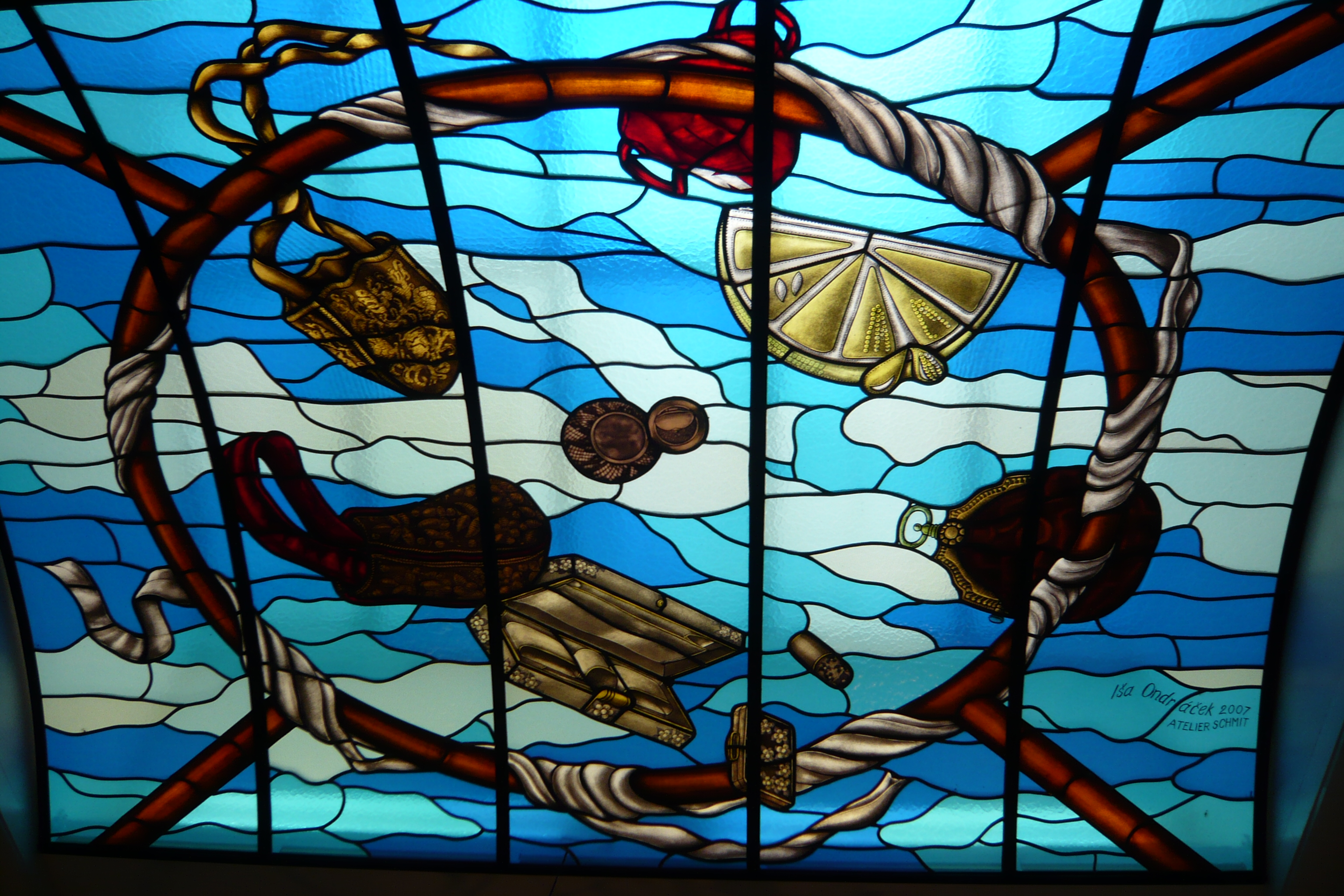
Tassenmuseum Hendrikje
The Museum of Bags and Purses ( nl, Tassenmuseum Amsterdam), was a museum devoted to the history of bags, purses, and their related accessories. Located in Amsterdam's historic central canal belt, the museum's collection included over 5,000 items dating back to the sixteenth-century. One of only three museums across the globe specialising in this field, it housed the world's largest collection of bags and purses.Yucel, Suzan"Handbag museum feeds female obsession" ''Reuters'', August 31, 2007. Accessed August 24, 2008."Bagging it" '''', November 8, 2007. Accessed August 24, 2008. The Museum of Bags and Purses was the first cultural institution in the Netherlands to announce its pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noorderkwartier
Noorderkwartier (; en, Northern Quarter) is a historical term referring to the part of the former Dutch province of Holland north of the river IJ, covering the regions Kennemerland, Zaanstreek, Waterland and West Friesland and now part of the modern province of North Holland North Holland ( nl, Noord-Holland, ) is a province of the Netherlands in the northwestern part of the country. It is located on the North Sea, north of South Holland and Utrecht, and west of Friesland and Flevoland. In November 2019, it had a .... Other historical terms for this area were "North Holland", "Noordeland", and "Noorderland". {{Coord missing, Netherlands Regions of the Netherlands Regions of North Holland ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sociëteit Van Suriname
The Society of Suriname (Dutch: ''Sociëteit van Suriname'') was a Dutch private company, modelled on the ideas of Jean-Baptiste Colbert and set up on 21 May 1683 to profit from the management and defense of the Dutch Republic's colony of Suriname. It had three participants, with equal shares in the costs and benefits of the society; the city of Amsterdam, the family Van Aerssen van Sommelsdijck, and the Dutch West India Company. Only through mutual consent could these shareholders withdraw from the society. Although the organization and administration was of the colony was limited to these three shareholders, all citizens of the Dutch Republic were free to trade with Suriname. Also, the planters were consulted in a Council of Police, which was a unique feature among the colonies of Guyana.Buddingh, H. (1995) Geschiedenis van Suriname, p. 26. Its governors included Cornelis van Aerssen van Sommelsdijck, Johan van Scharphuizen, and Paulus van der Veen. The Society was nationaliz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schutterij
Schutterij () refers to a voluntary city guard or citizen militia in the medieval and early modern Netherlands, intended to protect the town or city from attack and act in case of revolt or fire. Their training grounds were often on open spaces within the city, near the city walls, but, when the weather did not allow, inside a church. They are mostly grouped according to their district and to the weapon that they used: bow, crossbow or gun. Together, its members are called a ''Schuttersgilde'', which could be roughly translated as a "shooter's guild". It is now a title applied to ceremonial shooting clubs and to the country's Olympic rifle team. Function The ''schutterij'', civic guard, or town watch, was a defensive military support system for the local civic authority. Its officers were wealthy citizens of the town, appointed by the city magistrates. In the Northern Netherlands, after the formal changeover in civic authority after Beeldenstorm, which depending on the town, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
%2C_Hoorn.jpg)

_1572.jpg)